Bohr Rutherford & Lewis Dot Diagrams Chemistry Presentation
advertisement

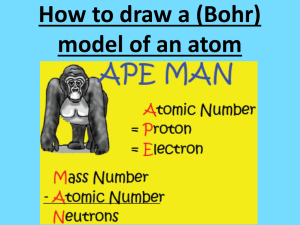
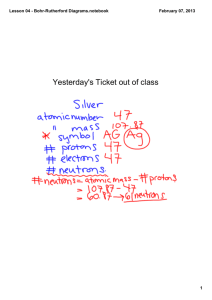
CHEMISTRY DIAGRAMS Bohr Rutherford and Lewis Dot Diagrams RECALL THE ATOM • ATOMIC NUMBER: denotes the number of protons and electrons in an atom • ATOMIC MASS: denotes the number of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of an atom HOW DO YOU FIND NUMBER OF NEUTRONS • # of Neutrons = ATOMIC MASS – ATOMIC NUMBER • EXAMPLE: How many neutrons are there in a Silicon atom? • SOLUTION: 28 Atomic Mass -- 14 = 14 -- Atomic Number = Number of Neutrons BOHR RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS • Used to show the atomic structure of an atom, isotope or ion. BOHR RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS • RULES for drawing Bohr Rutherford diagrams: 1. Place the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom 2. Place TWO electrons in the first shell. This shell takes a MAX of two electrons. 3. Place a MAX of eight electrons in all other shells. 4. OCTET RULE: No shell can have more that EIGHT electrons. If you have extra electrons, add another shell. PRACTICE • Draw a Bohr Rutherford diagram for: a. Boron b. Fluorine c. Argon LEWIS DOT DIAGRAMS • Used to show the number of electrons in the outer shell of an atom LEWIS DOT DIAGRAMS • RULES for drawing Lewis Dot Diagrams 1. Write the chemical symbol for the element. 2. Determine the number of electrons in the outer shell of that element. 3. Add electrons starting at the top of the chemical symbol and working CLOCKWISE around the symbol. 4. You MUST add ONE electron to each side of the symbol BEFORE you start pairing electrons. PRACTICE • Draw a Lewis Dot Diagram for the following elements: a.Boron b.Fluorine c.Argon