EG2
advertisement

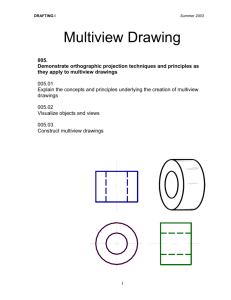
Engineering Graphics II Projection Theory and Multiview Drawings Prof. Paul Kurowski October 10, 2012 Projection Theory Scheme for representing 3-dimensional objects in a 2-dimensional medium (paper or computer screen) Can represent all 3 dimensions in a single image or use multiple views Working drawings are the practical result Projection Theory Based on two concepts: Line of Sight An imaginary ray of light between the observer’s eye and the object Start at single point for perspective projections and are parallel in parallel projections Plane of Projection An imaginary flat plane (paper, computer screen) upon which the image created by the lines of sight is projected Perspective Projection Parallel Projection Projection Theory Perspective projections mimic what the eye sees, but are more difficult to construct and do not show the true dimensions of the object Parallel projections are most commonly used in engineering graphics Orthographic Projection A parallel projection where the plane of projection is perpendicular to the lines of sight Can produce either pictorial drawings that show all three dimensions at once, or multiview drawings that show only two dimensions at a time Multiview Drawings Engineering drawings are used to manufacture or construct whatever the object is Pictorial drawings (perspective or orthographic) distort dimensions and/or angles, making fabrication difficult Multiview drawings show the true size and shape of the two dimensions shown Pictorial Distortion Distorted dimensions and distorted angles A Multiview Drawing by Albrecht Dürer (1471-1528) Multiview Projection True size and shape Angles are correct Circles are round Lengths are to scale Multiview Projection Set of 2-D views representing 3-D object. Views are projections on sides of ‘box’ containing object. Drawing formed by unfolding box Drawing formed by unfolding box Unfolding the glass box to produce a six view drawing Most Common Views Top (or Plan) Front View (or Elevation) Right Side View (or Profile) Cross sections show interior of object – later! Projection Angle In Europe, First Angle Projection is used In North America, and in ES1050, Third Angle Projection is used Be sure to select Third Angle Projection for your drawings First-Angle Projection (Europe) Third-Angle Projection (North America) Third-Angle Projection (North America) Standard Practices Choose front view as most descriptive Determine views to best represent object Use minimum number of views to completely describe object Align views correctly Line Conventions Hidden Lines Some features may not be visible in a given view, but are still important. E.g. holes, surfaces, change of planes Hidden features are represented with a dashed line Hidden Lines Line Conventions Center Lines Used to indicate the axes of symmetrical parts and features (holes, cylinders, etc.) Consist of alternating long and short thin dashes Center Lines Line Precedence Visible lines have top priority Hidden lines do not cross or have priority over visible lines Centre lines do not cross or have priority over visible or hidden lines How to Create 3-View Drawings Block in front, top and right side views using the overall width, height and depth. Sketch the front. Using construction lines project to top and right. Block in major features seen in each view How to Create 3-View Drawings How to Create 3-View Drawings How to Create 3-View Drawings Draw Multiview E-drawing solution Draw Multiview Draw Multiview Draw Multiview Draw Multiview Draw Multiview Draw Multiview Draw Multiview