General Wave Behavior - MIT Haystack Observatory
advertisement

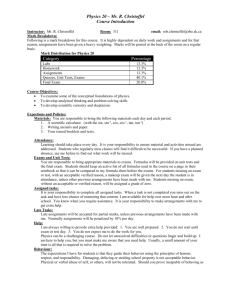
Wave Behavior Another McGourty-Rideout Production The Physics of Waves • All waves follow the laws of physics no matter what type • Waves can be reflected, refracted, diffracted, absorbed, scattered and experience interference Reflection • Reflection happens when a wave bounces off an obstacle. Specular reflection: smooth surface – Angle of incidence = angle of reflection Diffuse reflection: rough surface – Reflection in all directions because angle of incidence varies over the surface due to its roughness Law of Reflection angle of incidence= angle of reflection Reflection • An echo example of a reflection • Radar uses this principle to determine the size, characteristics of, and distance to an object Refraction • Occurs as waves move from one medium into another or within a medium, like air, that varies in density or temperature • Waves bend toward the normal when they move from a less optically dense medium (faster) to a more optically dense medium (slower) • Waves bend away from the normal when the opposite is true Snell’s Law of Refraction n1 sin 1 n2 sin 2 • Angles are measured with respect to the normal Refraction θ2 θ1 Index of Refraction n=c/v • nair = 1.0003 • nwater = 1.33 • nvacuum = 1.00 • Can you explain why “n” is a naked number? Can it ever be less than 1? Index of Refraction Redux n=√εμ ε = electric permittivity μ = magnetic permeability These describe how the material interacts with electric and magnetic fields Atmospheric Refraction • Causes gradual curve of light from stars and sun • Makes sun visible 2-3 minutes before sunrise and after sunset Dispersion The index of refraction of real materials actually depends on the frequency of the light being bent. Dispersion is the explanation for rainbows: Each color has its own frequency Each gets slowed down differently Each comes out at a different angle Diffraction • Waves that have longer wavelengths, or lower frequencies, diffract better than high frequency waves • Diffraction patterns are determined by both the size of the opening and the wavelength Absorption • Absorption happens when the medium has the ability to absorb the energy of the wave • When the wave is absorbed, its energy is transferred to the medium and the wave is gone • Gradual absorption as the wave penetrates the medium is called “attenuation” • Absorption of only specific frequencies will leave “gaps” in the continuing wave spectrum called “spectral absorption lines” Absorption • Absorption at the quantum level happens when an individual photon has the exact energy that corresponds to an energy gap between two energy states of the medium • The type of energy gap corresponds directly to the frequency of the photon Scattering • If the photon is absorbed and then re-emitted immediately, it is said to be scattered • How the light is scattered is dependent on the frequency of the light and the size of the particle it is scattering from • Some of the energy of the light is absorbed by the scatterer and so the re-emitted light has a little less energy Scattering • If the photon has a longer wavelength than the size of the scattering particle, it is called Rayleigh scattering • In Rayleigh scattering the very long wavelength light is hardly scattered at all but the shorter wavelength is much more strongly scattered • Since blue light is much ‘shorter’ than red, it gets more scattered by the molecules in the air: therefore the sky is blue! Interference • When two or more waves come together, they “superimpose” or add together • The total amplitude is simply the sum (positive & negative!) of all the individual amplitudes • The extremes of what can happen are called constructive interference and destructive interference Constructive and Destructive Algebraic Addition S S Partially Constructive (somewhat out of phase) Constructive (in phase) S Destructive (180° out of phase) S Non-coherent signals (noise) Interference Fringes • Interference fringes are a series of bright and dark bands • Sometimes straight, sometimes circular, sometimes more complicated Young’s Double Slit Experiment • Light diffracting through 2 slits produces fringes on a screen • Bright fringes are areas of constructive interference • Dark fringes are areas of destructive interference