Biologics Therapy in Paediatric Rheumatology
advertisement

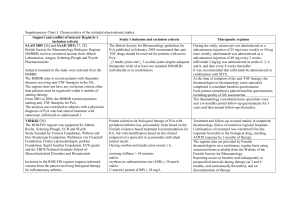
Biologics Therapy in Paediatric Rheumatology Rheumatology study day 2014 Alice Chieng • Prevalence of JIA 400:100,000 • Incidence of JIA 10-:100,000 Mannere et al Kunamo et al • Greater Manchester 100 new cases per year JIA Diagnosis • • • • History >6 weeks <16 yrs ≥ 1 joint with evidence of synovitis Exclusion of infection/ vasculitis Radiology imaging of Joints Synovial cytology ANA/RF/ HLAB27 JIA Classification • • Systemic Polyarticular • Oligoarticular • • • Psoriatic arthritis Enthesitis-related arthritis Other arthritis RF +ve RF –ve persistent extended ILAR ( International League of Associations for Rheumatology 2001) Management Family response Intra articular steroid injections New diagnosis JIA child MDT involvement Medical intervention Education Management orthopaedic Physiotherapy Occupational therapist podiatrist Medical treatment growth Exercises school Transitional Education Education Information Clinical Psychologist Social worker Rheum Nurse Ophthalmologist career Play therapist Medical treatment • Depends on subtypes of JIA • Intra articular steroid injections • DMARD: methotrexate/ sulphasalazine/ leflunomide • Biologics NICE guidance Failure or intolerance to DMARD by 3 months, Active joint disease Core Set Criteria Active Joint Counts Restricted Joint Counts Physician Global Assessment Score Parental VAS CHAQ ESR Which biologics agent should be used? Current views on pathogenesis of Inflammatory Arthritis- 1 Co- Stimulatory inhibitor- abatacept Smolen, J.S. et al., 2007. Lancet, Published online June13 Current views on pathogenesis of Inflammatory Arthritis - 2 Anti IL1 and IL6Anakinra Tocilizumab Anti TNFEtanercept Infliximab Anti-CD20 rituximab Smolen, J.S. et al., 2007. Lancet, Published online June13 Secretion of IL-1β by monocytes in inflammatory diseases in SOJIA A possible positive feedback cycle contributes to perpetuation of chronic inflammation in sJIA Anti IL1 and IL6Anakinra Tocilizumab Therapeutic Indications - UK Etanercept Rheumatoid arthritis (Enbrel) Ankylosing spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Plaque psoriasis Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis Infliximab Rheumatoid arthritis (Remicade) Ankylosing spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Plaque psoriasis Crohn’s disease Ulcerative colitis Adalimumab Rheumatoid arthritis (Humira) Ankylosing spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Crohn’s disease Psoriasis Poly articular Juvenile Idiopathic arthritis www.emc.medicines.org.uk Nomenclature ‒ ximab chimeric antibody ‒ zumab humanised antibody ‒ umab human antibody ‒ cept fusion protein Structure of Etanercept Human TNF Receptors Human Antibody Etanercept - Mode of Action Activated macrophage sTNFR:Fc Target cell TNF Signal sTNFR:Fc Etanercept - Mode of Action Etanercept • • • • Etanercept in Children with polyarticular JRA 0.4mg/kg twice weekly ACR 30 pedi- 74% 82% discontinue coticosteroids or taper below 5mg/day Safety: 0.12 events per patient year Lovell DJ, Giannini EH et al 2006 Etanercept • German Etanercept registryn=1300 66% for 4 years of treatment • Dutch Registry n=146 38% complete remission Etanercept • • • • BNDR Biologics New Drug Registry N=483 69% remained on drug after 2 years 20.7% discontinued- poor efficacy, non compliance Etanercept- Adverse Events • • • • • Injection site reaction 39% URTI 35% SAE 15% include severe infection Malignancy and demyelination is rare New onset uveitis and Cronhs Diseases Tauber et al 2006, Giannini 2009, Lovell et al 2008 Infliximab • chimeric human–mouse monoclonal antibody directed against TNF-α • 6 mg/kg at 0, 2 and 4 weeks • 4-8 weeks interval after • apoptosis of cells bearing TNF-α • Not licensed or FDA approved JIA • Crohns >6 yrs Infliximab • Lovell Ruperto 2007/ 2010 n=122 ACR pedi 50/70- 70%/52% at wk 52 Infusion reaction 32% Discontinued 34% Only 30% continue to wk 204 Infliximab Adverse events • 91% (71/78) reported AE • 1 patient died due to JRA flare with cardiac arrest • infusion reaction 32% • SAE 21.8% asymptomatic TB in 1 child flares of arthritis, pneumonia Adalimumab • Human Anti TNF IgG monoclonal antibody • Dose=24mg/m₂ subcutaneous Injection 2 weekly • Lovell, Ruperto et al 2008 n=171 ACR 30/50/70 monotherapy -74/64/46% ACR 30/50/70 + mtx- 94/91/71 Adalimumab • • • • • Safety: infection 25% Hypersensitive reaction 6% Adalumumab antibodies 16% ACR100 after 2 years: 40% More effective in uveitis associated with JIA Tocilizumab • Recombinant human interleukin 6 receptor antibody Tocilizumab • • • • • n=56, 8mg /kg 2 wkly infusion ACR pedi 30/50/70- 91/82/68% CRP<50 in 2weeks in 86% Wk 48, 98% still on medication ACR pedi 30/50/70- 98/94/90% Yokota et al Tocilizumab • Tender Trial- SOJIA n= 88 ACR 30 with no fever 88% ACR70/90- 89%/65% 48% reduction in coticosteroids 33 SAE- 12 attributed by tocilizumab 12 infections- 6 by tocilizumab Ruperto et al 2012 Cherish Trial for poly JIA Anakinra • Anti IL 1 receptor antagonist • Lequerre et al 2008 in SOJIA n=20, Duration 6 months Dose 1-2mg/kg/day ACR paed 50 in 20% AE in 4 patients with severe skin reaction, infection Anakinra • IL-1 receptor antagonist • 1–2 mg/kg (max 100 mg daily) by SC • Rosellini et al n=80 SOJIA, poly and oligo 73% responded SOJIA, ACR 30/5055/30% • Anajis Trial n=24, placebo/anakinra 67% responded Rilonacept • IL-1 R/IL1RacP/Fc fusion protein • Gianinni et al n=9 ACR 50 at 2/4 wks-55/78% sustained at 24 months 2 MAS • On going double blind placebo trial Abatacept (CTLA4-Ig) A receptor immunoglobulin fusion protein Adapted from Kremer, J.M., 2004. Rheum Dis Clin N Am, 30, pp. 381–391 Abatacept • • • • Phase III double blind withdraw trial in Poly JIA 10 mg/kg IV 4 weekly, n=199 ACR 30/50/70 in 64%/50%/28% achieved SAE: 6, one ALL, 2 flares of arthritis, joint wear, Varicella Zoster, ovarian cyst • AE: headache and nausea Safety with anti TNF • Minor URTI most common • TB reported in infliximab and adalimumab • Demyelinating disease, uveitis, IBD rare • Drug induced lupus rare • Malignancy- 48 reported by FDA 88% also received immuno-suppressive Lymphoma, leukaemia, melanoma and solid tumour Malignancies • Rheumatic conditions (20 cases in total, of which 5 are associated with infliximab, 14 with etanercept and 1 with adalimumab, and includes the conditions: JIA, 15 cases; ankylosing spondylitis, 3 cases; psoriatic arthritis, 1 case; sarcoidosis, 1 case) • Other conditions (28 cases in total, of which 26 are associated with infliximab, 1 with etanercept and 1 with adalimumab, and includes the conditions: Crohn disease, 21 cases; ulcerative colitis, 4 cases; in utero exposure, 2 cases; unknown, 1 case) Hashkets 2010 Nature Types of malignancy Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma* (10 cases) • Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (7 cases) • Hodgkin lymphoma (6 cases) • Leukemia (6 cases) • Malignant melanoma (3 cases) • Thyroid cancer (3 cases) • Basal cell carcinoma, lymphoma with acute myeloid leukemia, leiomyosarcoma, nephroblastoma, renal cell carcinoma, liver cancer, metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma, malignant mastocytosis, neuroblastoma, colorectal cancer, yolk-sac tumor, myelodysplasia, bladder cancer (1 case each) • Long Term Safety • British Society for Paediatric and Adolescent Rheumatology Biologic and New Drug Registry for JIA • All children on etanercept are on the national registry Summary • High cost with £8000 to £15,000 per year per patient • Accessibility is variable in UK • Well tolerated • Transition to adults • Long term safety