cordovez - Philippine Heart Association
advertisement

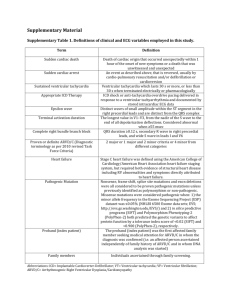
Genetic Testing in Patients with Arrhythmia and Risk for Sudden Cardiac Death : Indications and Implications for Practice Mary Gertrude Ong-Cordovez, M.D. Cebu City Inherited Cardiac Arrhythmias • Channelopathy (ion channel disease) • LQTS • CPVT • Brugada Syndrome • Primary Structural Heart Disease (cardiomyopathies) • ARVC/D • HOCM • Familial DCM Epidemiology • • • • 1:500 1:1000 1:2000 1:2500 (HOCM) (ARVD) (LQTS, CPVT, Brugada syndrome) (DCM) Ion Channel Diseases LQTS: KCNQ1, KCNH2, SCN5A, KCNE1, KCNE2 (65%) Brugada syndrome: SCN5A (25% to 30%) CPVT: RYR2 (60%), possibly CASQ2 Cardiomyopathies ARVD: PKP2, DSP, DSG2 (60%) HOCM: MYH7, MYBPC3, TNNT2 (60%) DCM: LMNA, MYH7, TNNT2, SCN5A (20% to 30%) LQTS Genotype-phenotype correlations in long-QT syndrome. Tester D J , Ackerman M J Circulation 2011;123:1021-1037 Copyright © American Heart Association LQTS • Management • Beta Blockers • Mexilitene, flecainide, propanolol • Treat hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia • ICD • Avoid QT prolonging drugs QT Prolonging Drugs • • • • • • • • • • Albuterol Alfuzosin Amiodarone Amphetamine Azithromycin Ciprofoxacin Clarythhromycin Diphenhydramin Dobutamine Dopamine epinephrine erythromycin famotidine flecainide gatifloxacin imipramine ketoconazole levofloxacin moxifloxacin ofloxacin roxithromycin salmeterol sertraline sotalol tamoxifen terbutaline SXT vardenafil www.qtdrugs.org Ion Channel Diseases LQTS: KCNQ1, KCNH2, SCN5A, KCNE1, KCNE2 (65%) Brugada syndrome: SCN5A (25% to 30%) CPVT: RYR2 (60%), possibly CASQ2 ARVD: PKP2, DSP, DSG2 (60%) Recommendations for Genetic Testing • Cardiac arrest survivor • Syncope • QTc abnormal • QTc borderline • QTc normal • Asymptomatic • QTc abnormal • QTc borderline • First degree relative • Proband genotype + • Proband genotype _ ++ ++ +/_ ++ _ ++ _ Canadian J of Cardiology 27(2011) 232-248 Brugada Syndrome Brugada Syndrome • Management • Beta blocker and amiodarone • Quinidine • Aggressive fever control • Avoid strenuous physical activity • ICD • Avoid sodium channel blocker Na Channel Blockers • Anti-arrhythmic drugs • Flecainide, propafenone, ajmalin, procainamide • Psychotropic Drugs • Amitriptyline, lithium, nortriptyline, trifluoperazine • Anesthetics/Analgesics • Bupivacaine, procaine, profolol • Others • Acetylcholine, alcohol, cocaine, ergonovine Ion Channel Diseases LQTS: KCNQ1, KCNH2, SCN5A, KCNE1, KCNE2 (65%) Brugada syndrome: SCN5A (25% to 30%) CPVT: RYR2 (60%), possibly CASQ2 Recommendations for Genetic Testing (Brugada Syndrome) • Cardiac arrest survivor • Type I Brugada ECG pattern • Type 2 or 3 ECG pattern • Syncope • Type I Brugada ECG pattern • Type 2 or 3 ECG pattern • Asymptomatic • Type I Brugada ECG pattern • Type 2 or 3 ECG pattern • First Degree Relative • Proband genotype positive • Proband genotype negative ++ __ ++ __ ++ __ ++ ___ CPVT CPVT • Management • Beta blockers • Flecainide/cardiac sympathectomy • ICD • Avoid intense physical exercise Ion Channel Diseases LQTS: KCNQ1, KCNH2, SCN5A, KCNE1, KCNE2 (65%) Brugada syndrome: SCN5A (25% to 30%) CPVT: RYR2 (60%), possibly CASQ2 Recommendations for Genetic Testing (CPVT) • Clinically suspected CPVT ++ • First degree relative • Proband genotype + ++ ARVD/C • Task Force Criteria • RV function • Tissue characteristic of the myocardium • ECG repolarization abnormalities • Arrhythmias • Family history • Genetic testing ARVD • Management • Avoid competitive sports • ICD • Documented ventricular arrhythmias Cardiomyopathies ARVD: PKP2, DSP, DSG2 (60%-70%) HOCM: MYH7, MYBPC3, TNNT2 (60%) DCM: LMNA, MYH7, TNNT2, SCN5A (20% to 30%) Recommendations for Genetic Testing (ARVD) • • • • Clinical ARVD Clincal ARVD no ID at risk family members Clinically suspected ARVD First degree relative • Genotype positive • Genotype negative ++ __ ++ ++ __ HOCM • Echocardiography • MRI Management • Asymptomatic • Treat risk factors- HPN, DM, dyslipidemia, obesity • Beta-blockers • Angina and dyspnea • verapamil • Septal reduction Rx • surgical septal myectomy/ alcohol septal ablation • Drug refractory and LVOT obstruction • ICD Indications for ICDs in HCM. *SCD risk modifiers include established risk factors and emerging risk modifiers (Section 9.4.2). et al. Circulation 2011;124:2761-2796 Copyright © American Heart Association Management • Asymptomatic • Treat risk factors- HPN, DM, dyslipidemia, obesity • Beta-blockers • Angina and dyspnea • verapamil • Septal reduction Rx • surgical septal myectomy/ alcohol septal ablation • Drug refractory and LVOT obstruction • ICD • Exercise restriction HOCM • Exercise • Permitted • Bowling, brisk walking, golf, skating, snorkeling, treadmill, biking • Strongly discouraged • Basketball, body building, rock climbing , sprinting, soccer, tennis , wind surfing, scuba diving Circulation 2011;124:2761-2796 Cardiomyopathies ARVD: PKP2, DSP, DSG2 (60%-70%) HOCM: MYH7, MYBPC3, TNNT2 (60%) DCM: LMNA, MYH7, TNNT2, SCN5A (20% to 30%) Recommendationf for Genetic Testing (HOCM) • Clinically diagnose HOCM • Family screening • Diagnosis • Risk stratification/Rx decisions ++ __ __ DCM • Cardiac imaging studies • Cardiac biopsy- diagnostic tool • Management • ACEI, B blockers, spironolactone • ICD - EF <35% • Biventricular pacing Cardiomyopathies ARVD: PKP2, DSP, DSG2 (60%-70%) HOCM: MYH7, MYBPC3, TNNT2 (60%) DCM: LMNA, MYH7, TNNT2, SCN5A (20% to 30%) Recommendation for Genetic Testing (DCM) • Clinically Dx DCM __ • Clinically Dx DCM w/ atrial arrhythmias/high grade conduction disease ++ (LMNA, SCNA5) Future Perspective • Gene sequencing will be faster and available more cheaply • Multidisciplinary approach • Gray areas • Gene therapy