Gas Laws
advertisement

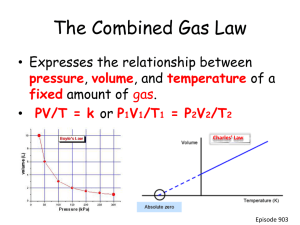
Gas Laws REVIEW GAME Question 1 A 4.3 liter tank of hydrogen is at a pressure of 6.2 atmospheres. What volume of hydrogen will be available if the hydrogen is used at pressure of 0.48 atmospheres? Boyle’s Law (4.3)(6.2) = 0.48V2 V2 = 56 L Question 2 What mass of oxygen gas must be placed in a container with a volume of 123.0L to produce a pressure of 1.87 atmospheres at 28.0°C? Ideal Gas Law 1.87(123) = n(0.0821)(301) n = 9.3 mol x 32 = 298 g Question 3 What is the pressure of 20.9 grams of neon gas at -19°C in a rigid container whose volume is 19.0 L? Ideal Gas Law 20.9 g Ne / 20 = 1.045 mol P(19) = 1.045(0.0821)(254) P = 1.2 atm Question 4 A 4.45 L balloon at 14°C contains carbon dioxide gas. If the balloon is taken outside where the temperature is -22°C, what volume will the balloon occupy? Charles Law 4.45 / 287 = V2 / 251 V2 = 3.9 L Question 5 A gas occupies a volume of 0.65 L at 118.3 kPa and a temperature of 0.00°C. What volume will the gas occupy at 2.50 atm and 50.0°C? Combined Gas Law 118.3 kPa x (1 atm/101.325 kPa) = 1.17 atm 1.17(0.65)/273 = 2.5V2/323 V2 = 0.36 L Question 6 A sample of gas occupies 25 mL at -142°C. What volume does the sample occupy at 65°C? Charles 25/131 = V2/338 V2 = 65 mL Question 7 When a container is filled with 6.000 grams of H2, 64.00 grams of O2, and 28.00 grams of N2, the pressure in the container is 5412 kPa. What is the partial pressure of O2? Dalton’s Law 6 g H2/2 = 3mol 64g O2/32 = 2mol 28 g N2/28 = 1mol 3+2+1 = 6 total moles PO2 = 2/6(5412) = 1804 kPa Question 7.5 Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2 How many grams of magnesium would I have to start with to make 3.5L of hydrogen gas at 130 kPa and 50. degrees celsius? 130(3.5) = n (8.314)(323) n = 0.17 mol H2 x 1/1 x 24.3 = 4.1 g Question 8 What is the volume occupied by 71.0 grams of chlorine gas at STP? Ideal Gas Law 71 g Cl2 / 71 = 1 mol 1V = 1(0.0821)(273) V = 22.4 L Question 9 A rigid container of O2 has a pressure of 185 kPa at a temperature of 458 K. What is the pressure at 283 K? Gay Lussac’s Law 185/458 = P2 / 283 P2 = 114 kPa Question 10 An unknown gas moves three times as fast as sulfur dioxide gas. What is the mass of the unknown gas? Su = 3 mu = ? Sso2 = 1 mso2 = 64 1/3 = Sqrt(m/64) m = 7.1 g/mol Question 11 How many moles of N2 are in a flask with a volume of 125 mL at a pressure of 2550 mm Hg and a temperature of 300.0 K? Ideal Gas Law 2550 mm Hg ( 1 atm / 760 mm Hg) = 3.36atm 3.36 (0.125) = n (0.0821) ( 300) 0.0171 mol N2 Question 12 The volume of a gas is 125 mL at 254 kPa pressure. What will the volume be when the pressure is reduced to 1.78 psi, assuming the temperature remains constant? Boyle’s Law 254 kPa ( 14.7psi / 101.325 kPa) = 36.85 psi 36.85(125) = 1.78V V = 2590 mL Question 13 A mixture of gases at a total pressure of 95 kPa contains N2, CO2, and O2. The partial pressure of CO2 is 24 kPa and the partial pressure of the N2 is 48 kPa. What is the partial pressure of the O2? Dalton’s Law 95 = 24 + 48 + Po2 Po2 = 23 kPa Question 14 A gas, collected over water, has a measured pressure of 1.23 atm and has a volume of 590 mL at a temperature of 47°C. What volume will the dry gas occupy at 25°C and standard pressure? Dalton and Combined 1.23 atm (101.325 kPa / 1atm ) = 124.6 kPa 124.6 kPa = Pgas + 10.62 Pgas = 113.98 kPa 113.98(590) / 320 = 101.325(V2) / 298 620 mL Question 15 Nitrogen gas diffuses into an empty container at a rate of 254 m/s. At what velocity will carbon monoxide gas move at the same temperature? Graham VCO / 254 = Sqrt (28/28) VCO = 254 m/s Question 16 A gas initially is present, in a balloon, at 25°C under 1 atmosphere of pressure. The volume of the gas under these conditions is 2.5L. What will be the new volume of the gas if it is taken outside on a hot day, where the temperature is 85°C and the pressure is 1.08 atmospheres? Combined 1(2.5)/298 = 1.08V2/358 V2 = 2.8 L Question 17 93.0 mL of O2 gas is collected over water at 0.930 atm and 10.0°C. What would be the volume of this dry gas at standard conditions? Dalton and Combined 0.930 atm x (101.325 kPa / 1atm) = 94.23 kPa 94.23 kPa = Pgas + 1.2281 Pgas = 93 kPa 93(93)/283 = 101.325V2/273 V2 = 82.3 mL Question 18 If 9.0 moles of nitrogen gas will fill a balloon that is 2.0 L in volume at 293 K, what volume will 28 moles of nitrogen gas fill at the same temperature? Avogadro’s Law 2/9 = V2/ 28 6.2 L Question 19 A large cylinder of He gas, such as that used to inflate balloons, has a volume of 25.0 L at 22°C and 5.6 atm. How many grams of He are in such a cylinder? Ideal 5.6(25) = n(0.0821)(295) 5.78 mol x 4 = 23 g Question 20 I begin with 460 mL of oxygen gas at a pressure of 740 mm Hg. How many liters of gas are present at standard pressure? Boyle 740(460) = 760(V2) V2 = 450 mL Question 21 Calculate the pressure of a gas whose temperature is increased from 15°C to 25°C and whose original pressure is 0.75 atm. Gay Lussac .75/288 = P2/298 P2 = 0.78 atm Question 22 A sample of gas at standard temperature and pressure is put into an expandable container. The original volume of the gas is 250 mL. What is the new volume if the gas is cooled to -15°C and the pressure is increased to 780 mm Hg? Combined (760)(250)/273 = 780V2/258 V2 = 230 mL Question 23 A balloon is filled with 150. mL of carbon dioxide gas at 900. mm Hg and 25.0°C. If the pressure is held constant, what will the new volume be if the temperature is raised to 75.0°C? Charles 150/298 = V2/348 V2 = 175 mL Question 24 Sulfur dioxide gas can move with a velocity of 150 m/s. How fast will carbon dioxide gas move at the same temperature? Graham V1/150 = Sqrt(64/44) 180 m/s Question 25 6 moles of nitrogen gas is placed in a 3 L container. What volume will 18 moles of gas occupy under the same conditions Avogadro 3/6 = V2/18 9 L Question 26 40.0g of neon gas is put into a 500. mL container at 15.0°C. What is the pressure within the container in kPa? Ideal 40 g Ne / 20 = 2 mol P(.5) = 2(8.314)(288) 9580 kPa Question 27 If a gas begins at a temperature of 27°C and a pressure of 150 kPa, what will the new pressure be when the temperature is raised to 50.°C? Gay Lussac 150/300 = P2/323 160 kPa Question 28 Hydrogen gas moves with a velocity of 400. m/s at 25°C. What is the mass of a gas that moves at 250. m/s at the same temperature? Graham 400/250 = Sqrt(m2/2) 5.12 g/mol Question 29 Oxygen gas is collected over water at 18°C at a pressure of 800. mm Hg and a volume of 100. mL. What is the volume of the dry gas at STP? Dalton and Combined 800 mmHg x (101.325 kPa/760 mmHg) = 106.7 kPa 106.7 = Pgas + 2.0644 104.6 kPa 104.6(100)/291 = 101.325V2/273 V2 = 97 mL Question 29 6Li + N2 2Li3N I have 40.0 grams of lithium metal. How many liters of nitrogen gas will react with it at 230. kPa and 17.0 degrees celsius? 40g/7 x 1/6 = 0.95 mol 230(v) = 0.95(8.314)(290) V = 9.95 L I have 25.0 L of nitrogen gas at 1.34 atm and 80.0 degrees celsius. How many grams of Li3N can I make? 1.34(25) = n (0.0821)(353) n = 1.15 mol N2 x 2/1 x 35 = 80.5 g Question 30 I have 80. grams of carbon monoxide gas, 55 grams of dinitrogen monoxide gas, and 100. grams of diphosphorus pentoxide gas. The total pressure of the mixture of gases is 1.67 atm. What is the partial pressure of each gas? Dalton’s Law 80 g CO / 28 = 2.86 mol 55 g N2O / 44 = 1.25 mol 100 g P2O5 / 142 = 0.70 mol TOTAL MOLES = 4.81 moles PCO = 2.86/4.81*(1.67) = 0.99 atm PN2O = 1.25/4.81*(1.67) = 0.43 atm PP2O5 = 0.70/4.81*(1.67) = 0.24 atm