Diagnosis and Management of TB - Croydon Health Services NHS
Diagnosis and Management of
TB
John Yates
Consultant Infectious Diseases
Diagnosis
• Generally sub-acute illness
• Any persistent symptom may indicate active tuberculosis
• May be relatively mild
• Any systemic symptoms – fever, weight loss, night sweats, malaise, anorexia – increase suspicion
• Exposure history usually irrelevant if high risk ethnic background
Sites of infection
• About 50/50 pulmonary/non-pulmonary
• 24% extra-pulmonary LNs
• 10% intra-throracic LNs
• 10% pleural
• 6% bone/joint ( 3% spine)
• 5% GI
• 3% CNS
• 2% miliary
• 1% GU
• Others – skin, eye, breast,
Diagnosis- pulmonary
• Persistent cough +/- haemoptysis
• Fever, weight loss, night sweats
• Symptoms may be very mild
• Usually stethoscope not useful
• Breathlessness uncommon unless severe, disseminated disease
• May be asymptomatic
• Main initial investigation – CXR
• Referral to TB clinic
Diagnosis - pulmonary
• CXR
• Sputum, if productive, x3 for smear and culture
• Basic blood tests
• HIV test
• Mantoux/IGRA
• CT to guide bronchoscopy/biopsy if unproductive
• Broncho-alveolar lavage/induced sputum for smear and culture
• PCR for smear positive cases/difficult diagnoses
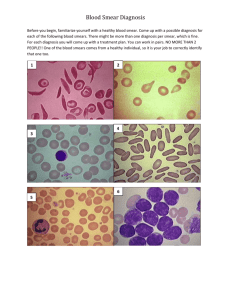
Early pulmonary disease
Patch of nodules
Early pulmonary disease
Late pulmonary disease cavity
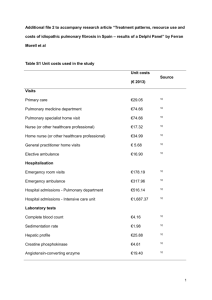
Lymphadenopathy
Asymmetrical hilar enlargement
Extra-pulmonary
• Cervical lymph nodes – mantoux +/- IGRA, biopsy for histology/culture
• Other sites imaging/biopsy
• Multifarious presentations
• Main aid to diagnosis is suspicion
• Don’t be put off by normal plain films of chest/abdo/spine/bone
Extra-pulmonary
• Persistent symptoms > 2 weeks
• +/- night sweats/weight loss/malaise
• High risk ethnic backgrounds
• Elevated ESR/CRP, normocytic anaemia, low albumin
• Back pain, abdo pain, headache etc
• Please refer to TB clinic
Diagnosis –extra pulmonary
• Immunological tests – negative in 10% active disease for mantoux
• Targeted imaging – but disease often multifocal e.g. peritoneum, lymph nodes, spine, chest simultaneously
• Biopsy for histology, smear and culture
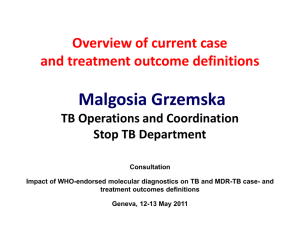
Ascites
Lymph node mass
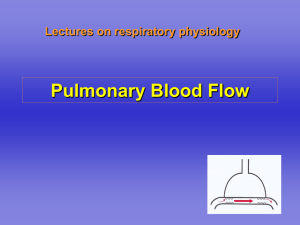
Abdominal TB
Spinal TB
Increased soft tissue around L4/5
Management
• Risk assessment for Multi-Drug Resistant -MDR TB – 1.5% cases resistant to rifampicin and isoniazid
• Smear positive cases sent for PCR for drug resistance
• Isolation of smear positive cases for 2 weeks– usually at home but in hospital if ill or unable due to shared accommodation/homelessness
• Initiate treatment – quadruple therapy – rifampicin/isoniazid/pyrazinamide, ethambutol or moxifloxacin
• Monitored treatment – TB nurses, clinic
• Review with culture results
• MDR cases referred to St George’s