Reflection and Refraction

Topic : Waves
Aim : Describe the properties and behavior of visible light.
Do Now : Take out reproduction packet.
Complete #2 on the back of your KE and PE reading notes.
HW : Reading Notes – Forces
CL Waves due Thursday
Which skier will have a greater potential energy? Support your answer.
Identify the electromagnetic wave described.
1. Has the highest energy.
2. Used to look at internal images of bones.
3. Needed for your cells to produce Vitamin D.
4. Lowest frequency and wavelength.
5. Visible light with the shortest wavelength.
6. Felt as heat.
7. Emitted by cell phones and satellite signals.
8. Produced during nuclear reactions.
Light
• Electromagnetic wave
• Transverse wave
Photon • Tiny bundle of energy
• Continue in straight line unless direction is changed
What occurs when light strikes an object?
Which is transparent, translucent, and opaque?
Opaque object
• Doesn’t transmit light
• Only absorbs & reflects
• Wood, metal…
Translucent object
• Transmits light, but with no detail
• Some light passes
• Waxed paper, frosted glass
Transparent • Transmits light easily object • Very clear
• Water, glass, air…
You can’t see the stem of this flower through the opaque vase. A blurry view of the stem is seen through the translucent vase. The entire stem can clearly be seen through the transparent vase.
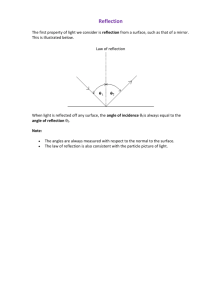
Reflection • Bouncing back of light
• Law of Reflection = angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Types of reflection
• Depends on surface
Regular Reflection Diffuse Reflection
SHARP IMAGE FUZZY IMAGE
Regular Reflection Diffuse Reflection
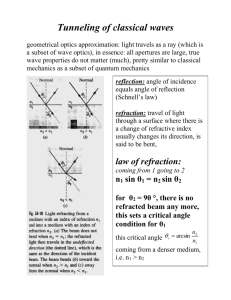
Refraction
• Bending of light
• Ray changes speed
Index of
Refraction
• Amount by which a material refracts light
• Greater = more light is bent
• Larger for solids
• Smallest for gases
B has a larger
Index of Refraction because it bends the wave a lot more than A
C has a larger
Index of Refraction because it bends the wave a lot more than D
Prism •Piece of glass
•Bends white light
2x
•Separates it into colors (different wavelengths)
• Longer wavelength less bending
Red light
•Longest wavelength
•Refracted the least
Violet
• Shortest wavelength
light
• Refracted the most
When water droplets act as a prism, a RAINBOW is formed.
Diffraction : light bends when it passes around an edge or through a slit
Mirages result when air near the ground is much warmer or cooler than air above. The density of air increases as air cools and light waves move slower in cooler air than warmer air. As a result, light waves are refracted as they pass through air layers with different temperatures.
Let’s summarize …
1. Compare the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection.
2. Describe the difference between reflection and refraction.
A student sees a mirror image of a duck in the water of a lake. What causes the mirror image?
a. Black light b. Refracted light c. Reflected light d. Absorbed light
What happens to the path of a light ray as it passes from air into water at an angle?
a. Its path widens.
b. Its path bends.
c. Its path becomes shorter.
d. Its path continues in a straight line.
Objects appear different in size and shape in a container of water due to a. refraction of light waves b. interference of the water and light waves c. polarization of the light waves d. diffraction of the light waves