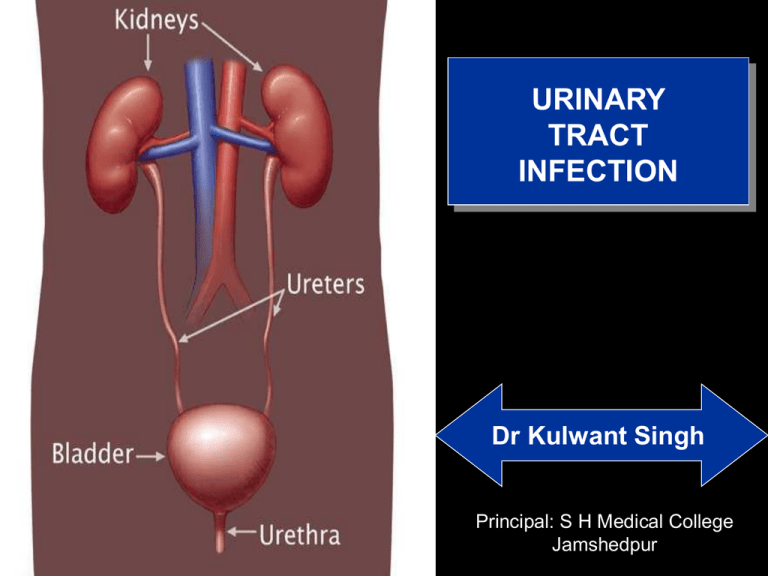
URINARY
TRACT
INFECTION
Dr Kulwant Singh
Principal: S H Medical College
Jamshedpur
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
• Second most common
infection
following
respiratory infections
• UTI occur when bacteria
(E.
coli)
from
the
digestive tract get into
the opening of the
urinary
tract
and
multiply
• Bacteria first infect the
urethra, then move to
the bladder and finally
to the kidneys
• UTI tend to occur more
in women than men
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
Urinary tract is normally
sterile due to the fact
that bacteria moving
upwards are regularly
washed out by
urination
Normal flora found in the
urethra consist of
lactobacillus and
staphylococcus to name
a few
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
Importance of Urinary
Tract Infections is
demonstrated by the
fact that 20% of women
between ages 20-65
suffer one attack per
year
Approximately 50% of
women develop a UTI
during their lives and
there is a prevalence
rate of 5% per year of
asymptomatic or covert
bacteriuria in nonpregnant women
between ages 21 and 65
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TYPES
LOWER TRACT INFECTION
UPPER TRACT INFECTION
URETHRITIS
PYELONEPHRITIS
PROSTATITIS
CYSTITIS
PERI NEPHRIC ABSCESS
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
AETIOLOGY
Background
1. Bacterial infections of urinary tract are a very common
reason to seek health services
2. Common in young females and uncommon in males under
age 50
3. Common causative organisms
• Escherichia coli (gram-negative enteral bacteria) causes most
community acquired infections
• Staphylococcus saprophyticus, gram-positive organism causes
10 – 15%
• Catheter-associated UTI’s caused by gram-negative bacteria:
Proteus, Klebsiella, Seratia, Pseudomonas
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
PATHOGENESIS
BACTERIA GET ACCESS FROM URETHRA AND
ASCENDS
FEMALES ARE MORE PRONE DUE TO:
• SMALL URETHRA
• GRAM NEGATIVE ORGANISM RADIATE FROM PERI
ANAL AREA TO URETHRA
• SEXUAL INTERCOURSE
• SUSCEPTIBILITY OF EPITHELIUM
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
PATHOGENESIS
WHETHER BLADDER INFECTION ENSURES IT,
DEPENDS ON THE FOLLOWING:
• FLUSHING AND DILUTING OF MICURITION AND
VOIDING
• ANTIBACTERIAL PROPERTIES OF BLADDER
MUCOSA AND URINE
• SIZE OF INOCULUM
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
PATHOGENESIS
• FEMALE SEX AND INTERCOURSE PREDISPOSES
• PREGNANCY: URETERAL TONE AND URETHRAL
PERISTALSIS DECREASES
• OBSTRUCTION IN FREE FLOW OF URINE: TUMOR,
STRICTURE, CALCULI AND BPH ETC.
• CATHETERISATION, URETHRAL DILATATION,
CYSTOSCOPY
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
PATHOGENESIS
The normal bladder is capable of clearing itself
of organisms within 2 to 3 days of their
introduction.
Defense mechanisms
(1) the elimination of bacteria by voiding
(2) the antibacterial properties of urine and its
constituents
(3) the intrinsic mucosal bladder defense
mechanisms
(4) an acid vaginal environment (female)
(5) prostatic secretions (male)
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
PATHOGENESIS
Two potential routes :
(1) the hematogenous route, with
seeding of the kidney during the
course of bacteremia
(2) the ascending route, from the
urethra to the bladder, then from
the bladder to the kidneys via the
ureters.
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
PATHOGENESIS
Hematogenous Infection
Because the kidneys receive 20% to 25% of the
cardiac output, any microorganism that
reaches the bloodstream can be delivered to
the kidneys.
The major causes of hematogenous infection are
S. aureus, Salmonella species, P. aeruginosa,
and Candida species.
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
PATHOGENESIS
Hematogenous Infection
Chronic infections (skin, respiratory tract)
blood circulation
small abscess
renal pelvis
kidney (cortex)
renal tubular
renal papillary
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
PATHOGENESIS
ASCENDING INFECTION
The ability of host defense
Urinary tract mucosal cells damaged
The power of bacterial adhesions(toxicity)
organisms
urethra,periurethral tissues
bladder
ureters
renal pelvis
renal medulla
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
PATHOGENESIS
Voiding dysfunction is characterized by
some or all of the following:
urgency
frequency
dysuria
hesitancy
dribbling of urine
overt incontinence
secondary to a UTI or to local irritants such
as pinworm infestation
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
PATHOGENESIS
The normal bladder is capable of clearing itself
of organisms within 2 to 3 days of their
introduction.
• Defense mechanisms
(1) the elimination of bacteria by voiding
(2) the antibacterial properties of urine and its
constituents
(3)the intrinsic mucosal bladder defense
mechanisms
(4) an acid vaginal environment (female)
(5) prostatic secretions (male)
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
PATHOGENESIS
CONTINITUATION OF UTI DEPENDS :
• Female sex and intercourse predisposes
• Pregnancy:
ureteral
tone
decreased,
ureteral
peristalsis decreased
• Obstruction in free flow of urine
• Catheterisation , urethral dilatation, cystoscopy
• Vesico-ureteric reflux: it occurs during voiding -pressure increase in bladder, flow from bladder to
kidney
• Impaired defence
• Neurogenic: spinal injury, sclerosis
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
Age-related Risk Factors for UTI
• Advanced Age
• Fecal incontinence/impaction
• Incomplete bladder emptying or neurogenic
bladder
• Vaginal atrophy/estrogen deficiency
• Pelvic prolapse/cystocele
• Insufficient fluid intake/dehydration
• Indwelling foley catheter or urinary catheterization
or instrumentation procedures
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Cystitis
• dysuria (burning or discomfort on urination)
• frequency
• nocturia
• suprapubic discomfort
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
• Fever with chill & rigor
• Haematuria
• Strangury
• Ineffectual desire
• Cloudy urine
• Offensive urine
• Pain lower abdomen
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Uncomplicated
• Cystitis
• Urethritis
• Female >>> male
• Sequel rare
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Complicated
• Pyelonephritis
• Prostate obstruction
• Relapse +++
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
INVESTIGATIONS
WBC ++++
Urine: C & S
Cystoscopy
Ultra Sound
IVU
P/R
PID
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
FLUID ++
ALKALI
EMPTYING OF BLADDER
HYGIENE
Recurrent U.T.I.s
that are reinfection.
Unresolved
Isolated
infections
infection
Classification of
U.T.I.
Recurrent infections resulting
from bacterial persistence.
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
ROAD MAP OF TREATMENT
To limit the period of suffering.
To minimise the severity of suffering.
To arouse the immunity of the patient to
prevent reinfection.
To avoid dialysis and kidney
transplantation.
To reduce the cost of treatment.
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
Eryngium aquaticum
Burning pain with frequent urge.
Prostatic fluid from slightest provocation
Tenesmus of bladder
Frequency / dysurea
Urine burns like fire
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
Eupatorium purpereum
Strangury
BHP
Chill runs upward
Burning while urinating
Cystitis in pregnant women
Sweetish smell urine
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
Chimaphila umbellata
Plethoric young women
BHP
Urine scanty loaded with ropy mucopurulent
sediment
Burning and scalding pain Violent tenesmus
Urinate only when bends forward and with feel
wide open
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
Equisetum
Fullness of bladder not relieved by
urination
Sharp cutting / burning pain
Right lumber region painful
Constant desire to urinate
Aggravation immediately after urination
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
Epigea repens
Chronic cystitis / dysurea
Strangury
Urge in continency
Mucopus and uric acid deposition and
renal calculi
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
Petroselinum
Urge in continence
Burning and tingling in urethra
Dysurea with BHP
Ameliorate by rubbing the urethra
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
PRUNUS SPINOSA
Forked urine – slow stream
Cramping pain in bladder <
walking
Sudden urge
Violent pain Thinking of complaints
ameliorates
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
CANNABIS SATIVA
Burning in bladder while urinating
Stitches in urethra
Urethra sensitive
Urine scalding and spasmodic closure of
sphincter
Fear of going to bed
Time passes slowly
Tickling sensation as of dropping water.
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
CANTHARIS
Inflammation are violent
Cystitis
Strangury
Haematuria with pain
Violent burning ,cutting ,stabbing pain
Urging for urination
Urine comes drop by drop with pain
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
PARIERA BRAVA
Radiating pain to thigh during efforts
urinate
Sensation as if the bladder is full
Urethritis
Urge incontinency
Contains thick stringy mucus
to
TREATMENT
THUJA OCC.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Fixed ideas
Anger from contradiction
Ill effects of vaccination
Urethra inflamed
Frequent urination with pain
Sudden urge
Left sided
Tickling in Urethra.
Must be used inter-currently to prevent
reappearance
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
TEREBINTHINA
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Confusion of mind
Irritability
Concentration difficult
Bleeding mucous membrane
Strangury
Urethritis
Urine scanty with odor of violet
Urine smoky , coffee ground
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
BERBERIS VULGARIS
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Indifferent / anxiety
Changeability /wandering pain
Pain aggravate by pressure
Left sided
Sticking / cutting / burning
Bubbling sore sensation in kidney
Frequent maturation
Burns when non urinating
Associated with renal calculi
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
ARSENIC ALBUM
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Restlessness
Fear of death
Anxiety
Burning like fire > by heat
Putrid discharges
Thirst unquenchable for small quantity
Craves of acids / warm food
Burning urethra during urination
Dysuria
Urine is black
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
APIS MEL
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Fearfulness , can not help crying
Apathy
Sudden shrill piercing screams
Ailment from suppressed sexual desire
Burning / stinging pain with swelling
Thirstlessness
Craving for sour
Nephritis / cystitis / prostatitis
Strangury
Last drop burn and smart
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
NITRIC ACID
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Irritable/ Vindictive/ Headstrong
Sensitiveness to noise
Discontented
Pain appear suddenly and disappear suddenly
Discharges are offensive
Love fat and salt ,hate meat and milk aggravates
Urine cold on passing
Burning stinging after urination
Frequent urge at night
URINARY TRACT INFECTION
TREATMENT
POPULUS TREMULOIDS
•
•
•
•
•
Urethritis
Dysurea –Scalding during pregnancy
Severe tenesmus
Pain behind pubis at the end of Urination
B.H.P.