4、丝虫 - 人体寄生虫学
advertisement
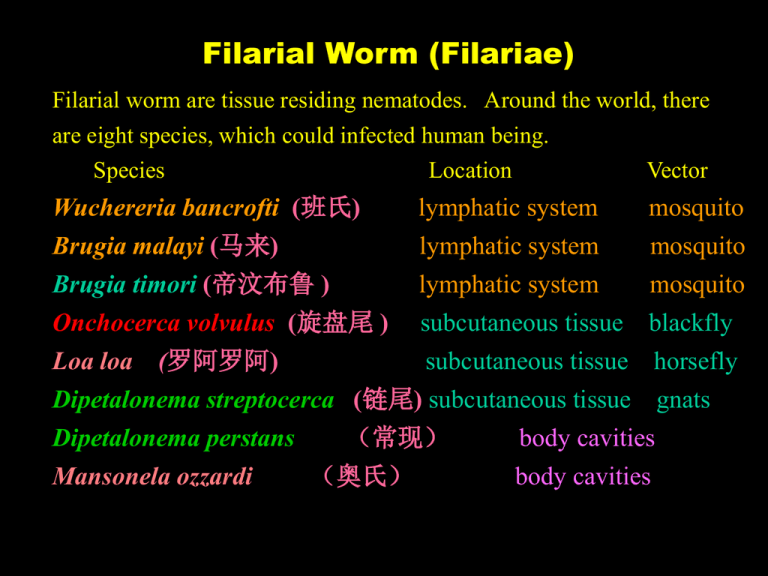
Filarial Worm (Filariae) Filarial worm are tissue residing nematodes. Around the world, there are eight species, which could infected human being. Species Location Wuchereria bancrofti (班氏) Brugia malayi (马来) Brugia timori (帝汶布鲁 ) Vector lymphatic system lymphatic system lymphatic system mosquito mosquito mosquito Onchocerca volvulus (旋盘尾 ) subcutaneous tissue blackfly Loa loa (罗阿罗阿) subcutaneous tissue horsefly Dipetalonema streptocerca (链尾) subcutaneous tissue gnats Dipetalonema perstans (常现) body cavities Mansonela ozzardi (奥氏) body cavities Wuchereria bancrofti & Brugia malayi 世界性分布,蚊是主要传播媒介 They are the most widely distributed filariae that are transmitted by mosquitoes. Morphology 成虫 (adult) They are elongated, thread-like worms. The adult female worm of W.bancrofti is larger than B.malayi. Female produce larvae known as microfilariae. 微丝蚴 (microfilariae) 头隙,体核,尾核 They are elongated and sheathed, with blunt anterior end and pointed caudal end. A large number of nuclei could be seen in the body after staining. 班氏微丝蚴与马来微丝蚴的区别 班氏 马来 大小 较大 较小 体态 柔和 僵硬 头隙 呈方形 长方形 体核 圆形,大小一致, 卵圆形,大小不一 尾核 清晰可数 排列密集 无 有 Differential characteristics of microfilariae between W.bancrofti and B.malayi (1) W.bancrofti Length ( m) Diameter ( m) Body curves Cephalic space Somatic nuclei Caudal nuclei 200-300 8 regular, smoothly curved small well separate none B.malayi 220-250 6 irregular twisted large over lapped two 区别的意义 1.致病性不同 班氏大 2.分布不同 班氏分布广 3.药敏性不同 马来对药敏感 difference in pathogenicity W.bancrofti more heavy difference in distribution W.bancrofti worldwide distributed difference in drug sensitivity B.malayi is more sensitivity in drug 在蚊体内有腊肠期蚴;丝状蚴, 感染期幼虫为丝状蚴(filariform larva) microfilariae in the mosquito first into a rhabditiform larva (Sausage shaped larva) then into an filariform larva------ infectious stage Life cycle The life cycle of two species are similar. The larvae develop in the mosquito which acts as vector, and the adults develop in the human. adlut lymphatic system microfilariae sausage shaped larva filariform larva peripheral blood thoracic musculature of mosquito labium of mosquito human infected larva enter the lymphatic system 成虫 (淋巴系统) 微丝蚴 (血液) 腊肠期幼虫 (蚊胸肌) 丝状蚴 (蚊下唇) 蚊 叮 吸 血 在蚊体内的发育, Development in the mosquito: The microfilariae ingested by the mosquito along with its blood meal migrate to its muscles. After 6 to 14 days of development, the larva force their way out of muscles, migrate to the proboscis (labium). During the blood meal the developed larva emerge from proboscis onto the skin of the new host. # some factors effected the development of larva in mosquito W.bancrofti: B.malayi vector Culex 淡色库蚊,致倦库蚊 Anopheles, Aedes 中华按蚊,嗜人按蚊,东乡伊蚊 在人体内的发育 Development in the human On penetrating the skin through the bite wound, the larva pass to the lymphatic vessels and nodes After copulation, the female produces microfilariae in about 3 months infection The microfilariae migrate from the parent worm the through the walls of the lymphatics to the neighboring small blood vessels or are carried in the lymphatic circulation to the bloodstream Microfilariae appear in the greatest number in the peripheral blood between 8 pm and 4 am nocturnal periodicity-------- the microfilariae, present in very small numbers or often undetectablein the peripheral circulation during the daytime, then appear in the greatest density at night, when absent from the peripheral circulation the microfilariae are found in the capillaries of the lung 夜现周期性(nocturnal periodicity) 微丝蚴白昼滞留于肺血管内,夜晚则出现在外周血液的现象。 Microfilariae of Wuchereria bancrofti Nocturnal periodicity of microfilariae Differential characteristics of microfilariae between W.bancrofti and B.malayi (2) W.bancrofti Location nocturnal periodicity reservoir host B.malayi deep or near surface lymphatic system near surface lymphatic system 10 pm—2 am 8 pm—4 am - + 致病 (Pathogenicity) 丝虫病主要是由成虫引起的 Filarial symptoms are caused mainly by the adult worms, living as well as dead and degenerating Microfilariae cause less pathology, although they have been associated with tropical pulmonary eosinopholia granulomas of the spleen, and allergic reactions following their destruction by drugs Clinically, the disease can be divided into incubation, acute, and chronic phase Incubation phase: 1. asymptomatic and may last for a year or more 2. may include low-grade fever caused by lymphatic inflammation Acute phase: Chronic phase: an allergic response to the products of dying and degenerating adult worms -----lymphangitis, funiculititis, orchitis, epididymitis filarial fever repeated lymphangitis granuloma fibrosis obstruction of lymph vessels lymph varices rupture of lymphatic proliferation of connective tissues elephantiasis elephantiasis hydrocele testis W.bancrofti chyluria 淋巴(结)管炎 液体外溢 增生性肉芽肿 破裂 曲张 1.淋巴液肿 (1) 象皮肿(elephantiasis) (2) 睾丸鞘膜积液 2.乳糜尿 纤维化(纤维组织增生) 压力↑ 管道阻塞 诊断 (一) 病原诊断 1.血检 2.体液和尿液检查微丝蚴 Examination of blood thick blood film-----detected microfilariae lysed blood check -----concentrated Examination of aspiration ( induction) 3.成虫检查 直接或以活检 Detection of adult worm (二)血清学检查 (三)其他 mAb, ELISA, PCR 流行因素 Epidemiology (一)分布: 世界性分布 W.bancrofti is worldwide distributed B.malayi is restricted to Asia (二)流行环节 1.传染源 Source of infection: patients, infected persons 2.传播媒介 :蚊是主要传播媒介,主要蚊媒如下: Transmission: mosquito Culex Anopheles, Aedes 淡色库蚊 嗜人按蚊 班氏丝虫 马来丝虫 中华按蚊 W.bancrofti: B.malayi 致倦库蚊 东乡伊蚊 3.易感人群 4.影响因素 防治原则 Treatment & Prevention (一)普查普治 海群生diethylcarbamzine (DEC) hetragan治疗 Diethylcarbamazine(hetrazan) is the first choice in treatment of filarial worm. A single-dose treatment of ivermectin plus Diethylcarbamazine has also proven highly effective, producing a 99 % reduction in the number of microfilariae (二)防蚊灭蚊 (三)加强监测 Mass treatment coupled with the use of screens, insect repellents and insecticides has proven effective in the filarial control Onchocerca volvulus Onchocerciasis is considered by WHO the world’s second leading infectious cause of human blindness Adult worms are found in fibrous nodules called onchocercomas in the subcutaneous connective tissues and viscera of humans Adult worms may cause minor pathological alterations When microfilariae invade the cornea, cause inflammation of the sclera, cornea, iris and retina, lead to impaired vision or the total blindness known as “ river blindness” The presence of microfilariae in the connective of the skin, produces severe dermatitis Worldwide, there are estimated to be 20 million (20000000) cases of onchocerciasis, approximately 96 % of the cases are in tropical Africa Microscopically demonostration of microfilariae in dermal lymph of skin biopsyis proof of infection, or identification of adults in skin nodules Ivemectin, administered in a single dose, the most effective treatment, Diethylcarbamazine(hetrazan) also, however, the drug does not affect adult worms------surgical Loa loa Loasis is limited to the African The parasite usually cause no serious damage to the host Adult worm in subcutaeous tissue, in eye, Calabar swelling Microfilariae can be seen in unstained fresh prepared blood Diethylcarbamazine(hetrazan) is the first choice in treatment of filarial worm. Trichinella spiralis 旋毛虫(Trichinella spiralis)成虫寄生在小肠下部的肠壁, 幼虫寄生在人体横纹肌中,引起旋毛虫病(Trichinellosis), 为人兽共患病。 食源性寄生虫病,特点:地区性、群体性、食源性、季节性 Trichinellosis is the disease among human and animal, a zoonosis. The infection is endemic in many areas of the world where raw or undercooked meat, mainly pork is consumed. 形态 Morphology 成虫 Adult small & slender male: female: 1.5 mm X 0.04 mm 3.5 mm X 0.06 mm deposited larva 幼虫 Larva enveloped, 0.25-0.5 mm X 0.21-0.42 mm 生活史 Life cycle 成虫和幼虫均寄生在同一宿主体内 完成生活史需更换宿主 Human infection results from consumption of meat, most communly poorly cooked pork, containing encapsulated larva. Life Cycle of Trichinella spiralis 成虫 交配 幼虫 4-6d 肠淋巴管或静脉 心 肺 全身各处 幼虫 (囊包) 食 入 脱 囊 2-3days 幼虫 4-6 days Adult lymphatic vessels heart lung Larva spread Larva another 2-3 days Larva Larvae can survive only in the skeltal muscle & become encysted in 2 to 3 weeks 致病 Pathogenicity Trichinellosis, mainly result from larval invasio of muscle & other tissues and the hperimmune reaction of the host to the metabolic by-products and secretions of the larvae 1.侵入期 肠道症状 Invasion stage: due to penetration of adult female & larva into the mucosa & submucosa, begins 24 hrsafter infection and lasts for 1 to 7 days asymptomatic or transient gastrointestipational complaints 2.幼虫移行期 全身症状、肌肉症状等一系列严重症状 Migration stage: begins about 1 week after infection and lasts after female worm die(4-6 wks) triad of myalgia palpebral edema eosinophilia fever 3.成囊期 Encystment stage: 诊断 病原诊断 Laboratory diagnosis 组织活检 免疫诊断 皮内试验、环蚴沉淀试验、皂土絮状试验、ELISA。 最近也将检测急性期的循环抗原作为手段之一。 •A parasitologic diagnosis is made by means of biopsy or at autopsy •Serologic tests EIA dot immunobinding to detect circulating parasitic antigen 流行和防治 Epidemiology, treatment, prevention 主要预防措施:不食生肉 mebendazole对成、幼虫均有效 This infection is much less common in Africa and Asia than in Europe and America. The drug of choice is Mebendazole, which can kill both the larva and adult worms. ( albendazole is also effective) No raw or undercooked meat