Palliative Chemotherapy
advertisement

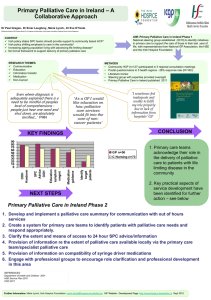
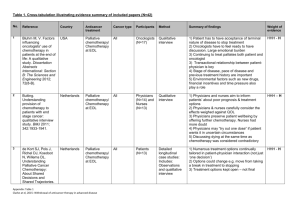
Palliative Chemotherapy Jason R. Beckrow, DO Lighthouse Oncology Objectives • Objectives: – Understand the concept of treat with curative intent vs. palliative intent. – Discuss the therapeutic goals of palliative chemo – Discuss targeted and palliative drug for various malignancies. Intentions of Treatment Palliative Curative The Problem: Conventional Care Model Fight or Quit What do we mean by Palliative Chemotherapy? GeriPal: A geriatrics and Palliative Care Blog • Is there anyone amongst the readership that can direct me to a list, a compendium of purely "palliative" chemotherapy regimens? • You can't find a protocol because there is no such thing. Chemotherapy produces symptoms, usually more symptoms than it relieves….Annonymous “I Already Do Palliative Care” anonymous oncologist Patients Reported Oncology Teams Often Do Not: • Consider psychosocial care as a part of their patients’ cancer care. • Understand their psychosocial needs, know about resources, or refer when needed. • President’s Cancer Panel 2003, 2004 Community Oncology Offices Cancer-Free Survival Treatment with Intent to Cure Managed Chronic or Intermittent Disease Diagnosis and Staging Treatment Failure Palliative Medicine Death IOM President’s Cancer Panel, 2003, 2004 Slide Courtesy of Jimmie Holland, MD Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center • Where majority of cancer care is given today • Where fewest psychological and social services available Conventional Care Anti-disease Therapy Presentation Hospice Care 6m Death Bereavement Care Model of palliative cancer care. Ferris F D et al. JCO 2009;27:3052-3058 ©2009 by American Society of Clinical Oncology The Relief of Suffering Physicians’ failure to understand the nature of suffering can result in medical intervention that (though technically adequate) not only fails to relieve suffering but becomes a source of suffering itself. Eric Cassel, 1982 The Goals of Palliative Chemotherapy • • • • • • Symptom Relief Attainment of Life Goals Portability Accessibility Cost efficiency Your thoughts…. Goals of Palliative Chemotherapy Early Palliative Care Study Procedures Palliative Care Guidelines Illness understanding and education Inquire about illness and prognostic understanding Offer clarification regarding treatment goals Distress Management Symptom management Pain Pulmonary symptoms Fatigue and sleep disturbance Mood Gastrointestinal Decision-making Assess mode of decision-making Assist with treatment decision-making Coping with life-threatening illness Patient Family/family caregivers www.nationalconsensusproject.org Prepared and Hopeful …Principles of Oncology ECOG Performance Status Grade Activity 0 Fully active, no restriction 1 Symptoms, restricted in strenuous activity 2 Ambulatory and capable of all self-care, no work activity. Up more than 50% of the day 3 Limited self care, confined to bed or chair >50% of the day 4 Completely disabled, unable to care for self, totally confined to bed or chair. 5 Dead Oken, MM et al. Am J Clin Oncol 1982 Conditions • • • • • • Breast Cancer Lung Cancer Prostate Cancer Multiple Myeloma Colo-rectal Lymphoma • • • • • • Brain Mets Bone Mets Hypercalcemia Chord Compression SVC Syndrome Hemoptysis Common Non Cyto-toxic Cancer Meds • Steroids • Biphosphanates Prostate Cancer • Androgen Deprivation – LHRH agonists – Anti androgens • Taxanes • Crizotnib Breast Cancer • Hormonal Therapy – Tamoxifen – Aromatase Inhibitors • Her-2 Receptivity – Trastuzamab – Lapatnib • Cyto-toxics – Taxanes Colon Cancer • VEGF-Bevacizumab • EGFR – Cetuximab – Pantiumumab • Cyto-toxics – 5-FU – Capecitabin Non Small Cell Lung Cancer • • • • Pemetrexed Taxanes Erlotnib Bevacizumab Small Cell Lung Cancer • • • • Platinum Etoboside Topotecan-Salvage Whole Brain RT Pancreatic Cancer • Gemcitabine • Erlotnib Multiple Myeloma • • • • Lenalidomide Bortezomib Chlorambucil Pulse Decadron Ovarian Cancer • Platinum • Taxane Non Hodgkin Lymphoma • Rituxamab-CD 20 + • Cytoxan Renal Cancer • Sorafanib • Sunitnib