ppt
advertisement
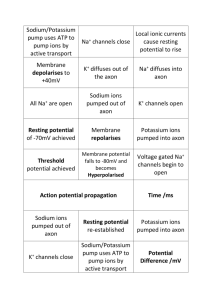
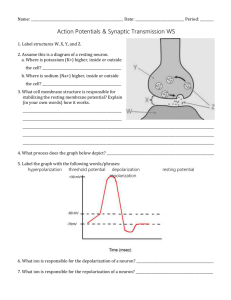
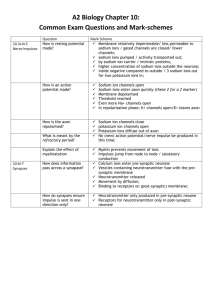
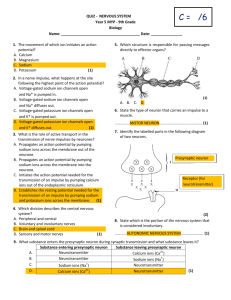
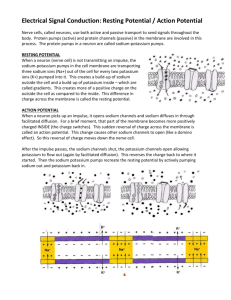
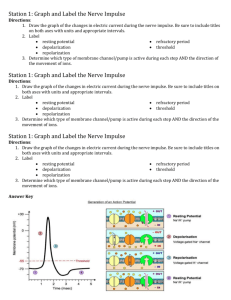
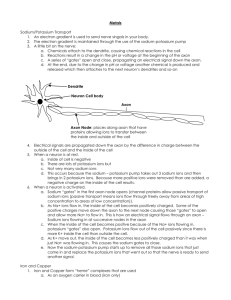
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM How do neurons communicate? THE ROAD TO CEPHALIZATION… TRY THIS! 1. Which letter represents the dendrite of the sensory neuron? 2. What type of cell is found only in the central nervous system? What structure conducts nerve impulses from the spinal cord to the gall bladder? 3. TRY THIS! 1. Which letter represents the dendrite of the sensory neuron? W 2. What type of cell is found only in the central nervous system? Interneuron What structure conducts nerve impulses from the spinal cord to the gall bladder? Motor Neuron 3. TRY THIS! What event occurs during repolarization? A. the sodium gates open B. the potassium gates open C. the net movement of sodium ions into the axon D. the net movement of potassium ions into the axon TRY THIS! What event occurs during repolarization? A. the sodium gates open B. the potassium gates open C. the net movement of sodium ions into the axon D. the net movement of potassium ions into the axon TRY THIS! Which of the following occurs between time X and time Y? A. repolarization B. depolarization C. resting potential D. refractory period TRY THIS! Which of the following occurs between time X and time Y? A. repolarization B. depolarization C. resting potential D. refractory period TRY THIS! What event occurs during depolarization? A. the sodium gates close B. the potassium gates open C. the net movement of sodium ions into the axon D. the net movement of potassium ions into the axon TRY THIS! What event occurs during depolarization? A. the sodium gates close B. the potassium gates open C. the net movement of sodium ions into the axon D. the net movement of potassium ions into the axon TRY THIS! Tell the story of how information travels from your spinal cord to the muscles of your arm to make them move. Include the following terms: Resting potential Action potential Depolarization Repolarization Refractory Period Propagation TRY THIS! Compare resting potential and action potential Resting Potential Action Potential TRY THIS! Compare resting potential and action potential Resting Potential Action Potential - Active transport with ATP - Passive transport with no ATP - Carrier protein sodium/potassium pump - Gated channel proteins: sodium gate and potassium gate - Maintains concentration gradients - Ions flow down concentration gradients -65mV -depolarization: -40mV (threshold) to +40mV; repolarization: +40mV to -65mV PROPAGATION OF THE NERVE IMPULSE TRY THIS! Where in the myelinated axon would an action potential actually occur? TRY THIS! Where in the myelinated axon would an action potential actually occur? TRY THIS! How does a neuron respond to a strong stimulus? A. It produces a larger action potential B. It causes more ions to move across the neuron membrane C. It causes more action potentials in a given period of time D. It causes action potentials to be conducted at a faster speed TRY THIS! How does a neuron respond to a strong stimulus? A. It produces a larger action potential B. It causes more ions to move across the neuron membrane C. It causes more action potentials in a given period of time D. It causes action potentials to be conducted at a faster speed TRANSMISSION ACROSS THE SYNAPSE Animation TRANSMISSION ACROSS THE SYNAPSE Nerve impulse reaches the axon bulb Ca2+ ions move into the axon bulb. Ca2+ ions interact with contractile proteins and pull the vesicles containing neurotransmitters to the surface of the presynaptic membrane. The vesicles merge with the presynaptic membrane and release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. TRANSMISSION ACROSS THE SYNAPSE The neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft. The neurotransmitters bind with specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. Depolarization occurs on the postsynaptic membrane if threshold is reached. The neurotransmitter is destroyed by an enzyme (ex. acetylcholinesterase) or reabsorbed back into the presynaptic membrane. TRY THIS! Which of the following describes the role of calcium ions during synaptic transmission? A. They cause Y to become inactivated. B. They act as carriers to move Y toward Z. C. They cause Y to undergo endocytosis at W. D. They initiate the process that results in X moving toward W. TRY THIS! Which of the following describes the role of calcium ions during synaptic transmission? A. They cause Y to become inactivated. B. They act as carriers to move Y toward Z. C. They cause Y to undergo endocytosis at W. D. They initiate the process that results in X moving toward W. TRY THIS! Tell the story of how information travels from your spinal cord to the muscles of your arm to make them move. Include the following processes: Resting potential Action potential Depolarization Repolarization Refractory Period Propagation Transmission across the Synapse