CCSSM Lesson 3
advertisement

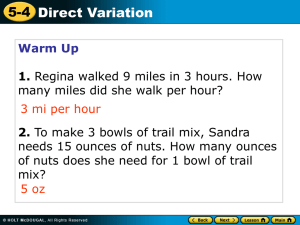
Lesson 3-B CCSSM Stage 3 Companion Text Warm-Up Cody rode his skateboard at a constant speed and then slowed down as he approached school. The story is shown on the graph below. Speed (miles per hour) 1. How fast did Cody ride his skateboard when he rode at a constant speed? (0, 8) (0.5, 8) 8 miles per hour 2. How long did he ride at a constant speed? Hours (0.75, 0) 0.5 hours (30 minutes) 3. How far did he ride at his constant speed? 4 miles 0.75 hours (45 minutes) 4. What does the point (0.75, 0) mean? into his ride, Cody stopped at school. Lesson 3-B Direct Variation Tables and Slope Vocabulary Direct Variation When a graph on a coordinate plane is a straight line that goes through the origin, it is called a direct variation graph. In a Table In Quadrant I Direct Variation Function A direct variation graph goes through the origin and forms a straight line. The equation for a direct variation function is: y mx y where m is the slope, or rate of change , of the x function. Example 1 Use the direct variation function y = 3x. a. Complete the table for the given input values. b. Draw a scatter plot of the ordered pairs in the table and connect the ordered pairs with a straight line. c. Find the slope of the function. Input, x 0 1 2 3 4 Function Rule y = 3x y 3 0 0 y 3 1 3 y 3 2 6 y 3 3 9 y 3 4 12 Output, y 0 3 6 9 12 Example 1 (continued) Use the direct variation function y = 3x. b. Draw a scatter plot of the ordered pairs in the table and connect the ordered pairs with a straight line. Input, x 0 1 2 3 4 Output, y 0 3 6 9 12 0,0 1, 3 2,6 3,9 4,12 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 c. Find the slope of the function. The slope is the coefficient of the x variable. y Also note that 3 for each ordered pair. x y 3x Slope 3 Example 2 Elliot wrote an equation, y = 4.5x, to show the relationship between the number of days, x, and the total miles, y, he ran. Jacob runs daily but only recorded his total miles in the table at 2, 5, 10, and 11 days. Who runs more miles, on average, per day? Elliot JacobTo find Jacob’s unit rate, or y = 4.5x slope, find the ratio y to x for any (x, y) pair from the table: Days, x Total Miles Run, y 0 0 2 8 Elliot: 4.5 miles per day 5 20 Jacob: 4 miles per day 10 40 11 44 8 miles 4 miles per day 2 days Elliot wrote an equation with a slope of 4.5. This slope represents his daily rate: 4.5 miles per day. Elliot runs 0.5 more miles per day than Jacob. Direct Variation Function A direct variation graph… goes through the origin, forms a straight line, and has an equation of the form y = mx where m is the y slope, or rate of change , ofthe function. x Exit Problems 1. Complete the input-output table and graph the function. Input x Function Rule y = 2x Output y 0 1 2 3 2. The table shows ordered pairs which model direction variation. Write an equation relating the x and y coordinates. x 0 1 2 3 4 y 0 3 6 9 12 Communication Prompt How does direct variation compare to a linear equation in the form y = mx + b?