Management of bleeding
advertisement

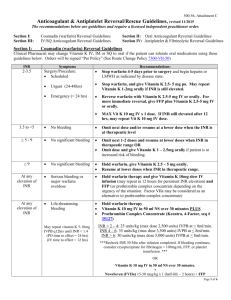
Management of bleeding Andrew McDonald Alberts Cellular Therapy “All bleeding eventually stops” n Modified Virchow’s triad Blood flow Size BP BLEEDING Coagulation Platelets Clotting factors Fibrinolytic system Vessel wall Endothelial activation Collagen disorders Age Corticosteroids n • n n n Thrombin generation LOW [Thrombin] • VIII activation and release from vWF HIGH [Thrombin] • Fibrin formation • TAFI activation • V activation and release from platelets • Platelet activation • XI activation • XIII activation • Protein C activation (with thrombomodulin) n Categories of patients •• Known “bleeders” n – Anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents – Other drugs • Starch vol expanders, cephalosporins – Inherited – Acquired • • • • ITP Inhibitors Cirrhosis Uraemia • Unknown – With bleeding history – Unexpected bleed • Type of bleed: – ACUTE vs CHRONIC – Minor – Major • Admission required • 2 units RBC • Critical organ – Life threatening • ICH • Massive GIT • Airway n • n Nutrition and bleeding risk n Strategies for stopping bleeding Make a better clot Drug • • • • • • DDAVP Oestrogen Factor 8 concentrate Activated rVIIa (Novoseven) PCC (plasma derived – Haemosolvex) Fibrin glue Transfusion • • • • FFP Platelets Cryoprecipitate [RBC] Hold on to clot • Make a better clot in the first place • Tranexamic acid Clotting factors Fibrinogen (I) Liver Cryoppt Prothrombin (II) Liver Factor V Liver Factor VII Liver Factor VIII Liver Factor IX Liver PCC Factor X Liver PCC Factor XI Liver (Factor XII) Liver Factor XIII Liver + Megakaryocytes Cryoppt vWF Endothelium + Megakaryocytes Cryoppt PCC (Cryoppt) PCC Cryoppt Factor 8 Factor 8 n • n n Anti-fibrinolytic agents • Tranexamic acid –synthetic lysine analogue – Blocks lysine binding site on plasminogen, preventing activation to plasmin • Oral / mouthwash / IV • Typical dose 1-1.5G 6-8 hourly (range dose 2.5-100mg/kg) • Useful in: – – – – Menorrhagia Dental extractions Major surgery – orthopaedic, cardiac, urologic Bleeding associated with • Mild Haemophilia A and VWD • Platelet disorders • Risk of thrombosis low n DDAVP • Modified analogue of ADH (AVP) • IV formulation (dose 0.3ug/kg/day) – NB tachyphylaxis (25% less effective on day 2) • Oral tabs and low dose nasal spray not effective for haemorrhage • Increases endogenous factor 8 and VWF levels (via V2 receptor) • Useful in mild Haemophilia A and Type 1 VWD • Also useful in platelet derived bleeding – Mild inherited cytopathies – Antiplatelet agents – Mild/mod thrombocytopenia • Contraindicated in known coronary artery disease • Side effect – headache, flushing, hyponatraemia rhVIIa (Novoseven) – – – – Massive trauma Massive APH / PPH Cardiac surgery ICH Percent of patients (%) • Registered for bleeding in haemophilia with inhibitors • Used as a general haemostatic in severe life threatening bleeding 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 ≥8 0 P= 0.019 Placebo NovoSeven® (N=52) (N=59) 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 RBC units within 48 hours Boffard KD et al. J Trauma 2005;59(1):8-18 • Expensive – reimbursement issues • Increased thrombotic events (OR 1.6) • Dose 90ug/kg; not effective in severe acidosis, hypothermia, and low platelets n Reversal of anticoagulation • All anticoagulants increase bleeding risk • Scoring systems to predict, but bleeding often unpredictable • HAS-BLED score – Hypertension,abnormal kidney/liver, Stroke, Bleeding history, labile INR, Elderly (>65), Drugs/alcohol Risk of bleed OLD NEW Difficulty in reversal n Reversal of anticoagulation Warfarin: Withhold warfarin only: • 2 older case series total 299 pts, with 352 INR values >6 • 2 pts (0.6%) suffered haemorrhage Glover et al 1995 Lousberg et al 1998 • 1104 pts with INR >5 • 30 day incidence of major bleeds low at 1.3% • Subanalysis of 42 pts (4.3%) with INR >9 - incidence major bleeds 9.6% (4pts) - more likely to receive Vitamin K (62% vs 7%) Garcia et al 2006 n Reversal of anticoagulation Warfarin: Withhold wafarin and give Vit K: • IV Vit K - 2 small studies – – – 31 pts (10 received 1mg, 21 received 0.5mg IV) 50% pts with 1mg INR @24h <2, all pts with 0.5mg between INR 2 - 5.5 @24h – Anaphylaxis est. 3 / 10 000 administrations • Oral Vit K 1 – 2.5 mg safe and no risk of warfarin resistance – – – – 7 small studies: less bleeding with Vit K use and more rapid control 59 pts with mechanical heart valve with INR 6 - 12 13/29 vs 4/30 with INR in range @24h with Vit K 1mg vs placebo 3/29 (10%) with INR <1.8 @24h with Vit K Ageno et al 2005 ORAL > IV > Subcut Shetty et al 1992 n Reversal of anticoagulation Warfarin: Urgent reversal • CNS or vital organ haemorrhage • Major bleed (requiring admission, transfusion RBC) • Uncertainty of variable vs fixed dose PCC Haemosolvex n Reversal of anticoagulation • UFH – Short T1/2 – expectant management possible – Reversal with protamine sulphate 1mg/100IU IV • Max 50mg in 10 min • LMWH – – – – Longer T1/2, but more predictable, less bleeding Prolonged effect in renal dysfunction Protamine sulphate 50-70% effective Dose as above or 0.5-1mg/mg enoxaparin • Fondaparinux – Long T1/2 of 20 hours, longer in renal failure – Protamine not effective – Novoseven ??? n Reversal of anticoagulation Dabigetran Rivaroxaban Anti –Xa Dose 10mg daily Tmax 2.5-4h T1/2 5-9h, 9-13h (elderly) Daily dose 66% faecal, 33% renal PCC / VIIA / FEIBA for bleeding • Assay: anti-Xa • Drug interaction CYP3A4 • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Anti-thrombin Dose 150-200mg Tmax 2h T1/2 14-17 h Daily or BD dose 80% renal, 20% fecal No current antidote • Possible dialysis • Assay: Ecarin clotting time • PPI decrease absorption n Reversal of anti-platelet agents DRUG ACTUAL T1/2 EFFECTIVE THERAPY for BLEED 15-30min 4-5 days DDAVP Platelet transfusion P2Y12 receptor inhibitors: clopidogrel 8h 5-7 days ? DDAVP Platelet transfusion P2Y12 receptor inhibitors: prasugrel 7 hours 5-7 days Platelet transfusion P2Y12 receptor inhibitors: ticagrelor 7 hours < 30% effect after 2 days Wait Aspirin n SUMMARY • Chronic bleeding – Lab tests – make a diagnosis • Acute bleed with anticoagulants – Reverse as per guidelines • Acute bleed – unexpected – TEG and lab – Tranexamic acid/DDAVP/FFP