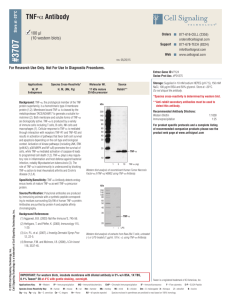
Cytokines and IBD - University of Connecticut
advertisement

Cytokines and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Alexander Lind University of Connecticut MCB5255 2014-04-09 Overview Background information about cytokines Cytokines and IBD Article 1 Article 2 Future studies, specific aims Cytokines Cell communication and regulation Involved in nearly all biological processes: Embryonic development Stem cell differentiation Inflammatory responses Used as prognostic and therapeutic agents in human disease http://www.genecopoeia.com/product/search/pathway/h_inflamPathway.php Cytokine storm http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3180813/ http://www.cytokinestorm.com/ Pro-inflammatory/ Anti-inflammatory cytokines Overview Background information about cytokines Cytokines and IBD Article 1 Article 2 Future studies, specific aims Cytokine imbalance contributes to IBD through: Macrophage, Dendritic cell recruitment and activation T-cells differentiation Crohn's disease Th1 cell mediated response Ulcerative ColitisTh2 cell mediated response http://www.nature.com/nrgastro/journal/v7/n2/fig_tab/nrgastro.2009.218_F1.html CROHN'S DISEASE ULCERATIVE COLITIS •Th1 cell induced differentiation mediated by IL-12 and IL-23 •Th2 atypical immune response •Lack of increased IFN-γ expression (abundant in CD) rather than the elevation of IL-4 the Th2-defining cytokine •Classical pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α •Th2 cytokines IL-10 and IL-13 play a key role, increased IL-13 production by NKT cells •TH17 cells producing IL-17 •Characterized by enhanced production of IFN-γ and TNF-α http://www.nature.com/nrd/journal/v5/n3/fig_tab/nrd1986_ft.html http://www.clinsci.org/cs/118/0707/cs1180707f03.htm TNF-α •TNF-α is upregulated in both CD and UC •Mostly produced by activated macrophages • Transmembrane protein, activated through proteolytic cleavage • Play an important role in the pathogenesis of IBD http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2731177/ Anticytokine therapies •Monoclonal anti-TNF-alpha antibodies has showed good results in both inducing and maintaining remission • Do not act only by neutralizing TNF-alpha: - Induce monocyte and T-cell apoptosis - Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity •Unclear why certain anti-TNF therapies are effective in IBD where as other are not Problems with current Anti TNF-α therapies • Liver Injury Secondary to Anti-TNF-Alpha Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Parekh et. al. 2014 •Incidences of serious infections and tuberculosis among patients receiving anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy. Yoo et. al 2014 •Recurrence of active tuberculosis following resumption of anti-TNFα therapy in a patient with Crohn's disease. Masia et. al. 2014 •Tuberculosis infection following anti-TNF therapy in inflammatory bowel disease, despite negative screening. Debeuckelaere et. al. 2013 •Immune-mediated inflammatory reactions and tumors as skin side effects of inflammatory bowel disease therapy Marzano et. al. 2014 Overview Background information about cytokines Cytokines and IBD Article 1 Article 2 Future studies, specific aims Article 1 “Orally delivered siRNA targeting macrophage Map4k4 suppresses systemic inflammation” by Aoudi et.al. 2009 Investigates the potential RNA interference to decrease inflammatory response http://silence-therapeutics.com/platform-technologies/rna-interference/ Figure 1. Experimental design Figure 2. Orally delivered Map4k4 siRNA containing vectors can be phagocytized by macrophages and silence messenger RNA expression Figure 2. (Continued) Conclusion: In vitro treatment of Map4k4 siRNA can silence messenger RNA expression and inhibit LPS induced TNFα production. Figure 3: What effect does Map4k4 silencing have on LPS activation of previously known pathways for regulation of Tnf-α production? Conclusion: Map4k4 is a new target for suppression of Tnf-α expression, activation occurs independently of previously known pathways Figure 4. Oral administration of Map4k4 siRNA decreases mRNA expression in lung, liver and spleen. Figure 4. ( Continued) Conclusion: Demonstrated that macrophages in the gut internalize orally delivered siRNA, undergo RNA interference mediated gene silencing and migrate into tissues throughout the body. Figure 5: What is the effect on TNFα expression after Map4k4 silencing? Conclusion:Map4k4-siRNA administration protects mice from LPS-induced lethality through inhibition of TNF-α in macrophages Conclusions from article 1 The results in this articles describes a new strategy for oral delivery of siRNA to weaken inflammatory responses in human disease Identification of Map4k4, a previously unknown mediator of cytokine expression. Silencing of Map4k4 in macrophages in vivo protected mice from lipopolysaccharide-induced lethality by inhibiting of TNF-α This article demonstrated promising results for anti-TNF-α protein therapeutics. Development of GeRP-mediated delivery of siRNA show promising results as inflammatory decreasing agents for several disease including IBD. Overview Background information about cytokines Cytokines and IBD Article 1 Article 2 Future studies, specific aims Article 2 “Gene silencing of TNF-alpha in a murine model of acute colitis using a modified cyclodextrin delivery system” by MacCarthy et.al. 2013 Investigates possibility of silencing TNF-α trough RNA interference in IBD Figure 1. Stability and delivery of siRNA siRNA has short half-life time in plasma due to nuclease degradation Cyclodextrin, natural occurring oligosaccharides http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlepdf/2010/MB/C001050M Figure 2.Investigation of vector-siRNA complex stability in simulated intestinal fluids Figure 3. Quantification of TNF-α and IL-6 expression in LPS stimulated cells Figure 4. Examination of inhibitory effect of TNF-α siRNA on LPSinduced cytokine secretion and expression Conclusion: TNF-α siRNA reduced LPS induced cytokine expression of TNF-α and IL-6 Figure 5. Clinical response after TNF-α siRNA delivery in DSS treated mice A trends towards clinincal improvement could be observed after TNF-α siRNA delivery: increased body weight, reduced colon weight Figure 6. Decreased TNF-α and IL-6 expression in proximal colon after TNF-α -siRNA delivery to DSS-treated mice Conclusions from Article 2 Showed in vitro studies that delivery of TNF-α siRNA could interfere with LPS induced activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines Intrarectal administration of TNF-siRNA in DSS-treated mice gave indications of: 1) clinical improvements of IBD associated features 2) Lower expression of TNF-α and IL-6 in proximal colon This article demonstrated promising results of a CD-based siRNA delivery system for silencing of pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α. Potentially used in future treatment of IBD. Overview Background information about cytokines Cytokines and IBD Article 1 Article 2 Future studies, specific aims Future studies There is a problem with side effects using current therapies RNA interference silencing Mp4k4 and TNF-α show promising results Combination of silence several genes? Other ways affecting TNF-α expression? Specific aim: To use RNA interference technique to try and silence gene expression of transcription factor LITAF known to regulate TNF-α expression References • Genecopoeia. Cytokines and Inflammatory Response http://www.genecopoeia.com/product/search/pathway/h_inflamPathway.php • Kindt TJ et.al.. Kuby Immunologi 6th edition, Figure 12. • Morens DM et.al. The 1918 influenza pandemic: Lessons for 2009 and the future. Critical Care Medicine. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3180813/ • Osterholm et. al.. Proposed Mechanism of the Cytokine Storm Evoked by Influenza virus. New England Journal of Medicine http://www.cytokinestorm.com/cytokine_storm.html • Audet CM et. al. Interplay between pro-inflammatory cytokines and growth factors in depressive illnesses. Cellular neuroscience. http://journal.frontiersin.org/Journal/10.3389/fncel.2013.00068/full • Melmed GY et.al. Future biologic targets for IBD: potentials and pitfalls. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology. http://www.nature.com/nrgastro/journal/v7/n2/fig_tab/nrgastro.2009.218_F1.html • Monteleone G et.al. T-cell-directed therapies in inflamatory bowel diseases. Clinical science. http://www.clinsci.org/cs/118/0707/cs1180707f03.htm • Joshua R et.al. Evolving knowledge and therapy of inflammatory bowel disase. Nature reviews. http://www.nature.com/nrd/journal/v5/n3/fig_tab/nrd1986_ft.html • Sanchez-Munoz et.al. Role of cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterology. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2731177/ • RNA interference. Silence therapeutics. http://silence-therapeutics.com/platform-technologies/rna-interference/