Recombinant Factor VIIA
advertisement

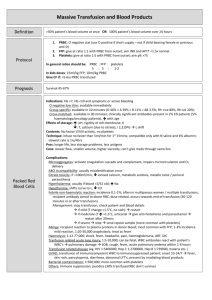
Recombinant Factor VIIA Sridhar ,V.M.D. Critical Care,Anesthesiology and Cardiology. Introduction.. Universal hemostatic agent. Originally developed for treatment of hemophiliac patients. Those with inhibitory antibodies to Factor VIII and Factor IX. Normal Hemostasis • First step in hemostasis is formation of a platelet aggregate • At the molecular level interaction of coagulation factors takes place on the surface of activated platelets • The Tissue Factor–FVIIa complex is the physiological activator of normal hemostasis Hemostasis Subendothelial matrix Nitric oxide Endothelial cell Coagulation Pathways Intrinsic Pathway Extrinsic Pathway IX Tissue Factor + VII Contact TF Pathway TF-VIIa X XI Common Pathway PL XIIa HKa Prothrombin XIa IXa PL (Tenase) VIIIa PL X a Va (Prothrombinase) Protein C, Protein S, Antithrombin III XIII Thrombin Fibrinogen Fibrin (weak) XIIIa Fibrin (strong) Mechanism .. The first step in all coagulation –Formation of Tissue Factor –Factor VIIa complex formation. This catalysis the coagulation cascade in normal persons and as well as in bleeding disorders. Mechanism of Factor VIIa .. TF+VIIa ->Thrombin . Which in turn activates platelets, and activates Factor X to Factor Xa. The activated platelets provide the template for further Factor X activation. General Instructions.. Binding of rFVIIa occurs only to activated platelets. Action occurs only at the site of bleeding. Effective doses 35 to 120mcg/kg. Standard dose 90 mcg/kg. Bolus infusion every 2 hrs. Hemophiliac patients.. Treat with recom DNA Factor VIII and Factor IX concentrates. Development of antibodies. Dose recommendation is 90 mcg/kg. Other options a. Large doses of Factor VIII. b. Prothrombin complex c. Porcine Factor VIII. Platelet Disorders.. Glanzmann Thrombasthenia. Bernard- Soulier syndrome.. First correct with platelets, FFP and Cryoprecipate. Can use Desmopressin Factor VIIa 50 to 100mcg/kg. Liver Disorders.. Coagulopathy in Liver Disorders.. Vit K dependent—FVII,C and S. Treatment includes Vit K, FFP, Desmopressin and platelets. Dose 100mcg/kg. Trauma and Surgery.. Dose 60mcg/kg. Used in intraoperative bleeding during liver surgery and in pulmonary hemorrhage. In Trauma 10 U PRBC 8 U PLTS 10 U Cryoprecipitate. Then 100 mcg/kg ,repeat dose in 20 mns Reversal of Anticoagulant Therapy.. Can be used if Vit K not effective alone Dose 20 and 90 mcg/kg. Intracerebral Bleeding. Volume of bleeding ---direct correlation with neurological outcomes. Incorporation of Factor VII a reduces the rate of hematoma formation. Other Conditions.. Type III Von willebrand disease. Congenital factor VII def. Factor XI and Factor IX def. Extensive Burns. Uremia. Cardiac Surgery.. Post operative bleeding is common. In US 10 to 15%of all blood donated is used by Cardiothoracic Surgery. Has been used Prophylactically Rescue Therapy. Need of RCT. Cost Factor. Safety.. Tissue Factor is in contact with plasma. Tissue factor is up regulated on the surface circulating monocytes (gram neg sepsis). Tissue factor is expressed in the lipid core of the plaque. Do not use with activated protein C. Use with caution when there is generalized activation of the haemostatic mechanism. Lab Tests in Trauma .. Repeat blood test after each 4 to 6 units PRBC. PT,APTT >1.5 X control 4 units FFP. Fibrinogen <1g/l 10 units Cryoprecipitate. Plt count <75k 4 units plts. Consider Calcium chloride. THE END