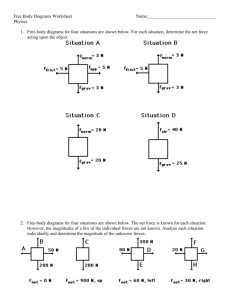
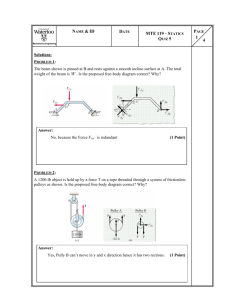
Lecture-18 - KFUPM Open Courseware
advertisement

COURSE: CE 201 (STATICS) LECTURE NO.: 18 FACULTY: DR. SHAMSHAD AHMAD DEPARTMENT: CIVIL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY: KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM & MINERALS, DHAHRAN, SAUDI ARABIA TEXT BOOK: ENGINEERING MECHANICS-STATICS by R.C. HIBBELER, PRENTICE HALL LECTURE NO. 18 EQUILIBRIUM OF RIGID BODIES Objectives: ► To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body ► To introduce the concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body LAWS OF EQUILIBRIUM It is necessary and sufficient condition for the equilibrium of rigid bodies that the summation of forces is equal to zero and that moments taken about any point inside or outside the body are zero. CONDITIONS FOR RIGID BODIES EQUILIBRIUM Let us consider various forces acting on a rigid body as shown in the following figure: According to the law of equilibrium, we have following conditions for the equilibrium: ΣF = 0 ΣMo = 0 FREE BODY DIAGRAMS: SUPPORT REACTIONS FREE BODY DIAGRAMS: EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FORCES • Only show the external forces, F, on the FBD because the net effect of the internal forces, f, is found to be zero • If a portion of the body is separated for drawing the FBD, show the internal forces also at the cut section FREE BODY DIAGRAMS: WEIGHT AND THE CENTER OF GRAVITY • Apply the weight, W, of a body at its center of gravity, G • For a uniform body, the G is located on its geometric center or centroid FREE BODY DIAGRAMS: DRAWING PROCEDURE • Draw outlined shape • Show all forces • Identify each loading and give dimensions PROBLEM SOLVING: Example # 1 Draw the free-body diagram of the 50 Kg paper roll, which has a center of mass at G and rests on the smooth hauler. Explain the significance of each force, acting on the diagram. PROBLEM SOLVING: Example # 1 The free-body diagram of the paper roll is drawn as shown below: In the free-body diagram: G B F 60 o 30o A F B A 50 kg Free-body diagram of the paper roll FA = reaction of the blade at A FB = reaction of the blade at B 50 kg = weight of the paper roll concentrating at the centroid (G) of the paper roll. PROBLEM SOLVING: Example # 2 Draw the free-body diagram of member AB, which is supported by a roller at A and a pin at B. Explain the significance of each force, acting on the diagram. PROBLEM SOLVING: Example # 2 The free-body diagram of member AB is drawn as shown below: 800 llb-ft A 60o FA 30o 4ft 8ft 390lb 13 12 5 B FHB FVB Free-body diagram of member AB In the free-body diagram: FA = Reaction of roller support at A. FHB = Horizontal reaction of pin support at B FVB = Vertical reaction of pin support at B 390lb = Inclined external force on the member. 800lb-ft = Counterclockwise external couple on the member PROBLEM SOLVING: Example # 3 Draw the free-body diagram of the crane boom AB which has a weight of 650 lb and center of gravity at G. The boom is supported by a pin at A and cable BC. The load of 1250 lb is suspended from cable attached at B. Explain the significance of each force, acting on the diagram. PROBLEM SOLVING: Example # 3 TBC 13 12 5 G FHA A ft 18 B 60o ft 12 1250 lb 650 lb FVA Free-body diagram of the crane boom AB FHA & FVA = reactions of pin support at A 650 lb = Weight of the crane boom 1250 lb = load suspended from cable at B TBC = Tension in cable BC PROBLEM SOLVING: Example # 4 Draw the free-body diagram of the spanner wrench subjected to the 20 lb force, as shown in the following figure. The support at A can be considered a pin, and surface of contact at B is smooth. Explain the significance of each force, acting on the diagram. PROBLEM SOLVING: Example # 4 FVA A FHA inch 1 20 lb B FB 1 inch 6 inch FHA & FVA = Horizontal and vertical reaction at pin support ‘A’ FB = Reaction at contact point B 20 lb = Vertical force on the spanner wrench Multiple Choice Problems 1. The number of unknown to be shown in the free-body diagram of member AB, as shown in the following figure, would be: (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 Ans: (c) Feedback: The hinge support at A will have two reactions and roller support at B will have one reaction. Multiple Choice Problems 2. The number of unknown to be shown in the free-body diagram of member AB, as shown in the following figure, would be: (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 Ans: (c) Feedback: The hinge support at A will have two reactions and the rope at B will have tension.