v plane
advertisement
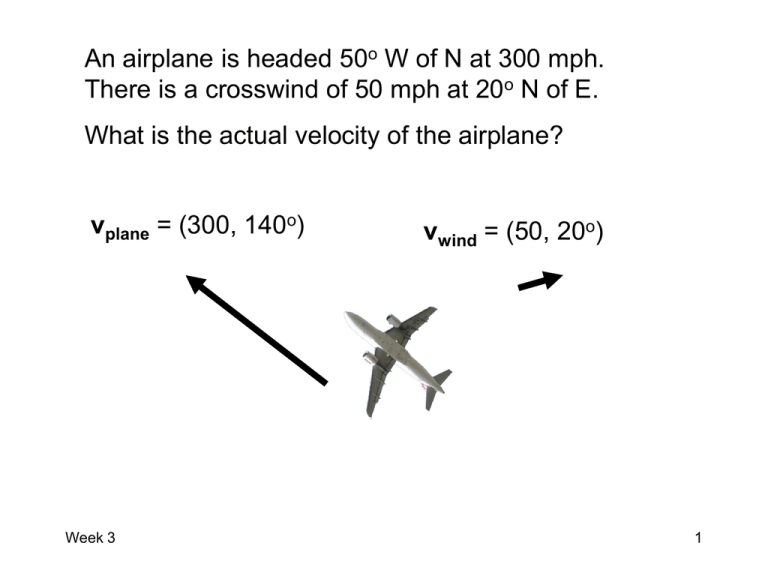
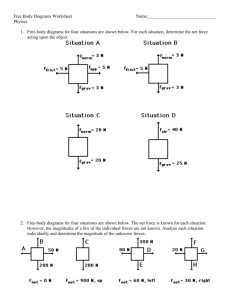
An airplane is headed 50o W of N at 300 mph. There is a crosswind of 50 mph at 20o N of E. What is the actual velocity of the airplane? vplane = (300, 140o) Week 3 vwind = (50, 20o) 1 For this motion, draw • A motion diagram with velocity and acceleration vectors • Graphs of •x • vx • ax •y • vy • ay You can neglect air resistance Week 3 2 Week 3 3 A man is shot out of a cannon at a 40o angle at 30.0 m/s. What is the man’s maximum altitude above the crowd? Week 3 4 A man is shot out of a cannon at a 40o angle at 30.0 m/s. How long is the man in the air? Week 3 5 A man is shot out of a cannon at a 40o angle at 30.0 m/s. How far away should we put the net to catch him? Week 3 6 You’re a shot putter. You let go of the shot put 1.5m above the ground at a 42.5o angle with an initial speed of 10 m/s. How far will the shot put go before hitting the ground? Week 3 7 A bullet is shot horizontally from a rifle at 300 m/s and hits a tree 50 meters away. The person shooting is holding the gun 5 feet (1.5 meters) above the ground. How far from the ground is the bullet hole in the tree? Week 3 8 A rocket drifts sideways in outer space from point “a” to point “b” as shown. Starting at position “b”, the rocket’s engine is turned on and produces a constant thrust at right angles to the line “ab”. The constant thrust is maintained until the rocket reaches point “c” in space. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Which of the paths below best represents the path of the rocket between points “b” and “c”? QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Week 3 9 QUIZ! • Each group take a launcher and tape measure • Choose an angle and set your launcher to that angle. • If launcher has a piece of tape, vi = 6.7 m/s • If no tape, vi = 6.3 m/s • Calculate how far away you need to be to hit a target at the same height. • Turn in calculations when done and help other groups. • When all calculations are done, get ball, rod and safety glasses for launching. Week 3 10 Week 3 11 Week 3 12 Week 3 13 Week 3 14 Week 3 15 Draw a free-body diagram for the situation: A frog is sitting on a leaf. Week 3 16 Draw a free-body diagram for the situation: A roofer is standing on a roof. Week 3 17 Draw a free-body diagram for the situation: A bowling ball, thrown by Barack Obama, rolls down the alley at a constant velocity. Week 3 18 Draw a free-body diagram for the situation: A person is falling off a cliff. Week 3 19 Draw a free-body diagram for the situation: The space shuttle is lifting off. Week 3 20 Draw a free-body diagram for the situation: A kid is speeding up as he goes down a big slide. Week 3 21 Week 3 22 LAB 3 OBJECTIVES • To develop a method for measuring forces reliably. • To learn how to use a force probe to measure force. • To explore how the motion of an object is related to the forces applied to it. • To find a mathematical relationship between the force applied to an object and its acceleration. Week 3 23 You’re pulling your kid sister in a wagon and she wants you to go faster. Graph the wagon’s position, velocity, acceleration and net force vs time as you make the wagon speed up. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Week 3 24