tb in malaysia - WHO Western Pacific Region
advertisement

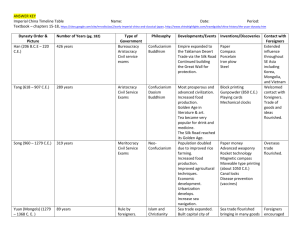
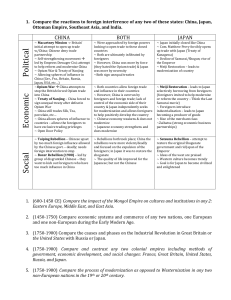
Country Progress Report MALAYSIA The ninth Technical Advisory Group and National TB Programme Managers meeting for TB control in the Western Pacific Region Manila, Philippines 9 -12 December 2014 1 SURVEILLANCE National TB Strategy/Policies National Strategic Plan for Tuberculosis Control, 20112015 was launched in 2011 It is in line with the 6 Strategies of TBC by WHO / Stop TB Org. Fund is allocated as proposed by National TB Coordinator under CDC, calculated on basis of planning as well as outcome of previous year Fund is solely by Ministry of Health, under jurisdiction of Finance Ministry TARGET 1 To Reduce 50% Inc. Rate by the year 2015 Relative to 1990 Level 2 To Increase 95% Case Detection Rate by year 2015 3 To Achieve Beyond 85% Cure Rate by year 2015 4 To Achieve Beyond 85% Treatment Success Rate by year 2015 5 To Reduce 50% TB Death Rate By the year 2015 Relative to 1990 Level INCIDENCE (NOTIFICATION) RATE OF TB (per 100,000) MALAYSIA, (1990-2013) 30000 90 77 72 25000 81 80 68 70 Number of case 20000 60 50 15000 40 10000 30 20 5000 10 0 0 Year Total Case Notification Rate/100,000 13 Treatment Outcome of New Smear Positive Cases (Cohort 2006 -2013) 100 90 80 70 60 46 67 69 78 78 79 78 77 % 50 40 30 20 10 0 2006 69 2007 46 2008 67 2009 78 2010 78 2011 79 2012 78 2013 77 Complete 1 3 5 1 1 1 1 2 Died 8 6 8 8 9 9 9 9 Defaulter 10 3 5 4 4 4 4 4 Failed 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Not Evaluated 12 42 15 9 8 7 8 8 Cure 15 TB MORTALITY RATE, MALAYSIA (1990-2013) 16 MDR-TB MALAYSIA, (2004-2013) Year Notified TB Cases Isolates tested for (All Forms) DST MDR Cases % MDR (By number of culture positive tested for DST) 2004 2005 2006 15429 15875 16665 5083 6309 6386 13 17 42 0.3 0.3 0.7 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 16918 17506 18102 19337 20666 6687 6264 7137 6963 10477 41 56 55 51 141 0.6 0.9 0.8 0.7 1.3 2012 22710 9722 74 0.8 2013 Okt, 2014 24071 17496 13777 14607 124 78 0.9 0.5 24 Treatment outcome of MDRTB cases Malaysia (2007-2011) Treatment success rate (%) 100 80 60 59 47 40 36 25 28 2010 2011 20 0 2007 2008 2009 Treatment success rate Target Note: Treatment outcome for MDRTB cases are using previous 2 years cohort analysis 25 TUBERCULOSIS IN FOREIGNERS In 2000, 10% of notified TB cases were in foreigners with majority (90%) from Indonesia and Philippines. (Iyawoo K, 2004) In 2003, a rate of 30% of foreign cases was reported among 425 patients at the national referral centre. Rates were higher in men compared to women. (Nissapatorn et al, 2007) Locals were older than foreigners (44 vs 30 years). Lost to follow-up and transfer out was greater in foreigners compared to locals. No difference in risk factors, new cases, smear negative cases. CONCLUSION There was significantly more cases of tuberculosis in foreigners than expected and this increase is disproportionately greater in women than men. Foreign cases were significantly younger and less educated. There were more sputum negative cases and relapsing/recurrent TB in locals. More foreigners moved away or were lost to treatment. Local cases were more likely to have risk factors such as diabetes, smoking, and HIV infection. Major Challenges Sustainability of the TB programme beyond 2015. An estimated (20-30)% of notified TB cases are not MTB confirmed and takes 3 weeks to 3 months for confirmed results. Ensuring the availability of quality assured TB drugs. Ensuring quality screening and clinical management of pulmonary TB, extra pulmonary TB and TB in children including contact investigation. Ensuring adequate infection control measures to limit infection transmission in health care facilities . Way Forward 1. Research on TB will be prioritized as policy research. 2. Public Private Partnership Project and Implementation 3. Safety assessment of targeted Public Health Facilities 4. Enhance use of Fluorescent Microscope in exchange to conventional microscope at clinic level. 5. Revive mass screening for TB targeted groups using mobile x-ray. 38