Liver function test
advertisement

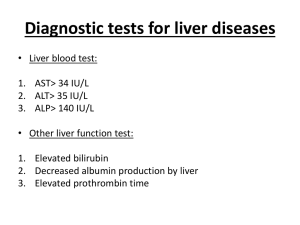
LIVER FUNCTION TEST LIVER FUNCTION TEST To assess - Capacity of liver - To detect the abnormality - For drug monitoring - Recovery Functions of liver • Metabolic functions: – Carbohydrate, lipid, protein, minerals & vitamin • Excretory functions: – Bile pigments, bile salts & cholesterol • Protective function & detoxification: – Kupffer cells, NH3 and xenobiotics detoxification • Hematological functions: – Formation of blood in embryo & plasma proteins in adult • Storage functions: – Glycogen, vitamins, trace elements Tests to access liver function • LFTs are the biochemical investigations to know the functions and damage of liver • Liver is a large size factory of safety so it can perform many of its functions almost normally despite of damage • Slelection of the right test is important in LFT VARIOUS LIVER FUNCTION TESTS A) Tests based on abnormal pigment metabolism – serum bilirubin and van den Bergh reaction – urine bilirubin – urine and fecal urobilinogen B) Tests based on metabolic capacity (i) carbohydrate metabolism - galactose tolerance - fructose tolerance (ii) lipid metabolism - serum cholesterol - cholesterol ester and their ratio - fecal fat (iii) amino acid metabolism - blood NH3 (iv) drug metabolism - hippuric acid test C) TESTS BASED ON SYNTHETIC FUNCTIONS - Total serum proteins - Serum albumin - A:G ratio - Plasma fibrinogen - Prothrombin time and index D) TESTS BASED ON EXCRETORY FUNCTIONS - Bile salts and bile pigments - Bromosulphathelein test (BSP retention test) E) TESTS BASED ON DETOXIFICATION - Hippuric acid synthesis test F) TESTS BASED ON SERUM ENZYMES DERIVED FROM LIVER - Transaminases - Alkaline phosphatases - 5`nucleotidase - glutamyltranspeptidase STANDARD L F T SERUM BILIRUBIN NORMAL RANGE total bilirubin conjugated unconjugated 0.2—1.0 mg/dl <0.2 mg/dl 0.2—0.8 mg/dl DIRECT AND INDIRECT REACTIONS Indirect positive--hemolytic jaundice Direct positive --obstructive Biphasic --hepatic LIVER ENZYMES A) TRANSAMINASES • • • • • • -Alanine transaminases (ALT)/SGPT -Aspartate transaminases (AST)/SGOT Indicate hepatocellular destruction ALT—cytoplasm—9-40IU/L—more sensitive AST---cytoplasm and mitochondria---9-45IU/L Markedly increased in hepatocellular diseases Mildly increased in obstructive diseases AST:ALT RATIO Severe damage - >1 Mild damage - 1 or <1 Alcoholic liver disease - >2.0 B) ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE (ALP) Cells lining the biliary canaliculi normal range :- 25-100 IU/L raised in obstructive liver diseases x3 hepatocellular diseases c) GAMMA GLUTAMYL TRANSPEPTIDASE provide sensitive index normal level:- <50U/L hepatic damage:- raised parallel with transaminases +++in biliary obstruction (along ALP) Alcoholism Drugs d) 5`NUCLEOTIDASE Normal range :- 2-15U/l Raised :- hepatobiliary diseases(along ALP) Advantage :- not altered in bone diseases e) others Serum LDH IDH Cholinesterase Total protein and ALBUMIN Most abundant serum protein is synthesized solely by liver Half life :- 21 days Good marker for chronic liver diseases Low levels :- chronic liver diseases - malnutrition - kidney diseases A:G ratio Normal---1.2 –1.5 : 1 PROTHROMBIN TIME (PT) All clotting factors are synthesized by liver Liver diseases :- decreased level of clotting factors Half life :- 5-72 hrs. PT:-acute/chronic liver diseases Role of vitamin K:- Required for the synthesis of II,VII,IX and X factors URINARY UROBILINOGEN Metabolites formed in intestines Being water soluble present in urine normally Increased mostly in:-hemolytic jaundice absent in obstructive pathology