Ecology: Population Interactions & Adaptations Worksheet

KEY
B __ 1.In a natural community, population sizes vary because
a. the populations are not affected by each other.
b. the populations all affect one another.
c. individuals in the populations decide to have big families.
d. the populations are able to grow without stopping.
INTERACTIONS BETWEEN ORGANISMS
7. Ecologists have listed four main ways that species and individuals affect other—competition,
________Predator__________and prey, symbiosis, and coevolution.
COMPETITION
8. When two or more individuals or populations try to use the same resource, it is called
_______Competition_______________.
9. Give an example of competition between individuals within a population and of competition between populations.
Competition Between Individuals of a Population: The elks in Yellowstone parks are herbivores that compete for the same food source within the park. Competition between populations : Different Species of trees compete for both space and sunlight.
PREDATORS AND PREY
A ___ 10. What word is used for an organism that eats another organism?
a. predator c. competitor
b. carrier d. prey
D ___ 11. What word is used for an organism that is eaten?
a. predator c. competitor
b. carrier d. prey
12. List two adaptations predators use to catch prey.
Camouflage and Speed.
13. List two ways prey have adapted to avoid predators.
Some use speed, group protection, warning colors, or camouflage to avoid prey while others use mechanical and chemical defenses.
14. Give two examples of animals using defensive chemicals against predators.
. Examples of chemical defenses would be: bad taste, deadly toxins, irritating acids (in bees/wasps), and bad smells (skunk and bombardier beetle)
15. How can being bright red, yellow, or orange help an animal avoid predators?
The bright coloration of prey is commonly known as “warning coloration.” These bright/fluorescent colors are associated with pain, illness, or unpleasant experiences for the predator warning them to look for a meal
elsewhere.
SYMBIOSIS
A ___ 16. A close, long-term association between two or more species is called
a. symbiosis. c. predator adaptations.
b. defensive chemicals. d. camouflage.
17. What are the three types of symbiosis?
There are three major types of symbiosis. They include mutualism, commensalisms, and parasitism.
Mutualism is a relationship in which both organisms benefit from the relationship. Commensalism is a situation in which one organism benefits, but the relationship neither benefits nor harms the other organism. Lastly, parasitism is a pairing in which one party of the relationship benefits (parasite) from the interaction while the other party is harmed (host).
18. Both organisms benefit in the type of symbiosis called __ mutualism____________.
19. When one organism benefits and the other is unaffected, the symbiotic relationship is called
____commensalism_________.
20. A symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is harmed is called
_____parasitism___________.
21. In parasitism, the organism that benefits is called the _____parasite__________.
22. The organism that is harmed by a parasite is called the ___host____________.
23. Do most parasites kill their hosts? Why or why not?
No, most parasites do not kill their host because parasites depend on their hosts for nourishment. If the parasite were to kill the host, they would be forced to find another home and food sources.
COEVOLUTION
24. What name is given to a long-term change that takes place in two species because of their close interactions with one another? Give an example.
Coevolution is the term used in reference to a long term change that takes place in two species because of their interactions with one another. An example of coevolution would include, the ant and the acacia tree.
Both species have coevolved to develop mechanisms that benefit the survival of each species. The ants protect the tree and the tree provides a food source for the ants.
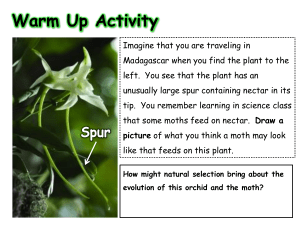
25. Describe an example of coevolution between a flower and its pollinator.
The flower and pollinator are a perfect example of coevolution. The flower has evolved over many years to develop methods to attract pollinators. Mechanisms developed in clued odor, color, or nectar. Once a pollinator is attracted to a given plant, the pollen of that plant is then pollinate other plants in which it comes in contact. Examples of pllinators include bees, hummingbirds, and bats.