Energy efficiency - wellswaysciences
advertisement

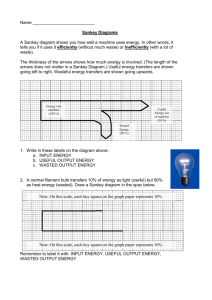
Conservation of Energy • Lesson Objectives: • All must know that energy an be neither created nor destroyed but it can be changed from one form into another. • All must know that some energy is wasted (usually as heat) when energy is transferred. • Most should be able to draw, label and use simple SANKEY DIAGRAMS. • Some may be able to work out efficiency for some electrical devices. • http://www.bbc.co.uk/learningzone/clips/ener gy-transfer/263.html What are the main energy transfers for a television? light electrical sound heat What are the main energy transfers for a car engine? kinetic chemical sound heat What are the main energy transfers for a radio? sound electrical heat In which two forms is energy usually wasted? A. Sound and light B. Heat and sound C. Heat and light D. Light and chemical © Boardworks Ltd 2003 What is the intended energy transfer for a Bunsen burner? A. Sound light B. Heat chemical C. Chemical light D. Chemical heat © Boardworks Ltd 2003 What is the energy change for a falling rock? A. Kinetic gravitational B. Gravitational kinetic C. Kinetic speed D. Mass speed © Boardworks Ltd 2003 In what form is energy wasted for all electrical devices? A. Heat B. Electrical C. Sound D. Light © Boardworks Ltd 2003 Sankey Diagrams • These are ways of representing USEFUL and WASTED energy. A simple filament light bulb. Which is the useful energy? The useful energy is shown by the HORIZONTAL arrow. The wasted energy is the curved, downward pointing arrow. It could also be shown as an upward pointing arrow. More Sankey Diagrams • Sankey diagram for energy saving light bulb. Why are energy saving light bulbs better value for money? Because they waste little energy as heat. Bills go down! Drawing an accurate Sankey diagram Energy Transfer diagrams Energy is measured in joules. Consider a light bulb. Let’s say that the bulb runs on 100 joules per second and transfers 20 joules per second into light and the rest into heat. Draw this as a diagram: Total input energy must = total output energy. “Input” energy 100 J/s electrical energy “Output” energy 20 J/s light energy 80 J/s heat energy (given to the surroundings) Example questions Consider a kettle: 2000 J/s electrical energy Sound energy Wasted heat Heat to water 1) Work out each energy value. 2) How much energy is wasted? Consider a computer: 150 J/s electrical energy 10 J/s wasted sound 20 J/s wasted heat Useful light and sound 1) How much energy is converted into useful energy? Energy Transfer Values Electrical energy 100% Kinetic energy 58% (Useful spinning of the drill bit) Kinetic energy 22% (Wasted vibration of the drill) Draw a Sankey Diagram for this drill. Heat energy 20% Sankey Diagram for an ipod. How much energy is wasted energy? Efficiency Efficiency is a measure of how much USEFUL energy you get out of an object from the energy you put INTO it. Efficiency = Useful energy given out by the device Energy put into it x100% e.g. if 2000 joules of electrical energy are put into a kettle and 500 joules of heat energy are gained from it, its efficiency is 500/2000 x 100% = 25% Efficiency for a radio If you have a radio and it is supplied with 300J of electrical energy which it converts to 96J of sound energy. a) How much energy is wasted? 204J b) In what form is the energy wasted? heat c) What is the efficiency of the radio? Efficiency = Useful Total = 96J/300J = 0.32 or 32% © Boardworks Ltd 2003 Energy efficiency Energy efficiency Energy efficiency Some examples of efficiency… 1) 5000J of electrical energy are put into a motor. The motor converts this into 100J of movement energy. How efficient is it? 2) A laptop can convert 400J of electrical energy into 240J of light and sound. What is its efficiency? Where does the rest of the energy go? 3) A steam engine is 50% efficient. If it delivers 20,000J of movement energy how much chemical energy was put into it? Working out efficiency from Sankey Diagrams Example questions Consider a kettle: 2000 J/s electrical energy Sound energy Wasted heat Heat to water What is the kettle’s efficiency? Consider a computer: 150 J/s electrical energy 10 J/s wasted sound What is the computer’s efficiency? 20 J/s wasted heat Useful light and sound If a plant converts 200J of light energy into 140J of chemical energy by photosynthesis, what is the efficiency of the process? A. 30J B. 30% C. 70J D. 70% © Boardworks Ltd 2003 • When you have finished the work set please follow the following and do the exercises. • Subjects>science>revision>Lonsdale Revision Guides>Physical Processes>70 Forms of Energy and 75 Transfer and Conservation of Energy © Boardworks Ltd 2003 © Boardworks Ltd 2003