Metabolic Balance® and Diabetes
advertisement

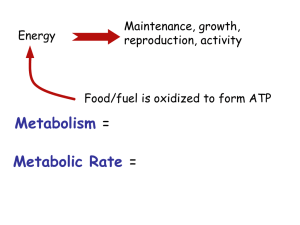
metabolic balance® and Diabetes © Dr. Wolf Funfack, MD, Specialist in Internal Medicine/Nutritional Medicine 1 © metabolic balance GmbH Diabetes worldwide 2 © metabolic balance GmbH Diabetes worldwide Update 2012 3 © metabolic balance GmbH Data from the Canadian Diabetes Association Prevalence of diabetes in Ontario adults >35 years year cases population Prevalence rate 1995 341.893 5 269.107 6,49% 2000 495.134 5 996.214 8,26% 2005 707.196 6 709.338 10,54% WHO: Until 2030 an increase of 40% is estimated for Canada! (Canadian Journal of Diabetes 2009;33(1):35-45) 4 © metabolic balance GmbH BMI and its sequelae Type 2 diabetes High blood pressure Gall stones Heart disease 5 From: Nature, special issue - Diabetes, 2001 © metabolic balance GmbH Waist measurement as a risk factor Risk of developing diabetes Waist circumference in men in women Low risk < 94 cm (37) < 80 cm (31,5 inches) Slightly increased risk > 94 cm > 80 cm Significantly increased risk > 102 cm (40) > 88 cm (34,65 inches) Average waist circumference e.g. in Germany: Women = 89 cm men = 98 cm The risk of diabetes is halved with a weight loss of only 4 kg. Other risk factor: high levels of triglycerides. From: German Health Report Diabetes 2008 © metabolic balance GmbH 6 Reduced life expectancy due to diabetes Age at the time of diagnosis In years 20 to <30 15 to 20 30 to <40 10 to 13 Over 65 2 to 5 Life expectancy in Germany Women: 83 years Men: 78 years Source: Health Report, German Federal Ministry of Health 2006 © metabolic balance GmbH 7 Increased risk of long term complications due to diabetes Disease Circulatory disorders - affecting the heart - affecting the limbs Risk of disease for diabetics 15 - 20 2-6 20 - 35 Stroke 2-3 Blindness 10 - 25 Chronic kidney failure 15 - 20 The average risk of disease in the population is 1 Source: Health Report, German Federal Ministry of Health 2006 © metabolic balance GmbH 8 The costs of diabetes in Europe Stroke: every 12 minutes Heart attack/amputation: every 19 minutes Dialysis dependence: every 60 minutes Blindness caused by diabetes: every 90 minutes 9 Liebl et al DMW 2001;126 : 585-89 CODE-2 Study (Costs of Diabetes in Europe) © metabolic balance GmbH Blood sugar regulation High blood sugar Pancreas Insulin release Glucose uptake from fat and muscle cells Normal blood sugar level © metabolic balance GmbH 10 Blood sugar regulation Low blood sugar High blood sugar Pancreas Glucagon release Glucose release by the liver Insulin release Glucose uptake from fat and muscle cells Normal blood sugar level © metabolic balance GmbH 11 How does glucose reach the cell? Glucose Glucose Glucose Glucose Glucose transporter 12 © metabolic balance GmbH Muscle contraction and glucose transporters Muscle contraction has the same effect as insulin! Glucose Glucose Glucose Glucose Muscle contraction Glucose transporter 13 © metabolic balance GmbH Blood sugar and serum insulin during i.v. glucose tolerance test in 8 test subjects of normal weight and 10 obese subjects Source: from Karam, J.H. et al. 1963 Blood- 450 sugar 400 (mg%) 350 Serum- 180 insulin (µE/ml) 160 140 300 120 Obese 250 100 200 80 150 60 100 40 50 Normal weight persons 0 Obese Obese Normal weight weight persons persons Normal 20 0 0 15 30 45 60 75 Minutes © metabolic balance GmbH 90 105 120 0 15 30 45 60 Minutes 75 90 105 120 14 Obesity and the metabolic syndrome 493 children + adolescents (age 4 - 20) exclusion: medication to treat hypertension, diabetes or lipids Normal weight Overweight Slight obesity Severe obesity Age (years) 11.7 11.9 12.8 11.3 MBI 18.4 24.5 33.4 40.6 Glucose (mg %) 87.4 86.8 89.6 89 Insulin (µU/ml) 10.3 14.6 31.3 38.6 Triglyceride (mg %) 48.4 83.1 104.6 96.5 HDL-Chol. (mg %) 58.5 46.7 41.1 39.9 CRP (mg %) 0.01 0.05 0.13 0.33 15 (Source: R. Weiss, NEJM, June 3, 2004; 350: 2362-74) © metabolic balance GmbH Insulinresistance and muscles Muscle cells do not store fat anymore and release it to the blood! Fat is transported into the liver! 16 © metabolic balance GmbH Insulinresistance and the liver Fat is stored in the liver cells! They do not react on insulin anymore, so the release of glucose is not blocked! Fat from the liver is transported into the a- and b-cells of the pancreas. 17 © metabolic balance GmbH Insulinresistance and the pancreas Insulinresistant a-Cells produce more Glucagon! Insulinresistant b-Cells produce more Insulin! 18 © metabolic balance GmbH Insulinresistance and the brain Insulinresistant cells of the brain cause stressreactions! In situations of stress the liver releases Glucose! 19 © metabolic balance GmbH Insulinresistance and the kidneys In Insulinresistance The kidney increases the Glucose levels by: 1. Gluconeogenesis 2. Increased Glucose Reabsorption Gluoneogenesis in the kidney can Increase by 300%!! 20 © metabolic balance GmbH Fructose leads to faster fat storage Fructose Glucose Not insulin dependent Insulin dependent No storage Metabolism Storage form Fatty liver disease! 21 © metabolic balance GmbH Reduction in Body Weight 62,5 % 50 % of participants need to reduce their weight by more than 5% and need to maintain it for more than one year. of participatns reduced their weight by more than 5% and maintained it at least for one year. metabolic balance® International recommendations for long-term success of an efficient weigh management program © metabolic balance GmbH 22 Comparison of weight reduction programs 31,0% 21,0% 26,0% 21,0% 15,7% 14,3% 17,0% 62,5% Weight watchers Slimming world Rosemary Conley NHS Size Down General Practice Pharmacy Exercise comparator metabolic balance® 50% Jolly, Kate et al. BMJ, 2011, 343; d6.500 “Comparison of range of commercial or primary care led weight reduction programmes . randomised controlled trial” © metabolic balance GmbH 23 Results of the evaluation study insulin requirements) 8.30% Before the study 8,3% of the participants were treated with insulin End of the study 3,9% were still on insulin 3.90% 53 % of diabetics could stop their insulin even after 1 year. Before Beginn der Studie Ende End der Studie 24 © metabolic balance GmbH Case history Mr G. L. a 47 year old teacher, with Type 2 diabetes, hypertension and impaired lipometabolism Medication: Depot insulin: morning 32 I.U., evening 16 I.U. short-acting insulin: 3x a day before meals depending on blood sugar values between12 and 18 I.U. daily insulin dose 70 - 90 I.U. Hypertension: 80 mg Metoprolol, 10 mg Amlodipin, 16 mg Valsartan, Other drugs: 40 mg Simvastatin, 100 mg aspirin Omeprazol 20 mg if required for stomach ache. 25 © metabolic balance GmbH Case history After 2 weeks: Weight loss 8.4 kg, depot insulin: only 1 x 12 I.U. before meals; short-acting insulin: between 8 and 12 I.U. other medication: 20 mg Metoprolol, 8 mg Valsartan, Amlodipin and Simvastatin were discontinued. It was no longer necessary to take Omeprazol at this stage. 26 © metabolic balance GmbH Case history In the 4th week: Weight loss has plateaued, frequent low sugar and hunger pangs during the day. He has been exercising more in the last week, e.g. Nordic walking and 1 day in the gym. Fasting blood sugar was higher in the morning than in the evening even if he did not eat anything in the night. After this, depot insulin was discontinued © metabolic balance GmbH 27 Case history Comparison of values at the start and end Initial weight: 127.0 kg BMI: 40,1 Final weight: 86.4 kg BMI: 27.3 Height: 1.78 m All medications were discontinued 28 © metabolic balance GmbH Case history BP HR Chol. LDL HDL Trigl. HBA1c LDL/HDL 02.04.2008 166/110 88/min 278 183 39 264 7.6 4.7 25.08.2008 125/80 72/min 167 119 53 134 6.2 2.2 29 © metabolic balance GmbH Source: http://www.evolvehealth.nl/mental-coaching/ Take the next Step Get Dr. Funfack's eBook at Amazon.Com “metabolic balance® – Nutrition basics: Introduction to the success program” Get Dr. Funfack's Book through our Offices „metabolic balance® – Your Personalized Nutrition Roadmap“ 3. Contact one of our Coaches via www.metabolicbalance.com 4. Contact our Canadian Office 30 © metabolic balance GmbH Canada: 1-289-291-3959 Many thanks for your attention! 31 © metabolic balance GmbH