Lesson 2 Sankey diagrams and efficien..
advertisement

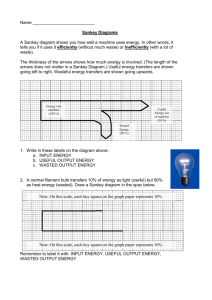
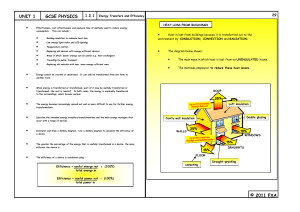
Do now! 1 Energy Types Word Scramble 2 Title – Energy Flow diagrams and the date Some examples of forms of energy Kinetic energy (KE) Nuclear energy Energy due to a body’s motion. Energy associated with nuclear reactions. Potential energy (PE) Energy due to a body’s position Electrical energy Thermal energy Energy associated with electric charges. Energy due to a body’s temperature. Chemical energy Energy associated with chemical reactions. Elastic energy Energy stored in an object when it is stretched or compressed. All of the above forms of energy (and others) can ultimately be considered to be variations of kinetic or potential energy. Learning Today • • • • • Energy flow diagrams Energy flow circus Sankey diagrams Potential Energy – P.E. Homework Potential Energy Sheet Other energy measurement examples 4200 joules (4.2 kJ) 1 food Calorie 1 000 000 J (1 MJ) Energy of a Mars bar 0.000 02 J Energy need to produce a syllable of a word 15 000 000 000 000 Energy received by the Earth from the Sun in one day 000 000 000 J Conservation of energy Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only be transformed from one form to another form. Conservation of energy also means that the total energy in the universe stays constant. Energy Flow diagrams – Copy please Energy flow diagrams show energy transformations. Work done = energy transformed For example, when a car brakes, its kinetic energy is transformed into heat energy in the brakes. Kinetic heat Energy changes 10/04/2015 To describe an energy change for a light bulb we need to do 3 steps: 1) Write down the starting energy: 2) Draw an arrow Electricity 3) Write down what energy types are given out: Light + heat Draw energy flow diagrams for the following…? 1) An electric fire 2) A rock about to drop 3) An arrow about to be fired Television What are the main energy transfers for a television (don’t forget the wasted energy)? light electrical sound heat Car engine What are the main energy transfers for a car engine (don’t forget the wasted energy)? kinetic chemical sound heat Radio What are the main energy transfers for a radio (don’t forget the wasted energy)? sound electrical heat Pendulum oscillation GRAVITATIOINAL POTENTIAL MINIMU ENERGY MAXIMU MM KINETIC MAXIMU ZER ENERGY MO The total energy, gravitational potential plus kinetic, remains the same if there are no significant resistive forces Wasted sound energy Can you name some devices that waste energy as sound? Hairdryer _____________ Washing machine _____________ Car engine _____________ Computer _____________ Microwave _____________ Bunsen burner _____________ Wind turbine _____________ Dish washer _____________ Wasted heat energy Can you name some devices that waste energy as heat? Radio _____________ Television _____________ Car engine _____________ Computer _____________ Turbine _____________ Motor _____________ Transformer _____________ Any electrical device _____________ What happens to wasted energy? What happens to the wasted energy you get whenever energy is changed from one form to another? Remember energy can not be c______ or d_______. Wasted e_____ spreads out (d_______) into the s_________. This makes the energy harder to r____. This is why it is important to r_____ the amount of wasted energy there is. Energy Transfer diagrams 10/04/2015 Consider a light bulb. Let’s say that the bulb runs on 100 watts (100 joules per second) and transfers 20 joules per second into light and the rest into heat. Draw this as a diagram: “Input” energy 100 J/s electrical energy “Output” energy 20 J/s light energy 80 J/s heat energy (given to the surroundings) Example questions Consider a kettle: 2000 J/s electrical energy Sound energy Wasted heat Heat to water 1) Work out each energy value. 10/04/2015 Consider a computer: 150 J/s electrical energy 10 J/s wasted sound 20 J/s wasted heat Useful light and sound 1) How much energy is converted into useful energy? 10/04/2015 Here is a more complex energy transformation diagram, the sort used by engineers. This one is for an aeroplane engine. Choose appropriate words to fill in the gaps below: Energy is required to do ________. work joules (J) Energy is measured in ________ Energy cannot be created or ___________ destroyed but can only change ________. form Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by __________ moving bodies. When an object is lifted up it gains gravitational potential _____________ energy. Heat or __________ thermal energy is often produced as a _________ wasted energy form, dissipated to the surroundings. WORD SELECTION: potential moving joules thermal work wasted form destroyed Gravitational Potential Energy 10/04/2015 Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object has because of its position in a gravitational field GPE (Joules) = Weight (newtons) x Change in height (metres) GPE W H Gravitational Potential Energy 10/04/2015 Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object has because of its position in a gravitational field GPE (Joules) = Weight (newtons) x Change in height (metres) GPE W H Some example questions… 10/04/2015 How much gravitational potential energy have the following objects gained?: 1. A brick that weighs 10N lifted to the top of a house (10m), 2. A 10,000N car lifted by a ramp up to a height of 50cm, 3. A 70kg person lifted up 50m by a ski lift. How much GPE have the following objects lost?: 1. A 2N football dropping out of the air after being kicked up 30m, 2. A 0.5N egg falling 10m out of a bird nest, 3. A 10,000N car falling off its 50cm ramp. 4. Mr Richards when bungi-jumping off a 110-metre high bridge in Zambia in August Don’t forget! Test! • Use the revision sheet to help you study! • Test on Thursday 26th January Energy Circus Around the room are a few examples of energy changes (some simple, some a little more complicated!) For each example I want you to write the name of the experiment and then the energy flow diagram for that experiment You will have 2 minutes on each example. Ready? Go! Sankey Diagram A Sankey diagram helps to show how much light and heat energy is produced Sankey Diagram The thickness of each arrow is drawn to scale to show the amount of energy Sankey Diagram Notice that the total amount of energy before is equal to the total amount of energy after (conservation of energy) Efficiency Although the total energy out is the same, not all of it is useful. Efficiency Efficiency is defined as Efficiency (%) = useful energy output x 100 total energy input Efficiency Efficiency is defined as Efficiency (%) = useful energy output x 100 total energy input Can you copy this (with title) please? Example Efficiency = 75 x 100 = 15% 500 Energy efficient light bulb Efficiency = 75 x 100 = 75% 100 Energy efficient light bulb Efficiency = 75 x 100 = 75% 100 That’s much better! More complex examples Let’s try some questions! Stick the sheet into your books and answer the questions