Reproduction, Pregnancy,
and Development
Chapter 18
Sections 1, 2, & 3
The Female Reproductive
System
Objectives
•
•
•
•
•
State the role of the female reproductive
system.
Describe the function of each of the organs
of the female reproductive system.
Describe the changes in the body during
the menstrual cycle.
Summarize 4 problems that can occur with
the female reproductive system.
List five things a female can do to keep her
reproductive system healthy.
When Does Puberty Begin &
What Happens To The Body?
•
•
•
•
•
•
Begins between ages 10-12
Develop arm pit & pubic hair
Hips widen
Breasts grow
Menstrual cycle begins
Ovaries begin producing estrogen &
progesterone
What Is The Function Of The Female
Reproductive System?
To Make Eggs & To Provide A Place
To Support & Nourish A Developing
Human
Key Vocabulary Words &
Definitions
• Sperm: the sex cell that
is produced by the testes
and that is needed to
fertilize an egg.
• Egg (ovum): the sex cell
that is produced by the
ovaries and that can be
fertilized by sperm.
• Fertilization: the process
by which a sperm and an
egg and their genetic
material join to create a
new human life.
How The Female Reproductive
System Works
The Female Reproductive System Is
Made Up Of Internal & External
Organs
Path Of The Egg
What Do The Ovaries Do
& Where Are They Found?
•
•
•
•
Produces eggs & the
hormones estrogen &
progesterone
Almond shaped
Stores & releases a
mature egg once per
month - ovulation
Found deep in the
pelvic area
What Are Eggs or Ovum?
• The sex cells that mature
in the ovaries & can be
fertilized by the sperm.
• Females are born with
hundreds of thousands of
immature eggs; a mature
egg can only be fertilized
for 24 hours.
• Ovulation – the release
of an egg from the ovary
(once per month)
What Are The Female Hormones?
• Estrogen:
• Causes the reproductive
organs to mature into
their adult shape
• Causes the growth of
pubic & underarm hair
• Helps strengthen the
bones
• Estrogen &
Progesterone:
• Regulates the monthly
release of an egg &
• Prepares the body for
pregnancy.
What Do The Fallopian Tubes
&Fimbria Do?
• Transports the egg from
the ovary to the uterus
• Where fertilization takes
place
• It’s the size of a strand of
spaghetti
Fimbria
• Flowerlike ends of the
Fallopian Tubes helps
move the egg from the
ovary into the Fallopian
Tube
What Does The Uterus Do?
• Provides a place to support
a developing human.
• Is found on the top of the
vagina between the
bladder and the rectum.
• A fertilized egg will implant
itself in the uterine lining &
in develop 9 months;
• Normal size = women’s fist;
• When pregnant, it expands
to the size of a medium
watermelon
What Is The Cervix?
•
•
•
Barrier
separating
the vagina
from uterus;
Normally very
hard
Dilates to 10
centimeters &
softens just
before birth
What Is The Vagina & What Does It
Do?
• Runs from the lower end
of the uterus to the
outside of the body.
• Receives sperm during
reproduction
• Allows menstrual flow to
exit the body
• Is the part of the birth
canal through which the
baby is delivered.
What Are The Exterior Parts Of The
Female Reproductive System?
Labia Majora
• The outer lips of the
vagina;
• Provide cushion – similar to
that of the scrotum on the
male
Labia Minora
• Inner lips;
• Swell & deepen in color
during sexual stimulation
What Are The Exterior Parts Of The
Female Reproductive System?
Clitoris
• Very sensitive
• Covered by a hood of
skin;
• Purpose is sexual
stimulation
Hymen
• Thin membrane over
the vaginal opening;
• Will tear during 1st time
sexual intercourse
What Are The Three Openings In The
Female Reproductive Area?
Urinary Opening
• Expels urine
Anus
• Expels feces
Vaginal Opening
• Receives penis during
sex
• Expels menstrual fluid
• Birth canal opening
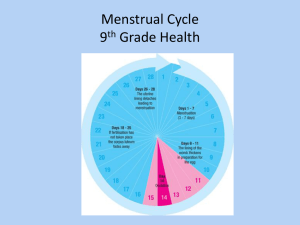
What Is The Menstrual Cycle?
Hormonal & physical changes
in the body that prepare
the uterine lining for pregnancy.
How Does The Menstrual Cycle Work?
•
•
Rising estrogen levels cause the uterine lining to
thicken
Increasing levels of the follicle stimulating & luteinizing
hormones cause the maturation & release of an egg Ovulation.
Menstrual Cycle Continued
• After ovulation, the uterine lining continues to
thicken.
• This helps nourish & support the baby during
pregnancy.
• If pregnancy does not occur, the uterine lining
breaks down & discharges through the vagina –
Menstruation. Estrogen & progesterone levels
rapidly decrease.
• Females use tampons or sanitary
napkins to absorb the blood.
The Menstrual Cycle
(Preparing for Pregnancy)
Days 22-28
Uterine lining
is complete
Days 1-7
Uterine Lining
Sheds
Days 3-7
Menstruation
Days 16-21
Uterine lining
thickens
Days 13-15
Ovulation Occurs
Days 8-15
Most fertile time
Uterus lining
begins to
thicken
Why Does The Menstrual Cycle
Vary?
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Environmental factors such as
stress,
diet,
travel,
exercise,
weight gain or loss, &
illness can influence the timing of the females cycle.
Problems Of The Female
Reproductive System
Problem
What is it?
Symptoms
Treatment
Cystitis
Inflammation of the urinary
bladder
Burning during urination,
strong-smelling urine, fever, or
blood in urine.
Antibiotics prescribed by
doctor.
Vaginitis
Vaginal infection in the vaginal
area from fungus, bacteria
protozoa, or STD.
Irritation or itching around the
vagina, vaginal secretion of
unusual color or unpleasant
odor.
Over the counter vaginal
cream or prescription by the
doctor.
Menstrual cramps
Cramps due to prostaglandin
(hormone like substance)
production during
menstruation.
Contractions of uterine
muscles, lower abdominal
pain, & occasional nausea and
vomiting.
Over the counter medication &
a warm bath; further treatment
provided by the doctor.
Premenstrual syndrome
(PMS)
Mental & physical changes
related to menstrual cycle, but
not completely understood
Irritability, mood swings,
depression, abdominal
bloating, & breast tenderness.
Determined by doctor
Toxic shock syndrome
(TSS)
Poisoning of the body from
bacterial toxins; often related
to tampon use
Fever, chills, weakness, & rash
on palms of hand
Antibiotics & immediate
medical treatments.
Endometriosis
Can lead to infertility
Growth of tissue from uterine
lining outside the uterus
Severe cramping and pain in
lower abdominal area or pelvis
Determined by a doctor;
hormone therapy or surgery
may be required.
Ovarian Cyst
Failure of follicle in ovary to
rupture & release an egg; may
also be from growth of cancer
Pain in lower abdomen or
pelvis for a month
Determined by a doctor; cysts
often go away on their own but
sometimes require surgery
Cervical cancer
Abnormal division of cell s in
the cervix; may also be from
an STD
Vaginal bleeding, discharge, or
pelvic pain, may not be any
symptoms
Surgery, radiation, &/ or
chemotherapy.
What Are 7 Ways To Keep
Healthy?
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Exercise regularly & maintain a balanced diet.
Gently wash the genital area everyday with warm
water & mild soap. Do not use feminine hygiene
spray or powders.
Wipe the vaginal opening from front to back after
urination.
Change sanitary napkins or tampons every 4-6
hours when menstruating.
Avoid wearing tight clothing that can cause
discomfort.
Do a breast self exam each month.
Have an annual pelvic exam with a doctor.
What Is Cervical Dysplasia
& Carcinoma-In-Situ?
•
•
•
•
Abnormalities are on the
surface lining (or "skin") of
the cervix.
Cervical dysplasia is
pre-cancerous, not cancer.
Mild dysplasia often goes
away without any treatment
Severe dysplasia can
become invasive cancer
if not treated.
What Are The Parts Of the Breast &
What Is Its Purpose?
Fatty Tissue
The more fatty tissue the larger the breast;
Where breast cancer usually occurs
Milk Glands
Produce milk
Milk Ducts
Moves milk from the milk gland to the nipple
Nipple
Feeds the baby
Areola
Dark shade of skin that
surrounds the nipple
Breast Have 2 Purposes
• Breast feeding &
• Sexual pleasure
How Do You Perform A Monthly
Breast Self Exam (BSE)?
1 out of 9
women will
get breast
cancer
Early Detection Of
Breast Cancer
• The chance is higher if it runs in the family
• When performing a self-exam, feel for
unusual lumps & thickening under the skin
• Women over 40 need to begin getting
regular Mammograms
What Is A
Mammogram?
A procedure or test for breast cancer.
Normal Fatty
Breast Tissue
Normal Dense
Breast Tissue
Mastectomy specimen containing
a very large cancer of the breast
Breast cancer (dark pink) in & around a lymph node
(purple).
Breast cancer can metastasize (spread) to the
nearby lymph nodes, usually those under the arm.
That is why surgery for breast cancer always
involves some type of surgery for the glands under
the arm. Once cancer enters the lymph nodes, it
can spread throughout the body.
Breast Cancer
Patient with advanced local-regional
recurrence of breast cancer with an
ulcerating axillary mass
Mastectomy
Preventing Sexually Transmitted
Diseases
• You & your partner should be examined
before considering intercourse – check for
STDs & HIV/AIDS
• Use condoms
• Limit the number of sexual partners
• Know the signs of problems in the
male & female reproductive system
What Is Vaginal Irritation & How
Do You Prevent It?
Vaginal Irritation
• A redness, itching, or slight discomfort around the
opening of the vagina.
Prevention
• Regular bathing,
• Wear loose cotton clothes & cotton underwear,
• Avoid scented products that touch skin in the
genital area, &
• Avoid pantyhose, tight jeans, & wet clothes
What Are Menstrual Cramps &
How Can You Relieve Them?
Menstrual cramps
• Caused by contractions of the uterine
muscles
Relief
• Take a warm bath,
• Eat a balanced diet,
• Exercise regularly,
• Use anti-inflammatory drugs
• Reduce caffeine & sugar intake
What Is Infertility & What Are The
Causes?
Infertility
• The inability to
get pregnant
Causes Can Be
• Genetic
• Endometriosis or
• STDs
What Is A Pelvic Exam?
A breast & genital exam,
plus a Pap smear.
What Is A Pap Smear?
Examines the cells of the
cervix to detect &
prevent cervical cancer.
Section 18.2 Review
Key Terms
• Define Ovaries
• The female reproductive organs that
produce eggs & the hormones estrogen &
progesterone
• What is “the female reproductive organ
that provides a place to support a human
being?”
• The Uterus
Key Ideas
• What is the purpose of the female
reproductive system?
• To produce eggs & provide a place to
support & nourish a developing human
• What is the female reproductive organ
that transports the egg from the ovary to
the uterus?
• The Fallopian Tube
Key Ideas
• What is the path of the egg through the female
reproductive system?
• Ovary
• Fallopian Tube
• The Uterus
• Exits the Vagina if unfertilized
Key Ideas
• What are the changes that occur in the
female reproductive during the menstrual
cycle?
• Menstruation
• Ovulation
• Thickening of the uterine lining
Key Ideas
• What are the symptoms of menstrual
cramps?
• Contractions of uterine muscles
• Lower abdominal pain
• Occasional nausea & vomiting
• What are the symptoms of vaginitis?
• Irritation or itching around the vagina
• Vaginal discharge
What Are 7 Ways To Keep
Healthy?
1.
2.
Exercise & eat a balanced diet
Gently wash the genital area everyday with warm
water & mild soap
- Do not use feminine hygiene spray or powders
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Wipe the vaginal opening from front to back
Change sanitary napkins or tampons every 4-6 hours
Avoid wearing tight clothing
Do a breast self exam each month
Have an annual pelvic exam with a doctor
Critical Thinking
• What can a girl do if she has severe
menstrual cramps?
• Take an anti-inflammatory drug (Midol,
Tylenol, Aleve, Advil…)
• Take a warm bath
• See a doctor of severe