Gases and the Kinetic-Molecular Theory
advertisement

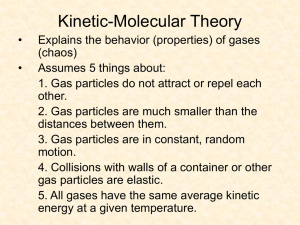
Gases and the Kinetic-Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases 1) Gases are made up of tiny molecules. 2) Gas molecules are always in constant motion. 3) The forces of attraction between gas molecules are negligible. 4) Gas molecules undergo elastic collisions. 5) The average kinetic energy of gas molecules is proportional to the Kelvin temperature of the gas. An Overview of the Physical States of Matter The Distinction of Gases from Liquids and Solids 1. Gas volume changes greatly with pressure. 2. Gas volume changes greatly with temperature. 3. Gases have relatively low viscosity. 4. Most gases have relatively low densities under normal conditions. 5. Gases are miscible. The three states of matter. Gases can be measured and described with four properties or variables. A) B) C) D) Pressure (P) Volume (V) Temperature (T) Amount of Gas (n) Gases at STP (Standard Temperature Pressure) is equivalent to 22.4 L at 1 atm and 273.15K. Volume = Liter (L) Temperature = Kelvin (K) K = OC + 273.15 Amount of Gas (n) n= given mass/molar mass of gas Pressure is defined as the force pushing over a certain area. FORCE A R E A P = Force / Area Effect of atmospheric pressure on objects at the Earth’s surface. A mercury barometer. Two types of manometer closed-end open-end Common Units of Pressure Unit Atmospheric Pressure Pascal (Pa); 1.01325 x 105 Pa; kilopascal (kPa) 101.325 kPa atmosphere(atm) millimeters of mercury(Hg) torr pounds per square inch (psi or lb/in2) bar 1 atm* 760 mm Hg* 760 torr* 14.7 psi or lb/in2 1.01325 bar Scientific Field SI unit; physics, chemistry chemistry chemistry, medicine, biology chemistry engineering meteorology, chemistry, physics *This is an exact quantity; in calculations, we use as many significant figures as necessary. A container of gas measures the pressure to be 104.9 kPa. Convert this pressure to psi. Solution: Use dimensional analysis 104.9 kPa x 14.7 psi 1 101.3 kPa = 15.2 psi The safety disk in a scuba tank will blow at a pressure of approximately 25000 kPa. Convert this pressure to mm Hg. 25 000 kPa x 760 mm Hg = 187515.42 mm Hg 101.325 kPa = 187515 mm Hg Converting Units of Pressure PROBLEM: A geochemist heats a limestone (CaCO3) sample and collects the CO2 released in an evacuated flask attached to a closed-end manometer. After the system comes to room temperature, Dh = 291.4 mm Hg. Calculate the CO2 pressure in torrs, atmospheres, and kilopascals. PLAN: Construct conversion factors to find the other units of pressure. SOLUTION: 291.4 mmHg 760 torr = 291.4 torr 760 mmHg 291.4 torr 1 atm 760 torr 0.3834 atm = 0.3834 atm 101.325 kPa 1 atm = 38.85 kPa Exercises 1) A container of gas measures the pressure to be 104.9 kPa. Convert this pressure to psi. 2) Atmospheric pressure is reported as 30.1 inHg. Convert this to torr. 3) Many pneumatic tools operate at an air pressure of 90 psi. What is the equivalent pressure in kilopascals (kPa)?