Nephrotic syndrome - oedematous and oliguric
advertisement

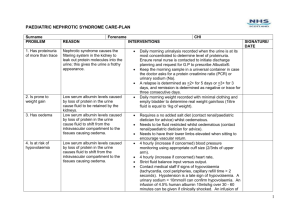
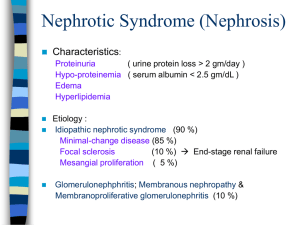
Nephrotic syndrome-oedematous and oliguric 22nd June 2012 Rachel Lennon Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist Royal Manchester Children’s Hospital Nephrotic syndrome: Most common glomerular disorder in children Endothelial cells GBM Podocyte 1 million glomeruli in each human kidney Glomerular filtration barrier 180 litres of water and small solutes- almost no proteins Glomerular endothelial cells GBM Slit diaphragm Podocytes A clinical syndrome: Triad Albumin <25g/l Oedema Massive proteinuria Aetiology • Congenital – Congenital infections – Genetic mutations • Eg. Nephrin, podocin • Acquired – No clearly identified mechanism – Association with viral infections – Circulating factors • Recurrence of FSGS post renal transplant • Materno-fetal transmission Minimal change nephrotic syndrome (MCNS): Commonest in children Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis Mesangioproliferative GN Membranous nephropathy Minimal change nephrotic syndrome Electron microscopy Induction and maintenance therapy • Glucocorticoids: ISKDC regime – 90% with MCNS initially respond • 33% no further relapse • 33% infrequent relapse • 33% frequent relapse • Prophylactic penicillin • 2nd line therapy – Cytotoxics • Cyclophosphamide • Ciclosporin Complications • Thrombosis – – – • Haemoconcentration Increased fibrinogen, factor VII, X, VIII Decreased anti-thrombin III and plasminogen Infections – Immunological losses • • Pneumococcal infections Primary peritonitis Acute management of nephrotic syndrome Case 1 • 3 year old boy – – – – – – • • • • Facial swelling for 2 weeks Treated with antihistamines Urinalysis 3+ protein 1+blood HR/BP/CRT normal Periorbital and lower limb oedema Albumin 15, Urea 4.5 Creat 30, Urine Na 30 Treatment? Prednisolone 60 mg/m2/day (Prednos trial?) Penicillin V Daily monitoring until remission Δ Nephrotic syndrome Estimate dry weight ABC HR/BP/CRT normal Oedema • Predinsolone 60mg/m2/day • Fluid restriction to 70% • Low salt diet • Diuretics: Furosemide and spironalactone Close monitoring Daily weight Fluid balance Case 2 • 7 year old boy with SSNS – – – – – • • • • • • • Unwell with D&V for 3 days, Urine 3+ protein Lower limb oedema HR 130, BP 100/78, CRT 5 seconds Albumin 12, Urea 9.5, Creat 42, Urine Na 10 Treatment? IV fluid bolus (10ml/kg 4.5%HAS) Reassess Urine output Prednisolone 60 mg/m2/day Penicillin V Daily monitoring until remission Δ Nephrotic syndrome ABC HR/BP/CRT normal Urine Na Haematocrit Hypovolaemia Estimate dry weight Fluid bolus: 1020ml/kg 4.5% HAS Reassess Oedema • Predinsolone 60mg/m2/day • Fluid restriction to 70% • Low salt diet • Diuretics: Furosemide and spironalactone Close monitoring Daily weight Fluid balance Case 3 • 5 year old girl with FRNS – – – – – Ciclosporin Oedematous for 2-3 weeks Symptomatic oedema HR 120, BP 105/80, CRT <2s Albumin 8, Ur 7.5, Creat 52, Urine Na 15 • Treatment? • Cautious use of 20% albumin (2.5-5ml/kg dry weight) over 4 hours with IV furosemide at 2 hours. • Risk of life threatening pulmonary oedema • Daily 20% albumin • Prednisolone 60 mg/m2/day • Penicillin V • Daily monitoring until remission Δ Nephrotic syndrome ABC Estimate dry weight Urine Na Haematocrit HR/BP/CRT normal Oedema Symptomatic oedema • Predinsolone 60mg/m2/day • Fluid restriction to 70% • Low salt diet • Diuretics: Furosemide and spironalactone 0.5-1g/kg (0.25-5ml/kg) 20% salt poor albumin Over 4 hours Furosemide (1mg/kg) at 2 hours In consultation with Paediatric Nephrologist Close monitoring Daily weight Fluid balance 3.5g/kg 4hrs 2.5g/kg 3hrs no diuretic 1g/kg over 1 hour ISKDCmortality in MCNS Δ Nephrotic syndrome ABC Urine Na Haematocrit HR/BP/CRT normal Hypovolaemia Oedema Symptomatic oedema • Predinsolone 60mg/m2/day • Fluid restriction to 70% • Low salt diet • Diuretics: Furosemide and spironalactone Estimate dry weight Fluid bolus: 1020ml/kg 4.5% HAS Reassess 0.5-1g/kg (0.25-5ml/kg) 20% salt poor albumin Over 4 hours Furosemide (1mg/kg) at 2 hours In consultation with Paediatric Nephrologist Close monitoring Daily weight Fluid balance Questions?