Rhythm Recognition.
advertisement

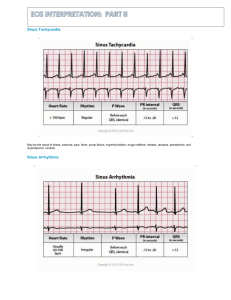
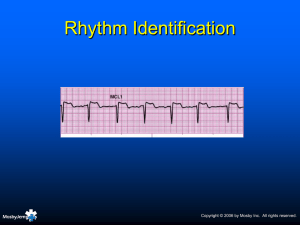
Rhythm Recognition. Sinus, Atrial, Junctional / Nodal, Ventricular, Blocks, others. Aims and Objectives. To be able to calculate heart rate from ECG. To understand features of normal sinus rhythm. To recognise rhythm abnormalities from a variety of causes. To understand rhythms which may need immediate / emergency action. Calculating HR. 1500 / small squares 300 / large squares Is it normal sinus rhythm? Rate 60 - 100bpm? Regular p wave to each regular QRS? Normal P wave appearance? Normal and constant PR interval? Sinus Node Rhythms. Sinus Tachycardia and Sinus Bradycardia. All features of normal sinus rhythm EXCEPT - Rate <60bpm (bradycardia). Rate >100bpm (tachycardia). Sinus Arrhythmia. Rate 60-100bpm. Varies with respiration (more common younger). Retains all features of sinus rhythm - except regularity of QRS complex. Usually cyclical. Sinus Arrest. Time period without sinus node activation. Clear pause in normal rhythm. Often terminated by escape beat. Rhythm before and after usually normal. SA Block. Blocks occur as a multiple of the p-p interval. Measure out. Non-conducted beat from normal pacemaker. Rhythm before and after normal. Atrial Rhythms. Premature Atrial Ectopic Beat. Premature firing of atrial cell (faster than SA node). Earlier complex. Compensatory or noncompensatory pause. Return to normal rhythm. Premature Atrial Ectopic Beat Run of Premature Atrial Beats. Can occur in isolation or short runs. Atrial bigeminy / trigeminy. Longer runs should really be termed as SVT. Symptoms :- Rarely Causes :- More often in older pts. Lung Disease Stimulants Treatment :- Anti-arrhythmia’s Wandering Atrial Pacemaker. Irregularly irregular rhythm. Multiple atrial pacemakers firing at own rate. Different p wave morphologies. Different p wave distance from QRS. Different QRS rate. Atrial Tachycardia. Ventricular rate >100bpm. Atrial rate 160-250bpm. Varying levels of conduction (1:1, 2:1, 3:1 etc). P waves abnormal or not easily seen. Sometimes seen as part of T wave or QRS. Atrial Tachycardia. Symptoms Palpitations, which can be skipping, fluttering or pounding in the chest. Chest pressure or pain. Shortness of breath & Fatigue Fainting, also known as syncope, or nearsyncope. Lightheadedness or dizziness Causes Cardiomyopathy Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Ischaemic heart disease Rheumatic heart disease Sick sinus syndrome Digoxin toxicity Treatment Depends on the type and severity Medications:- anti-arrhythmic drugs Radio-frequency catheter ablation (RFA) Cryo-ablation Atrial Flutter. Atrial rate 250350bpm. Usually regular QRS (can be variable conduction). Most commonly 2:1 conduction (150bpm ventricular and 300bpm atrial). Classic 'saw tooth'. Atrial Flutter. Causes MI & Ischaemic Heart disease. Hypertension Cardiomyopathy (congestive heart failure) Mitral valve disease Symptoms Palpitations Syncope & SOB Angina anxiety Treatment Digoxin & Sotalol (lowers ventricular rate). DC Cardioversion RF Ablation Anti-coagulants:- stroke Atrial Fibrillation. Irregularly irregular Fast or slow AV QRS. conduction. No p waves - atrial rate Irregular baseline. >350bpm. Atrial Fibrillation. Causes Mitral Valve Disease Thyrotoxicosis Cardiomyopathies Symptoms Often no symptoms Light-headedness & dizziness Palpitations Chest pain Treatment Digoxin & Sotalol (lowers ventricular rate). DC Cardioversion AF supression pacemakers R-F Ablation - PVI Junction and AV nodal Rhythms. Junctional Premature Contraction. Premature beat originating from AV node. Maybe antegrade or retrograde P wave. Compensatory / noncompensatory pause before restoration of sinus rhythm. Junctional Escape Beat. Failing of normal pacemaker (SA node). Pause in electrical activity (Sinus arrest). Escape mechanism from further down in pathway. AV node (slower intrinsic rate). Junctional Rhythm. Rate 40-60bpm (AV node intrinsic rhythm). Regular. P wave retrograde, antegrade or none. No SA nodal activity. Pacemaker AV node. Conduction normal from this point. Accelerated Junctional Rhythm. Rate 60-100bpm. Otherwise maintains all features of junctional rhythm. Junctional Tachycardia. Rate >100bpm. Maintains all other features of junctional rhythm. AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia. Re-entry circuit in the AV node - abnormal pathway to ventricle. Commonest type of SVT. Rate usually 150+bpm. Ventricular Rhythms. Ventricular Premature Contraction. Premature firing of a ventricular cell. Ventricles already depolarised before SA node impulse conducted through. Wide, bizarre complex. No p wave. Often normal variant but can be associated with ischemia. Ventricular Ectopic Beat VE Bigeminy Trigeminy Ventricular Escape Beat. Pause in regular activity (e.g. Sinus arrest, slow AF). Ventricular focus takes over as an escape mechanism. Wide, bizarre complex. Usually followed by restoration of underlying rhythm. Idio-ventricular Rhythm / Ventricular Escape Rhythm. Rate 20-40bpm (intrinsic ventricular rate). Regular rhythm. No p wave. Wide abnormal QRS. Usually connected to 3rd degree HB. Accelerated Idio-ventricular Rhythm. Rate 40-100bpm. Exactly same features as ventricular rhythm. Ventricular Tachycardia. Rate 100-200bpm. Regular. Occasional dissociated p waves. Wide, bizarre QRS. LBBB in V1 indicates RVOT origin (pulse). RVOT also associated with VF (Brugada). RBBB in V1 indicates LV origin (usually no pulse). Other Features to distinguish VT. Capture beats - normal looking beat. Occurs at exactly right time to be conducted through. VT continues immediately following. Fusion beats combination of sinus and ventricular beat. Torsade de Pointes. Twisting of the axis. Rate 200-250bpm. Regular or irregular. Sinusoidal pattern. May revert to VF or back to SR. Associated with electrolyte abnormalities. Ventricular Fibrillation. Chaotic ventricular activity. Rapid contraction unable to produce cardiac output. If patient is fine and awake - it is not. Check leads or get defibs. Heart Blocks. First Degree Heart Block. Rate depends on underlying rhythm. Regular. Prolonged PR interval >0.2secs. Physiologic block in the AV node. Caused by Medication, vagal stimulation, disease. Mobitz I Second Degree HB. (Wenckebach). Rate depends on underlying rhythm. Regularly irregular. Increasing PR interval. Dropped beat. Cycle starts over. Diseased AV node with long refractory period. Mobitz II Second Degree HB. Rate depends on underlying rhythm. Same PR interval for all conducted beats. P waves usually regular. Some p waves not conducted. Can be 2:1, 3:1, 4:1 etc. Usually progresses to CHB. Complete Heart Block (3rd Degree HB). Atrio-ventricular dissociation. Regular p waves. Regular QRS. No relationship. Rate depends on intrinsic rhythm (e.g. escape rhythm). Needs pacemaker. Other rhythms. Asystole. No cardiac activity. Check leads. Resuscitation. Chest compressions may cause ECG waveforms. Important to stop to assess rhythm. Usually poor prognosis. Check for p waves - may respond to pacing. Paced Rhythm. Pacing spike. Single / dual chamber. Bi-ventricular. Implantable defibrillator.