Introduction to basic Crystallography
advertisement

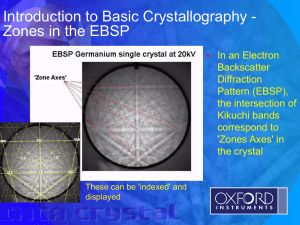
MODULE 2 - Introduction to Basic Crystallography • Bravais Lattices • Crystal system • Miller Indices • Crystallographic Direction • Zone Axis • Zones in the EBSP Determining the Orientation • Indexing Describing Orientations • Euler Angle • Euler Space - ODF's • Orientation Matrix • Ideal Orientation Nomenclature • Misorientation Crystal Forms Describing Planes and Directions Describing Misorientations Introduction to Basic Crystallography Bravais Lattices • There are 14 Bravais Lattices: Note: • Body Centered Cubic (BCC) and • Face Centred Cubic (FCC) forms • From these 7 crystal systems are derived Introduction to Basic Crystallography Crystal System • These terms describe the geometry of the unit cell - the structure that is repeated throughout the crystal. • There are seven Crystal systems: 1. Cubic 2. Hexagonal 3. Trigonal 4. Tetragonal 5. Orthorhombic 6. Monoclinic 7. Triclinic The lengths of the sides of the unit cell are shown below as a, b and c. The corresponding angles are shown as alpha, beta and gamma. Introduction to Basic Crystallography - Miller Indices • For a cubic example, Miller indices can be derived to describe a plane • Consider a cubic unit cell with sides a b, c, with an origin as shown Introduction to Basic Crystallography Crystallographic Direction • A crystallographic direction describes the intersection of specific faces or lattice planes • Miller Indices can be used to describe directions For a cubic material the plane and the normal to the plane have the same indices Introduction to Basic Crystallography - Zone Axis • ‘Zone’: faces or planes in a crystal with parallel intersections. • Zone Axis: The common direction of the intersections