File - NURSING FDTC Batch Spring 2011
advertisement

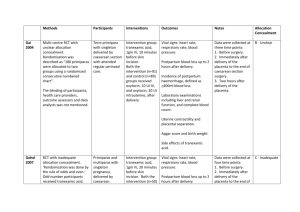
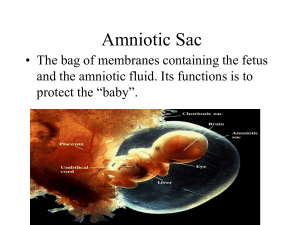
OB REVIEW OB TERMS Gravidity- Number of times woman has been pregnant Parity- number of deliveries after 20 weeks gestation regardless of outcome. Not the # of fetus (twins). GTPAL Gravida-# of pregnancies T-Term deliveries; 37 weeks + P-preterm deliveries; between 20 and 37 weeks A-abortion; delivery before 20 weeks L-living children OB terms Antepartum- conception till delivery Visit OB physician once monthly until 28 weeks gestation; then every 2 weeks till 36 week gestation, then weekly till delivery Assess in office: BP, weight, FHT, urine for protein, other. Focused assessment on pregnancy complications. Intrapartum Postpartum Nagele’s rule Due date determined by LMP date- three months + 7 days. LMP- 7/1/2011- what is EDC (estimated date of confinement)? LMP- 3/1/2011- what is EDC LMP- 11/14/2011? LMP- 12/3/2011? Common discomforts of pregnancy Urinary frequency or incontinence Fatigue Backache Nausea/vomiting Leg cramps Heartburn/indigestion Braxton hicks contractions Constipation/hemorrhoids FETAL ASSESSMENT TESTS Ultrasound- non-invasive, abdominal vs. transvaginal Biophysical profile-NST and ultrasound (breathing, movement, fetal tone, HR, amniotic fluid volume?) Amniocentesis-14 weeks till delivery-genetic disorders, lung maturation. Risks-hemorrhage, infection, labor, ROM, miscarriage. Chorionic Villus Sampling-less than 10 weeks gestation-genetic disorders. Alpha-Fetoprotein-16-18 weeks gestation( high values-neural tube defects; low values-Down’s syndrome. Pregnancy disorders Abortion-spontaneous vs elective 50% of time no known cause Vaginal bleeding, cramping. Nursing diagnoses: Anticipatory grieving related to risk of loss of pregnancy Acute pain related to uterine cramping Fear related to potential for losing pregnancy. Cardiac disease Congenital heart disease Acquired Ischemic Pregnancy is the great “un-masker” of hidden issues Circulatory volume increased by 40-50% Nursing diagnoses: activity intolerance r/t decreased CO Risk for fetal injury t/t effect of cardiac disease on pregnancy Abruptio placenta Premature separation of a normally implanted placenta later 20 weeks gestation- may be complete or partial. Patient presents with bleeding and abdominal rigidity (boardlike) Assess vital signs, FHT. Monitor Pt, PTT, platelets- mom is bleeding! If clotting factors consumed could lead to DIC. Placenta previa Attachment of the placenta in the lower uterine segment near or covering the internal cervical os. May be complete, partial, or a low-lying placenta (not covering the os). Painless vaginal bleeding. No vaginal exams!! Nursing diagnosis: anxiety r/t unknown outcome for patient and infant Risk for infection r/t blood loss and open vessels near cervix Gestational Diabetes Insulin resistance increases in pregnancy. Increased insulin needs in 2nd and 3rd trimesters. Risks for fetus-macrosomia, hypoglycemia, respiratory distress syndrome. Monitor FBS during labor Possible diabetic teaching in antepartum period Hyperemesis of pregnancy Nausea and vomiting severe enough to lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance and significant weight loss. monitor intake Monitor weight Dietary consult Provide nausea meds appropriately. Infections T-toxoplasmosis-hydro or microcephaly O-Other-Syhphillis, varicella, mumps, HIV R-Rubella-hearing loss, IUGR, cardiac defects C- cytomegalovirus-mental retardation, blind, deaf, seizures H- Herpes simplex-vesicles or encephalitis. Hypertensive pregnancy disorders Chronic HTN-before 20 weeks gestation and after 12 weeks postpartum Pre-eclampsia- increased BP after 20 weeks gestation with proteinuria Eclampsia- pre-eclampsia complicated by seziure or coma HELLP syndrome- liver dysfunction from worsening preeclampsia Delivery is the only cure!!! Labor and Delivery True labor vs. false labor Regular, rhythmic contractions in a pattern resulting in cervical change. Phases of labor: Stage 1- start of true labor to full dilation Stage 2- full dilation to birth of infant Stage 3- delivery of placenta Stage 4- delivery of placenta to 4 hours postpartum Which is the longest stage? Labor and delivery procedures: Induction of labor- pitocin Cervical ripeningForceps delivery Vacuum extraction External version Nursing care during labor Evaluate labor pattern- effective? Evaluate pain managementAssess fetus- FHR, engagement, presentation NPO status for mom- why? Labor and Delivery complications Cord prolapse Precipitous labor Amniotic fluid embolism Post-term labor Labor complications Pre-term labor-definition, risks, management, tests Dystocia-difficult, prolonged, risks DIC-s/s, labs, impact on fetus Ceserean section- elective vs. urgent- client preparation VBAC- one on one management, risks Postpartum care B-Breasts U-Uterus B-Bowels B-Bladder L-Lochia E-episiotomy H-Homan’s sign E-Emotions N-Nutrition Postpartum complications Infection Postpartum hemorrhage Thromboembolic disease Postpartum depression Postpartum psychosis Pharmacology Drugs used during labor Demerol, Stadol, Nubain- implications for fetus? Epidural- consents, time out Pharmacology-OB Pregnancy risk categories: ABCDX Teratogens