Deep Tendon Reflexes: Examination & Grading Guide
advertisement

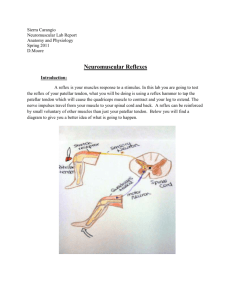
Deep Tendon Reflexes Kimberly Victorian, RN, BSN Sheeba Jacob, RN, BSN Objectives Understand and define deep tendon reflexes Distinguish between hyper and hypo-tonic deep tendon reflexes Gain a basic knowledge of DTR grading Understand how to do a DTR examination Identify different DTRs Identify different diseases that may manifest by an alteration in DTRs Definition Normal process when muscle tendon is tapped briskly Muscle contracts due to a two-neuron reflex arc involving the spinal or brainstem segment that innervates the muscle Afferent neuron innervates the muscle or golgi tendon organ associated with the muscles Cerebral cortex and some brainstem nuclei exert influence over the sensory input of muscle spindles Hyper VS Hypo-reflexia Hypo – absent or diminished response to tapping. Disease involving one or more of the components of the two-neuron Hyper – hyperactive or repeating (clonic) reflexes. Diseases involving an interuption of corticospinal and other descending pathways that influence the reflex arc due to a suprasegmental lesion Grading Grading based on varied degree of response Grade 0 Grade 1+ Grade 2+ Grade 3+ Grade 4+ Grading Reflex 0: absent reflex 1+: trace, or seen only with reinforcement 2+: normal 3+: brisk 4+: nonsustained clonus (i.e., repetitive vibratory movements) 5+: sustained clonus Examination Examine upper extremity reflexes with upper examination Abnormality found or suspected take into account the entire group with focus on the technique of the examination Assure patient is relaxed Method of Eliciting Reflexes http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WGNC Xqa-y3o http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hvkT0 8HYEbM http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid= 4041078352780880433&ei=IijsSoWBBpLiq gLskeHLAQ&q=deep+tendon+reflexes&hl =en# Physical Maturity Infants Children Adults Examples of Reflexes Jaw Jerk Biceps reflex Triceps reflex Brachioradialis reflex Finger jerk Knee Jerk Ankle jerk Testing Reflex http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MVH9 qmd-xgc&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pXNe Npmw9yE&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4hOS kmDYAR4&feature=related Disease Processes Absent reflex causes: – Peripheral neuropathy – Alcoholism – Vitamin deficiencies – Diabetes Clonus or Hyper-active reflexes http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9XWmpBz4BVo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=liE9fVMYZPU&feature=rel ated http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bWKTr Ujxkqs&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uWzsA vF7M0k&feature=related Summary Definition Hypo VS Hyper-active reflexes Grading Examination Examples Diseases DTR Test Of the following, what best defines a deep tendon reflex – A. a specific bundle of nerve fibers – B. an unintended muscle spasm – C. a normal process that occurs when the tendon is tapped Answer 1 C. DTR Test True or False A hypo-tonic deep tendon reflex is indicated by an absent or diminished response to tapping Answer True DTR Test True or False There are 5 grades of Deep tendon reflexes Answer 3 True DTR test What portion of the examination is most important to keep in mind? A. The maturity of the patient B. Assure patient is relaxed C. Mental cognition of the patient Answer 4 B. DTR Test Identify which of the following is not a DTR A. Ankle jerk B. Jaw jerk C. Finger jerk D. Ear skip Answer 5 D. DTR Test True or False Diabetes is associated with absent or hypo-tonic DTRs Answer 6 True Resources Walker, K . (1990). Clinical Methods, The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. Retrieved October 20, 2009 from www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi ?book=cm&part=A2361