The Combined Gas Law
advertisement
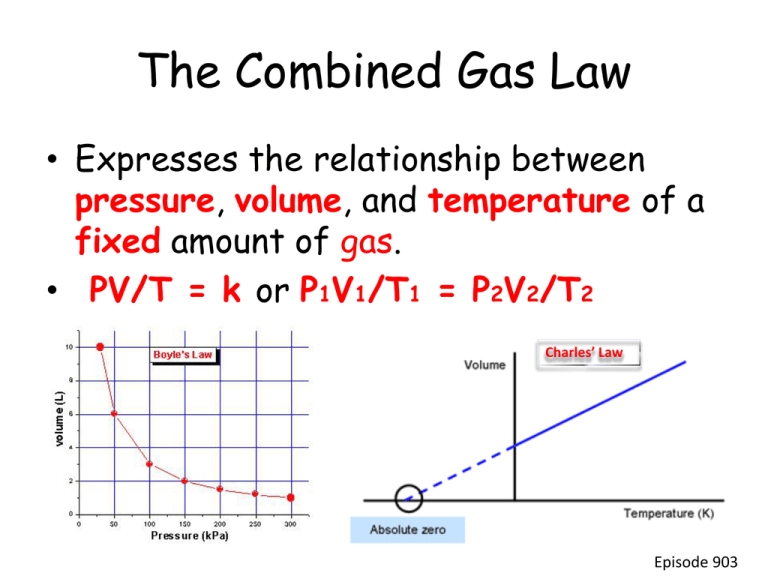
The Combined Gas Law • Expresses the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature of a fixed amount of gas. • PV/T = k or P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2 Charles’ Law Episode 903 • Ex: A sample of gas has a volume of 201 L when its temperature is 293 K and its pressure is 224 mm Hg. What volume will the gas occupy at STP? • Given: – – – – – – V1 = 201 L P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2 P1 = 224 mm Hg T1 = 293 K (224 mmHg)(201L)/293 K = (760 mmHg)V2/273 K V2 = ? P2 = 760 mm Hg (224mmHg)(201L)(273 K) = V2 T2 = 273 K (760mmHg)(293 K) 55 L= V2 Episode 903 Diffusion • The spontaneous spreading or mixing of a substance. Graham’s Law of Diffusion • Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, gases diffuse at a rate inversely proportional to the square root of their density (or molar mass). • v1/v2 or d2/d1 or m2/m1 Episode 903 Ideal Gas Equation • PV = nRT • New variables – n = amount of gas in moles – R = Universal Gas Constant • • • • • • Proportionality constant value depends on units used for pressure and volume value of R when using kPa and liters R = 8.314 kPa•L/mol•K Value of R when using atm and liters R = 0.0821 atm•L/mol•K Episode 903 Ex: The average lung capacity for a female student is 3.9 L. At normal body temperature, 37⁰C, and 110 kPa, how many moles of air could her lungs hold? Given: P = 110 kPa V = 3.9 L T = 37 ⁰C (310 K) n=? R = 8.314 kPa•L/mol•K PV = nRT (110 kPa)(3.9 L) = n(8.314 kPa•L/mol•K)(310 K) 0.17 mol = n Episode 903 Avogadro’s Law • Equal volumes of different gases under the same conditions have the same number of particles. • Conversely, if samples of different gases at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of particles, then the volumes of all the samples must be equal. • At STP, one mole of any gas occupies a volume of 22.4 Liters. • 22.4 Liters is the molar volume of a gas. Episode 903 Ex: 3.2 moles of KNO3 are heated, producing O2 and KNO2. Calculate the volume of O2 in liters, that could be obtained at STP. 2KNO3 O2 + 2KNO2 ? Liters O2 = 3.2 moles KNO3 3.2 mol KNO3 1 mol O2 22.4 L O2 2 mol KNO3 1 mol O2 = 36 L O2 Episode 903 Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures • The pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the individual pressure of each gas alone. • PT = P1 + P2 + P3 + … Episode 903 Ex: Oxygen gas has been collected over water at a total pressure of 95.0 kPa and a temperature of 25⁰C. What is the pressure of the dry oxygen gas? PT = PH2O + PO2 PT = 95.0 kPa 95.0 kPa = 3.17 kPa + PO2 PH2O @ 25⁰C = 3.17 kPa 91.8 kPa = PO2 (Look on water vapor chart) Episode 903











