05. Breathing mechanics Blood gases Exercise tests
advertisement
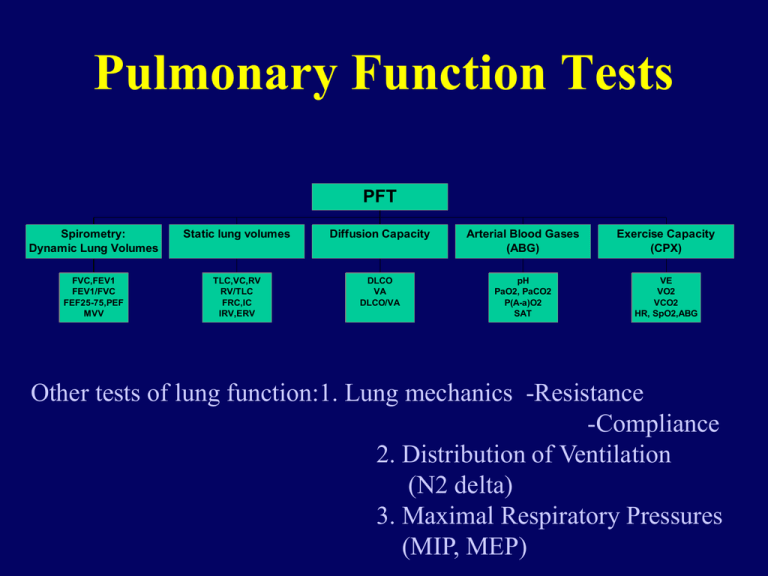
Pulmonary Function Tests PFT Spirometry: Dynamic Lung Volumes Static lung volumes Diffusion Capacity Arterial Blood Gases (ABG) Exercise Capacity (CPX) FVC,FEV1 FEV1/FVC FEF25-75,PEF MVV TLC,VC,RV RV/TLC FRC,IC IRV,ERV DLCO VA DLCO/VA pH PaO2, PaCO2 P(A-a)O2 SAT VE VO2 VCO2 HR, SpO2,ABG Other tests of lung function:1. Lung mechanics -Resistance -Compliance 2. Distribution of Ventilation (N2 delta) 3. Maximal Respiratory Pressures (MIP, MEP) V/Q ratio V/Q mismatch (3-compartment model) Lung volumes and capacities How to measure FRC? • Nitrogen washout method • Inert gas dilution technique • Plethysmography Resistance Volume dependence of airway resistance (Raw) RV SRaw (cmH2O/L/sec) 4 3 2 1 TLC 0 2 4 6 Lung Volume (liters) 8 Compliance Compliance Ventilatory Mechanics: Healthy 100 % VC Pcw 80 PRS 60 40 20 PL 0 -60 -40 -20 0 Pressure (cmH2O) 20 40 60 Ventilatory Mechanics: Healthy 100 ΔV ΔP % VC ΔP 80 ΔV elastic WOB 60 RV 4 elastic and resistive work of breathing is minimized when tidal breathing occurs 3 within the compliant portion of the respiratory systems 2P-V curve ΔP 20 SRaw (cmH2O/L/sec) 40 ΔV 1 TLC resistive WOB 0 -40 -20 0 20 40 4 6 Lung Volume (liters) 0 -60 2 60 Pressure (cmH2O) SRaw as lung volume because the airways distend as the lungs inflate, and bigger airways have lower resistance (*Poiseuilles’ Law*). The opposite is also true, of course! 8 Ventilatory Mechanics: Healthy Begin Exercise IC IC VT Ventilatory Mechanics: Healthy 8 TLC Volume (liters) EILV 6 4 EELV VT EELV 2 0 IRV R V - 0 10 20 30 40 50 40 30 20 10 Pressure (cmH20) IC Dynamic hyperinflation during exercise IRV IRV Diffusion capacity (DLCO, DLCO/VA, Tco, Kco) Mechanism of hypoxaemia Hypoxaemia, hypercapnia in clinical cases Respiratory and metabolic shifts chronic acute acute chronic Exercise tests in lung diseases 1. Exercise-induced asthma (EIA) - FEV1 2. Interstitial lung disease (ILD) - SAT 3. Exercise tolerance in rehabilitation (COPD) cardiopulmonary exercise (CPX). Important variables: - work rate (watts), SpO2, ABG - VO2, VCO2, RQ, VE - lactate threshold (LT) - breathing reserve (1-VEmax/MVV) - heart rate reserve (1-HRmax/220-age) Mechanism of exercise-induced hypoxaemia Noninvasive determination of lactate threshold by the V-slope method Respiration during exercise ( Wasserman K, 1999 )











