Identifying & Managing Acute Renal Injury
advertisement

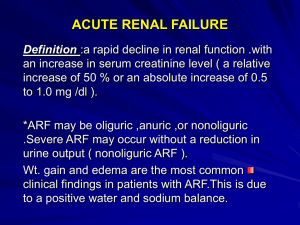
Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CSC, PCCN-CMC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Discuss the significance of the RIFLE classification for renal dysfunction. Differentiate between pre – renal, intra – renal and post – renal failure with regard to etiologies, diagnosis and treatment. Utilizing a case study, identify management strategies of a patient with renal dysfunction Definition rapidly progressive potentially reversible cessation of renal function UO < 0.5 mL/kg/hr Renal Failure Index (RFI) RFI = UNa x SCr/UCr Intrepretation RFI < 1 (prerenal failure) RFI > 1 (intrarenal failure) Fraction Excreted Sodium (FENa) FENa = Una X PCr / Pna X Ucr x 100 Intrepretation FENa < 1 (prerenal failure) FENa > 1 (intrarenal failure) Renal Failure Index (RFI) RFI = UNa x SCr/UCr Example RFI < 1 UNa < 20 mEq/L FENa < 1% UCr/SCr > 30 Renal Failure Index (RFI) RFI = UNa x SCr/UCr Example RFI > 1 UNa>40 mEq/L FENa > 2-3% UCr/SCr<20 Renal Biomarkers Urine interleukin – 18 (IL – 18) Urine or blood NGAL neutrophil gelatinase – associated lipocalin Increase 24 to 48 hours earlier than creatinine Prerenal Etiology (PRE) most common type volume cardiac function use of vasopressors Prerenal Etiology (PRE) Diagnostics BUN/Creatinine ratio RFI/FENa urinalysis Postrenal (POST) obstructive process • structural • functional lower tract or bilaterally in upper tracts Intrinsic Diagnostics BUN/Creatinine ratio RFI/FENa urinalysis Intrinsic - kidney acute tubular necrosis (hypoxic or nephrotoxic) glomerular disorders (AGN), rhabdomyolysis, postinfectious Intrinsic - kidney Vascular lesions – blood flow compromise (HUS) Interstitial nephritis (AIN) reactions to drugs or infections Intrarenal Etiology Diagnostics BUN/Creatinine ratio RFI/FENa urinalysis Treatment underlying cause prevention on injury high risk patient hydration limit exposure Management Principles maintain fluid balance manage hyperkalemia • glucose & insulin • calcium gluconate • sodium bicarbonate Clinical Manifestations hyperkalemia hypocalcemia hypermagnesemia hyperphosphatemia uremia acid – base imbalance Management Principles control hypertension in presence of encephalopathy bicarbonate for severe acidosis (pH < 7.2) manage anemia Renal Replacement Therapies Treatment Replacement Therapies acidosis HCO3 < 10 mEq/L K+ > 6.5 mEq/L need high protein diet deteriorating Treatment: Types hemodialysis peritoneal dialysis continuous renal replacement therapy Treatment fluid balance anticoagulation prevent clotting prevent blood loss ultrafiltration Rhabdomyolysis Causes trauma burns compression syndrome infection Rhabdomyolysis Causes vascular occlusion prolonged shock electrolyte disorders drugs (cocaine, alcohol) Rhabdomyolysis Clinical Manifestations myalgias muscle swelling & weakness DIC color of urine Rhabdomyolysis Lab Values elevated muscle enzymes hyperkalemia hyperphosphatemia hypocalcemia Rhabdomyolysis Treatment volume replacement treat electrolyte abnormalities protect renal perfusion alkalinization of urine fasciotomy Case Study 1 45 – year old female with history of peptic ulcer 10 – day history of intractable vomiting and abdominal pain drinking small amounts of water @ frequent intervals weaker, now complaining of dizziness Case Study 1 Vital Signs (Supine) Vital Signs (Sitting) BP 96/50 HR 110 RR 20 Temp 99°F BP 72/38 HR 140 Case Study 1 Physical Exam: tenting of the skin sunken eyes dry mucous membranes flat jugular veins epigastric tenderness Case Study 1 Serum Electrolytes ABGs Na K Cl CO2 Glucose Creatinine BUN pH PaCO2 PaO2 SaO2 HCO3 134 2.6 70 41 80 4.5 112 7.55 50 90 95% 40 Case Study 1 Urine Chemistries Na K Cl Creatinine Urea Osmolality 15 40 <10 200 2000 700 Urinalysis Color dk amber pH 5.0 SG 1.020 Ketones + Protien Blood - Sediment WBC RBC Casts 0-1 0-1 None Case Study 2 20 – year old male with friends “doing drugs – cocaine” Police break up party – male runs from police but collaspes – states legs became so weak that he fell Admitted to ED – lower extremity weakness and severe pain in legs Case Study 2 Serum Electrolytes ABGs Na K Cl CO2 Creatinine BUN Ca Mg PO4 pH PaCO2 PaO2 SaO2 HCO3 141 6.7 104 7 4.5 20 5.0 2.0 11.2 7.11 27 97 98% 7 Case Study 2 Serum Enzymes CK LDH 4,780 812 Hematology Values Hct WBC Clotting Profile 30 PT 18,400 PTT Platelets 28 >180 80,000 Case Study 2 Urinalysis Color SG pH Reddish brown 1.008 5.0 Sediment RBC WBC Casts 0-1 4-5 granular & epithelial Urine Chemistries Urine Na Urine Osm 42 280