小兒神經學理學檢查

小兒神經學理學檢查
Fellow 黃意評
2010-11-25
檢查大綱
• Mental status
• Cranial nerve,
• Motor,
• Cerebellar,
• Sensory examinations
• Newborn:
• Primitive reflex
• Jitterness and clonus
GCS:E4M6V5
Vital sign: 36.9 ℃ /94bpm/24/min, BP:113/81 mmHg
1. J udgement : 紅綠燈過馬路、火災時會打 119
2. O rientation: Person~ Time~ Place~
3. M emory: a. immediate recall 3 objects: 醫院 ( 具體 ) 、紅色 ( 顏色 ) 、勇敢 ( 抽象 ) b. recent : 為何住院 ? c. remote : 住址、電話、姓名
4. A bstract thinking: 蓮霧與西瓜異同、誠實與謙虛
5. C alculation: a. Series of 7 b. Series of 3
6.Language:
Fluency: OK
Comprehension: OK
Naming: OK
Repetition: OK
7.Hallucination:
Visual: denied
Auditory: denied
Sensory: denied
• 純感覺 : CN1,2,8 ; 純運動 : 3,4,6,11,12
• CN 1 : anosmia (Frontal lobe tumor)
• CN 2 : 20/150 20/20(6m/o); visual field
• CN 2,3 : Pupillary light reflex(+)
• CN 3.4.6: EOM full
• CN 5 : face: sensory:OK, Mastication: ok
• CN 7: No facial palsy, corneal reflex(+) symmetric nasolabial fold
• CN 9, 10 : Swallowing(+) ; gag reflex(+)
• CN 11 : Head rotation/shoulder elevation(+)
• CN 12 : tongue: deviation(-) ; slur speech(-)
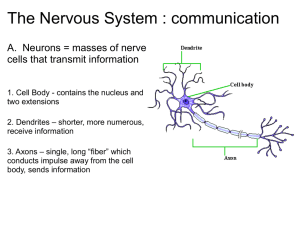
Cranial Nerves ( I )
• Olfactory nerve (I)
• Optic nerve (II):
– Visual acuity
– Visual field: confrontation test
Cranial Nerves ( II )
• Extra-Ocular Muscles:
– Oculomotor nerve (III)
– Trochlear nerve (IV)
– Abducens nerve (VI)
• Trigeminal Nerve (V):
– Three divisions
– Motor: masseter, temporalis
Cranial Nerves ( III )
• Facial Nerve (VII):
– Motor –
• Facial expression
• Naso-labial fold
• Eye blinking
• Wrinkles
– Sound damping, taste
– Central vs peripheral facial palsy
Cranial Nerves ( IV )
– Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve (VIII)
– Glossopharyngeal (IX) & Vagus (X)
Nerves
• Taste
• Voice
• Gag reflex
Cranial Nerves ( V )
• Spinoaccessory Nerve (XI):
– Trapezius muscles
– Sternocleidomastoid muscles
• Hypoglossal Nerve (XII):
– Tongue atrophy
– Fasciculation
– Deviation
– Strength
Cranial Reflex
– Light reflex (II-III)
– Corneal reflex (V-VII)
– Gag reflex (IX, X)
Motor
Muscle power/muscle tone
DTR/ pathologic reflex
Babinskin’s sign
Hoffmann's sign
Involuntary movement
Tremor
Clonus/Myoclonus
Chorea
Cerebellar sign:
Finger-nose-finger
Romberg test
Gait
Pyramidal: no rigidity, no cross DTR, no ankle clonus
Extra-pyramidal: no hypotonia, no spasticity, no dystonia, no chorea, no athetoid
MRC System
• 5 normal power
• 4 against resistance : 4+, 4, 4-
• 3 against gravity
• 2 horizontal movement (no anti-gravity)
• 1 muscle contraction
• 0 no movement
Upper motor neuron sign
DTR (Knee jerk, strech reflex)
Supraspinal control
• Inhibitory signals on gamma neurons through lateral reticulospinal tract from
• Motor Area 6
• Paleocerebellum
• Red nucleus
• Facilitatory signals on gamma neurons through ventral reticulospinal tract from
• Motor Area 4
• Neocerebellum
• Vestibular nucleus
Babinski sign (Plantar reflex)
-Pyramidal / Lateral corticospinal tract
• In infants
• This happens because the corticospinal pathways that are not fully myelinated at this age, so the reflex is not inhibited by the cerebral cortex .
• The extensor response disappears and gives way to the flexor response around 12-24 m/o.
Motor
Muscle power/muscle tone
DTR/ pathologic reflex
Babinskin’s sign
Hoffmann's sign
Involuntary movement
Tremor
Clonus/Myoclonus
Chorea
Pyramidal: no rigidity, no cross DTR, no ankle clonus
Extra-pyramidal: no hypotonia, no spasticity, no dystonia, no chorea, no athetoid
Cerebellar sign:
Finger-nose-finger
Romberg test
Gait
• Pyramidal tract
Movement disorder
= Extrapyramidal disorders
Coordination
• Romberg test :
• Cerebellar dysmetria:
– Finger-nose-finger test
– Heel-to-shin test
• Rapid alternating movement (RAM) ex.
• Gait: ataxia
1. Limb ataxia = cerebellar lobes
2. Gait ataxia = anterior vermis
3. Truncal ataxia = posterior vermis
Proprioceptive and tactile stimuli are projected as shown in the upper (inverted) homunculus and the lower (split) homunculus.
The striped area : the region from which evoked responses to auditory and visual stimuli are observed.( 聽、視覺刺激後的反應 ( 動作 ) 區 )
Sensory Examination
a. Light touch : OK b.Pinprick : OK c. Joint position sense : OK (fingers and toes) d.Vibration e.Temprature :
•
Newborn
Neurology examination
http://library.med.utah.edu/pedineurologicexam/html/home_exam.html