Understanding metals (12 slides) (6.2MB PPT)
advertisement

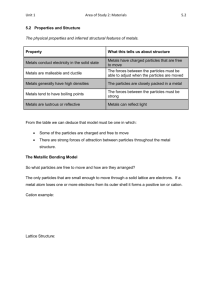
Understanding metals Why are metals used to make these items? Properties of metals What property of metals is being utalised in the images on the previous slide? • Fishing sinker • Cooking pot • Electrical wires • Bread ties • Mirror • Car body Metallic bonding model How can we explain the properties exhibited by metals? What do the silver spheres represent? What do the red spheres represent? Metals form a crystal lattice Each metal atom loses outer shell electrons to form a positive cation The cations form a rigid framework: “a lattice of cations” “a sea of delocalised electrons” The electrons move freely through the lattice: Delocalised: able to move freely, not fixed to one atom 5 The lattice is held together by the strong electrostatic attraction between cations and delocalised electrons 6 Metal cations pack to form crystals They form regular geometric patterns: body – centred cubic co-ordination no.: 8 (Na, K, Cr, Ba) face – centred cubic co-ordination no.: 12 (Au, Ag, Cu, Al) hexagonal close packing co-ordination no.: 12 (Ti, Zn, Mg) 7 Explaining properties of metals Metals are hard, with a high melting point Due to the strong electrostatic attraction between cations and delocalised electrons Metals are dense Due to the close packing of the cations in the lattice 8 Metals conduct electricity The delocalised electrons are able to move freely through the lattice and carry electrical charge. Metals conduct heat Electrons move faster when heated, they can carry the energy through the lattice Metals are lustrous They are shiny when polished: the delocalised electrons are able to reflect light. 9 Metals are malleable and ductile (not brittle) Malleable: able to be beaten into a sheet Ductile: able to be drawn into a wire Layers of atoms can slide past each other: the delocalised electrons can move with them to maintain the electrostatic attraction 10 Questions Explain the following properties of copper: a) Hard The electrostatic attraction between the metal cations and delocalised electrons is very strong b) Malleable and ductile When layers of cations are distorted, delocalised electrons are able to move to maintain the electrostatic attraction c) Good electrical conductor The delocalised electrons are free to move and carry charge through the metal d) lustrous when polished The delocalised electrons reflect light 11 Alloys • Mixing metals can change their properties. There are two main types of alloys. • Substitutional alloys those made from metals of a similar size where the second metal takes the place of the first in the lattice.