Droporcontinueproductlinedecision
advertisement

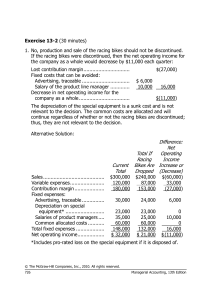
Decision Making By Ghanendra Fago Drop Or Continue Product Line Decision When a firm or company is divided into many departments, divisions, sections, branches and product lines to produce and sell various types of product, it is not necessary for earning profit by each product line, division, department, and branch. In case of loss or low profit from one or more, management should taken decision whether to drop or continue product line in the future. The management should take decision based on the segment margin of the department or division, or product line which is the basic criteria whether to drop or continue decision. Segment margin is the margin which can be obtained deducting departmental fixed cost/segment fixed/traceable fixed cost from contribution margin of the department/ product line/ division. To take decision drop or continue product line, segment margin should be taken as basis of criteria. If the segment margin is greater than zero, then it will be better to continue and if more than zero, better to drop the product line. Factors considerations While taking drop or continue product line decision, it is very important to consider the following points. Alternative utilization of idle capacity like machine, labour, land etc. Continuity of constant cost/fixed cost Departmental or traceable fixed cost Opportunity cost Government rules and regulation regarding drooping product Union activity Effect on other product lines Response of material suppliers Regular customers etc. CASE The Regal Cycle Company manufactures three types of bicycles – a dirt bike, a 10 speed bike, and a touring bike. Data on sales and expenses for the past six months follow: Particulars Total Dirt bikes 10–speed Touring bikes bikes Sales Less: Variable manufacturing & selling expenses Contribution margin $ 300,000 120,000 $ 90,000 $ 150,000 $ 60,000 27,000 60,000 33,000 180,000 63,000 90,000 27,000 30,000 23,000 35,000 60,000 10,000 6,000 12,000 18,000 14,000 9,000 13,000 30,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 12,000 Total fixed expenses 148,000 46,000 66,000 36,000 Net income (loss) $ 32,000 $ 17,000 Less: Fixed expenses: Advertising, direct Depreciation of special equipment Salary of line supervisor Common, but allocated* $ 24,000 $ (9,000) Management is concerned about the continued losses shown by the touring bikes and wants a recommendation as to whether or not the line should be discontinued. The special equipment used to produce touring bikes has no resale value. Required: Should production and sale of the touring bikes be discontinued? Show computations to support your answer. CASE 2: A discount department has three major departments: Groceries, General Merchandise and Drugs. The department is thinking of dropping the Groceries departments which has constantly shown a net loss. The present annual net income of the store is as follows: in Thousands) ] Sales Variable expenses cost and Contribution margin Groceries General Merchandi se Drugs Total $. 1,000 $. 800 800 560 60 1,420 200 240 40 480 150 100 15 265 60 100 20 180 210 200 35 445 $. 100 $. 1,900 Fixed costs: Separable Joint allocated Total fixed cost but Required: 1. Which alternative would you recommend either to drop or continue the grocery department? Assume that the total assets invested will not be affected by decision. Also assume that the vacated space will be idle. 2. Should the groceries department be closed under the condition that the space made available by the dropping of groceries would be used by an expanded G. Merchandise Department? The sales will be increase by $ 500, generates a 30% contribution margin and have separable fixed costs of $ 70 by doing it.