lec8.Treatment of Cough
advertisement

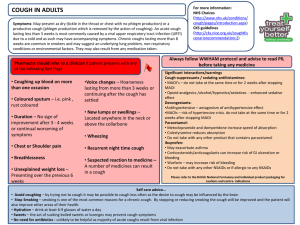
TREATMENT OF COUGH TREATMENT OF COUGH Cough is a useful physiological mechanism that serves to clear the respiratory passages of foreign material and excess secretions. It should not be suppressed تمنع- تكبت indiscriminately. There are, however, many situations in which cough does not serve any useful purpose but may, instead only annoy the patient or prevent rest and sleep. TREATMENT OF COUGH Chronic cough can contribute يساهم فيto fatigue, especially in elderly patients, in such situations the physicians should use a drug that will reduce the frequency or intensity شده of the coughing. Cough reflex اقرا الفيسيو للشرحis complex, involving the central and peripheral nervous systems as well as the smooth muscle of the bronchial tree. TREATMENT OF COUGH It has been suggested that irritation of the bronchial mucosa causes bronchoconstriction, which in turn, stimulates cough receptors( which probably represent a specialized type of stretch receptor) located in the tracheobronchial passages. TREATMENT OF COUGH Afferent ناقل لالشاره نحو المركز ( المخ او الحبل الشكوكي ) مهمهconduction from these receptors is via fibers in the vagus nerve; central components of the reflex probably involve several mechanisms or centres that are distinct تختلف عنfrom the mechanisms involved in the regulation of respiration. TREATMENT OF COUGH The drugs that directly or indirectly can affect this complex mechanism are diverse متنوع. مهمهFor example , cough may be the first or only symptom in bronchial asthma or allergy, and in such cases bronchodilators(e.g., 2 – adrenergic receptor agonists have been shown to reduce cough without having any significant central effects, other drugs act primarily on the central or the peripheral nervous system components of the cough reflex. COUGH Forceful release of air from lungs Sudden, often involuntary (protective) reflex and major defensive mechanism وسيله دفاعيه للجسم Cont….. Causes of cough : Expulsion اخراج- طردof respiratory secretion or foreign particles or irritant or excessive mucus from air passages Symptom عرض لمرض قلبي او رئويof an underlying respiratory and/or cardiovascular pathology مهمه ) اذا بتنبه واحد تكح عشان ينتبه ( اهم وحده: السبب االخير Mechanism of cough Stimulation of mechano-or chemoreceptors (throat, respiratory passages or stretch receptors in lungs) Afferent impulses to cough centre (medulla) Efferent impulses via parasympathetic & motor nerves to diaphragm, intercostal muscles & lung Increased contraction of diaghramatic, abdominal & intercostal (ribs) muscles noisy expiration (cough) Cough Reflex اماكن وجودها : -1على امتداد القناة التنفسيه -2في المعده -3في الجيوب االنفيه Types of cough A) B) Acute cough =lasting<3 weeks Chronic cough =lasing >8 weeks Cough may be i) Un productive (dry) cough OR ii) Productive cough (sputum) cont. Most common causes of cough Common cold, Upper/lower respiratory tract infection Allergic rhinitis Smoking Chronic bronchitis Pulmonary tuberculosis Asthma Gastroesophageal reflux Pneumonia Congestive heart failure Bronchiectasis Use of drugs (e.g., Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors) الدكتور ركز عليها Treatment of Cough 1) Antitussives (cough centre suppressants) ادويه تقوم بحظر مركز السعال في المخ 2) Expectorants الطارد للبغلم بواسطه تحويله لماده اخف ( مما هو عليه فيخرج بسهولهMucokinetics) 3) Mucolytics 2 نفس فكره رقم: المحلل للبلغم 4) Antihistamines 5) Bronchodilators 6) Pharyngeal Demulcents الملين 1) Antitussives (cough centre suppressants) Drugs suppress cough & produces symptomatic relief تعافي من االعراض MOA Mainly suppress cough centre in medulla (both central & peripheral effects) E.g., Opoid drugs (codeine, pholcodeine, noscapine, dextromethorphan) Opioid = most effective for cough i) Codeine Codeine= prodrug metabolized to morphine It is an alkaloid ماده قاعديهfound in Opium poppy plant Has less addiction ادمان اقل من المورفين+ resp. centre depressant ↓ Has useful antitussive المضاد للسعال action at low doses (<15 mg) Produce drowsiness, thickening of sputum & constipation ii) Noscapine & Pholcodeine Related to papaverine دواء مريح للعضالت: البابافارين Do not have addictive ادماني, analgesic & مسكني constipating امساكيproperties Do not interfere يتعارض معwith mucocilliary movement Noscapine (15 mg) & pholcodeine (10 mg)=syrup شراب iii) Dextromethorphan Available in syrup, tablets, spray forms MOA NMDA receptor antagonist Uses Cough suppressant, temporary relief of cough caused by minor throat & bronchial irritation (accompanies with flu & cold), pain relief Ad Effects= Nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, dizziness, blurred vision 2) Expectorants (Mucokinetics) Act peripherally يعني بعيدا عن المخ Increase bronchial secretion OR Decrease its viscosity facilitates its removal by coughing Loose cough ►less tiring & ح ّدهmore productive Cont…. Classification of Expectorants Classified into b) Directly acting E.g., Guaifenesin (glyceryl guaiacolate), Na+ & K+ citrate or acetate, b) Reflexly acting E.g., Ammonium salt i) Sodium & potassium citrate or Acetate They act directly Actions: ▲Bronchial secretion by salt action ii) Guaifenesin Expectorant طارد للبلغمdrug usually taken by mouth Available as single & also in combination MOA=Increase the volume & reduce the viscosity of secretion in trachea & bronchi iii) Reflexly acting يعني تؤثر على المعده مما يؤدي الثر عكسي وهو زياده السيكريشن في القصبات االهوائيه وايضا زياده التعرق Ammonium salts Gastric irritants reflexly bronchial secretions + sweating 3) Mucolytics Help in expectoration طرد البلغمby liquefy التحويل اكثر سيوله ذو لشكل the viscous tracheobronchial secretions E.g., Bromhexine, Acetyl cysteine, i) Bromhexine Synthetic derivative of vasicine vasica) Cont…. (alkaloid= Adhatoda MOA of Bromhexine a) Thinning & fragmentation mucopolysaccaride fibers b) ↑ volume & ↓ viscosity of sputum ii) Acetylcysteine Given directly into respiratory tract cont. of MOA of acetylcysteine Opens disulfide bond رابطه في بروتين البلغمin mucoproteins of sputum =↓ viscosity Uses Cystic fibrosis (to viscosity of sputum) Onset of action quick---used 2-8 hourly Adverse effects Nausea, vomiting, bronchospasm in bronchial asthma 4) Antihistamines Added to antitussives/expectorant formulation Due to sedative & االثر المهدئanticholinergic actions produce relief in cough but lack selectivity for cough centre No expectorant action =▼secretions (anticholinergic effect) Suitable for allergic cough (not for asthma) E.g., Chlorpheniramine, promethazine diphenhydramine, 5) Bronchodilators Bronchospasm or stimulation of pulmonary receptors = induce or aggravate زياده cough + bronchoconstriction e.g. β2-agonist (salbutamol, terbutaline) MOA of bronchodilators in cough ▲surface velocity of air flow during cough→ Clear secretions of airway مهمهNot used routinely for every type of cough but only when bronchoconstriction is present 6) Pharyngeal demulcents مطري Soothe يهدئthe throat (directly & also by promoting تحفيزsalivation )اللعاب ▼ afferent impulses from inflamed/irritated pharyngeal mucosa Provide symptomatic relief in dry cough arising from throat E.g. lozenges, cough drops, glycerine, liquorice, honey ) العسل ( طب شعبي Specific treatment approach to cough Etiology of cough Treatment 1) Upper/lower respiratory tract infections Appropriate 2) Smoking/chronic bronchitis Cessation of smoking 3) Pulmonary tuberculosis 4) Asthmatic cough antibiotics Antibiotics Inhaled β2-agonists/iprat- ropium/corticosteroid 5) Postnasal drip (sinusitis) Antibiotics, nasal decongestants, antihistamines