ABDOMINAL EXAMINATION
advertisement

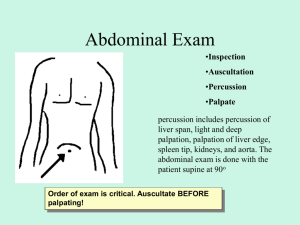
ABDOMINAL EXAMINATION Anatomy 2. Regions 3. Common presenting symptoms 4. Examination Inspection Auscultation Percussion Palpation Liver and spleen 5. Specific maneuvers 1. Regions Common presenting symptoms of Gastrointestinal disorders Abdominal pain, acute or chronic Indigestion, nausea, vomiting including blood, loss of appetite, early satiety Dysphagia / odynophagia Diarrhea, constipation Jaundice For each symptom, try to elicit all of its attributes SOCRATES (site, onset, character, radiation, associated factors, timing, exacerbating/relieving factors, severity) Example: Typical pain in Acute appendicitis Site: poorly localized, periumbilical pain followed usually by RLQ pain Onset: vague Character: dull periumbilical pain, may be cramping Radiation: periumbilical RLQ Associated factors: anorexia, nausea/vomiting, low fever Timing: Periumbilical (4-6h), RLQ (depends on intervention) Exacerbating/relieving factors: if subsides temporarily, suspect perforation of the appendix, movement/cough. Severity: periumbilical (mild but increasing), RUQ (steady/more severe) Inspection The skin: scar, striae, dilated vein, rashes and lesions The umbilicus: contour, inflammation, bulges The contour of the abdomen: flat, rounded, protuberant, scaphoid Peristalsis Pulsations: abdominal aorta in the epigastric region. SCAR PINK-PURPLE STRIAE OF CUSHING’S SYNDROME DILATED VEIN OF HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS RASHES UMBILICAL HERNIA IN NEWBORN Contour of the abdomen PROTUBERANT SCAPHOID (newborn with diaphragmatic hernia) AUSCULTATION Before performing percussion and palpation because these maneuvers can alter the bowel sound Bowel sounds (5-34/min) diarrhea, intestinal obstruction paralytic ileus, peritonitis Bruits (renal artery stenosis) PERCUSSION Percuss lightly in all four quadrant Distribution of tympany and dullness. PALPATION Light palpation: tenderness, muscular resistance, superficial organs and masses. Deep palpation: delineate abdominal masses Assessment for peritoneal inflammation: Cough Palpation (guarding, rigidity) rebound tenderness LIVER Percussion Palpation SPLEEN Percussion: 2 techniques Percuss the left lower anterior chest wall Check splenic percussion sign Palpation Time for test! A D C C “Abdomen is protuberant with active bowel sounds. It is soft and non-tender; no masses or hepatosplenomegaly. Liver span is 7 cm in the right midclavicular line; edge is smooth and palpable 1 cm below the right costal margin. Spleen not felt” “Abdomen is flat. No bowel sounds heard. It is firm and boardlike, with increased tenderness, guarding, and rebound in the right midquadrant. Liver percusses to 7 cm in the midclavicular line; edge not felt. Spleen not felt” VN English Ăn uống bình thường, đi cầu bình thường Không đau bụng, không nôn, không buồn nôn Bụng không chướng, Âm ruột bình thường, không nghe tiếng thổi động mạch Bụng mềm, không đau, không sờ thấy u cục Gan 1cm dưới bờ sườn, cao 8 cm trên đường trung đòn, lách không lớn No anorexia (no change in dietary patterns), no diarrhea or constipation (no abnormalities in stool patterns or characteristics) No abdominal pain, no nausea or vomiting No abdominal distension Bowel sounds present (active bowel sounds), no bruits Abdomen soft and non-tender, no masses, Liver span is 8 cm in the right midclavicular line, edge is palpable 1 cm below the RCM Speen not felt (no spleenomegaly)