Coevolution Power Point
Warm Up Activity
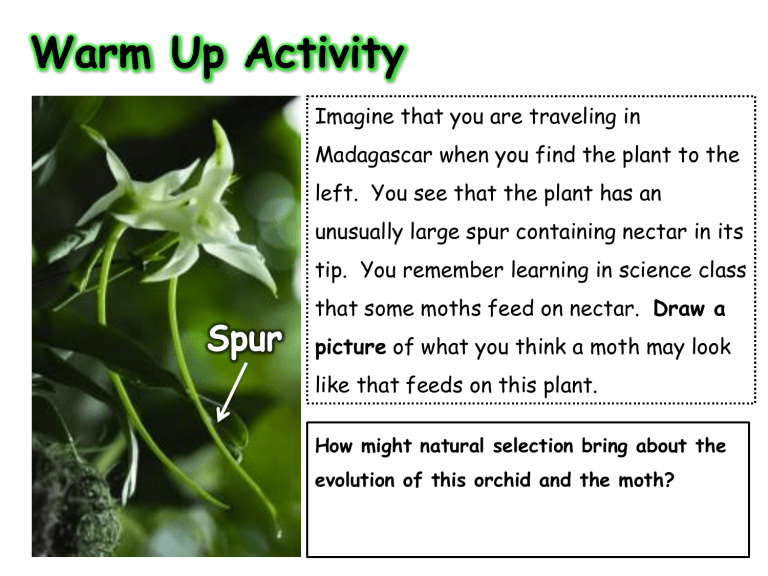
Imagine that you are traveling in
Madagascar when you find the plant to the left. You see that the plant has an unusually large spur containing nectar in its tip. You remember learning in science class that some moths feed on nectar. Draw a
picture of what you think a moth may look like that feeds on this plant.
How might natural selection bring about the evolution of this orchid and the moth?
The Star Orchid and the
Hawk Moth
Coevolution
Coevolution
Sometimes organisms that are closely connected to one another by ecological interactions evolve together.
An evolutionary change in one organism may also be followed by a corresponding change in another organism.
The process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other over time is called coevolution.
Coevolution
Symbiosis
Many relationships formed through coevolution are symbiotic relationships.
Symbiosis: relationship in which two species live closely together.
Some types of symbiosis are; predator-prey,
mutuality, parasitic, and commensalism relationships.
Predator-Prey Relationships
A predator is an organism that eats another organism. The prey is the organism which the predator eats.
Example: Lion (predator) and Zebra (prey)
The words “predator” and “prey” are almost always used to represent animals that eat
other animals. However, the same concept exists for animals
that eat plants.
Example: mouse(predator) and berry (prey)
Mutuality
A mutuality relationship is when two organisms of different species "work together," each benefiting from the relationship.
Example: Cleaner fish and Nassau Grouper
Plants and the animals that help them pollinate each other
(called pollinators) have coevolved.
Parasitic Relationships
A parasitic relationship is one in which one organism, the parasite, lives off of another organism, the host, harming it and possibly causing death. The parasite lives on or in the body of the host.
Example: The cat (host) and the flea (parasite).
Commensalism
• A commensalism relationship is an
interaction where one organism benefits from the interaction and the other is not affected. Example: Zebra (unaffected) and cattle egret (benefits)
Mimicry
• Mimicry is a type of commensalism that exists in nature. One organism evolves to look like the other in order to benefit itself. The mimic benefits from the situation while the organism it mimics in unaffected.
Example: Orchid flowers that mimic female wasps
Sources
Warm Up Activity http://tywkiwdbi.blogspot.com/2010/12/xanthopan-morgani-darwins-moth.html
Images: http://animals.about.com/od/evolutio1/ss/evolution101_9.htm
http://farm4.static.flickr.com/3664/3470867040_9f5609f1b1.jpg
http://netsyscon4hr.wordpress.com/ http://www.flearemoval.net/flea-removal-dog-flea-treatment/ http://www.allposters.com/-sp/White-Footed-Mouse-Peromyscus-Leucopus-Eating-a-Berry-
Ohio-Posters_i6016034_.htm
http://animals.howstuffworks.com/mammals/man-eating-lion.htm
PowerPoint Information: http://facstaff.unca.edu/tforrest/BIOL%20107%20Principles%20of%20Evolution/BIOL%201
07%20Fall%202009%20Lecture%2013%20Coevolution.pdf
http://www.poliza.de/starship/sciencenew/symbiosis.htm
http://www.necsi.edu/projects/evolution/co-evolution/co-evolution_intro.html
http://facstaff.uwa.edu/jmccall/Evolutionary%20Biology/Coevolution.ppt
Webquest: http://www.nearctica.com/ecology/pops/commens.htm#monarch http://www.necsi.edu/projects/evolution/co-evolution/co-evolution_intro.html