Medical Gas testing - NHS Education for Scotland
advertisement

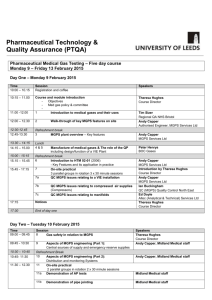
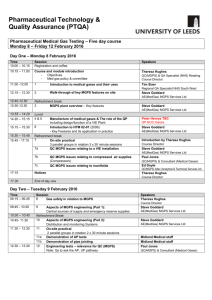
Medical Gases Lynn Morrison Regional QA Pharmacist NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde Medical Gases Introduction and session objectives To describe the different medical gases found within a hospital To understand the design and construction of a medical gas pipeline system (MGPS) To be aware of the system of controls applied to facilitate the safe and secure operation of a medical gas pipeline system To understand the roles and responsibilities of key personnel involved in medical gases To understand the role of the Quality Controller (MGPS) To have an awareness of medical gas testing To appreciate the role of the EDC pharmacist in an emergency situation Medical Gases – what gases are found in hospitals? Oxygen Nitrous oxide Medical Air Surgical Air Oxygen / Nitrous oxide mixture 50:50 “Equanox” or “Entonox” Vacuum What are the medical gases used for? Oxygen – used to sustain life Medical air – used to drive ventilators Surgical air – used to operate surgical tools Nitrous oxide – used in theatres for anaesthetic purposes Equanox / Entonox – used as an analgesic, home delivery Vacuum - suction What other gases could you find? Carbon dioxide Helium / oxygen mixtures Nitric oxide What are these gases used for? Carbon dioxide – clinical and physiological investigations Helium/oxygen mixtures – respiratory assessment and treatment e.g. COAD Nitric oxide – aids oxygen exchange in respiratory distress conditions How are the gases supplied to the hospital? Oxygen – delivered as a liquid via a tanker to a liquid oxygen tank compound with vacuum insulated evaporators - VIE Nitrous oxide – cylinders Medical air – cylinders or compressors Equanox / Entonox – cylinders Other gases – cylinders NHS Scotland - national contracts for supply of medical gases Where are the gases stored? Liquid Storage Tank with VIE – oxygen Cylinder store – various gases Manifold rooms – e.g. medical air, nitrous oxide, Equanox/ Entonox Medical and surgical air compressor systems and receiver tanks Other locations – e.g. ready use stores ambulances patient transport Oxygen tank – VIE tank “Duty” tank and a “stand by” tank Vacuum insulated evaporator Valve box (with test point) Alarm panel Copper pipework – medical gas pipeline system - connecting tanks to the hospital pipeline system Oxygen tank and VIE Oxygen tank – control panel Cylinder store Visit the cylinder store on site Cylinder stores should be :separate from other buildings no “naked flames” clean, tidy, locked full cylinders should be stored separately from empty each gas type to be stored separately etc Can you think of any other storage requirements? separate cylinders by size temperature control log of issue and return Cylinders Currently :Oxygen – black body / white shoulders Nitrous oxide – blue Medical air – grey body / black and white shoulders Equanox / Entonox – blue body / blue and white shoulders Heliox – black body / brown and white shoulders Carbon dioxide - grey Future :EU Directive – all cylinders will have white body and colour coded shoulders as above Implementation to be completed by 2025 Manifold rooms A manifold is defined as a set of pipework to which a series of cylinders is attached. “Duty” and “stand by” bulk supply to the hospital Must be in date Must be checked regularly Oxygen manifold Medical air manifold Medical / Surgical air compressors How do the gases get to the patient ? Medical Gas Pipeline System (MGPS) Copper pipelines Pressure reducing valves AVSU – area valve service unit Terminal outlets Flow meter and tubing Mask / nasal canulae Cylinders – valve and flowmeter Area Valve Service Units Terminal Units Safety issues Medical gases Oxygen – supports combustion – patient’s clothing and bedding can become saturated Nitrous oxide – causes headaches, drowsiness, cumulative effects, teratogenic effects, can cause asphyxia in confined spaces also supports combustion Equanox / Entonox – combination of the above Safety issues Cylinder handling Never carry a cylinder by its neck Use correct trolleys Protective equipment Never roll cylinders!! Never eat/smoke while handling cylinders Etc!! Training vital!!! Control systems - Documentation HTM 02-01 Part A ; Design, installation, validation and verification Part B ; Operational Management In Scotland (s)HTM 02-01 Control systems - Documentation Permit to work system controls any engineering work to be carried out on the MGPS safeguards the integrity of the MGPS and patient safety 4 part documentation signed by all those involved in the work activity Operational policies Controlled document Scope Responsibilities and training for staff Record drawings and accompanying documentation Description of MGPS, valves, alarms etc Medical gas committee Emergency procedures Control systems - Documentation Health and Safety at Work legislation Manufacturer / supplier product material safety data sheets C11 CHIP SPQAG testing protocols Control systems – defined roles and responsibilities Designated Medical Officer or Nursing Officer Authorised Person Competent Person QUALITY CONTROLLER (MGPS) Control systems – defined roles and responsibilities QUALITY CONTROLLER (MGPS) responsible for the quality control of medical gases as terminal units and plant accepts professional responsibility for the last independent check of a MGPS must be able to provide evidence of training, competence registered - QC (MGPS) register Your involvement with medical gases Clinical function Clinical need Equipment Understand operation of MGPS Understand safety considerations for cylinders Regulators, flowmeters and associated tubing etc Emergency situations Must be aware of day to day operational aspects of MGPS / cylinder management to ensure have fundamental knowledge to cope with emergency situation Examples Procedure to be followed Operational policy documents and emergency information cards Emergency situations YOUR ROLE to ensure back up supply is made available and additional cylinders sourced as required to contact suppliers and arrange delivery Must ensure you know :where back up supply (cylinders / tank) stored on site how to contact suppliers (cylinders or liquid supply) how many cylinders to ask for the size of cylinder to ask for the delivery location BEFORE AN EMERGENCY OCCURS !! Medical gases Testing Medical gas testing RQAS Med Gas test team Tests carried out – commissioning new installations modifications to existing systems de-commissioning of systems routine compressor testing Medical gas testing Tests completed Identity / purity Particulate contamination Non specific contamination Water vapour Carbon Dioxide Carbon Monoxide Oil Sulphur dioxide Nitrous fumes Line pressure Vacuum pressure Acceptance criteria (Ph. Eur.) Identity and purity – acceptance criteria oxygen - > or equal to 99.5% (absence of nitrous oxide) oxygen in medical / surgical air – 20.4% to 21.4% nitrous oxide - >98% (absence of oxygen) oxygen / nitrous oxide mixture 48% to 52% of each component Particles – absence of particles e.g. copper oxide, copper, “verdigris” Non- specific contamination – polytest tube – absence of colour change in crystals Water vapour – not more than 0.05mg/L / 67vpm Acceptance criteria (Ph. Eur.) CO2 – not more than 500ppm / 300ppm CO – not more than 5ppm Oil – not more than 0.1mg/L – medical / surgical air to ensure no carry over from compressor motors Sulphur dioxide – not more than 1ppm Nitrous fumes – not more than 2ppm Vacuum – not less than 400mmHg Visit to Medical Gas storage facilities and wards/ departments Visit the following : Oxygen tank and VIE plant Medical air compressor plant Nitrous oxide manifold Visit a ward :What gases are supplied via a piped system? - look out for terminal units, area valve service units (AVSU) What gases are supplied in cylinder form? Quiz Please complete multiple choice questions