File
advertisement

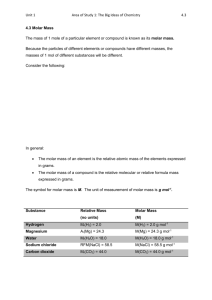
Quiz 1. In an experiment 1.500 g of Mg was burnt to heat up 125 g of water, the Initial temperature for water is 25.0oC, the final temperature is 72.3oC. Calculate the heat released by the magnesium 2. Would the reaction release or take in heat if the energy in the products is less than the energy in the reactants. 3. Would the reaction release or take in heat if the energy in the products is more than the energy in the reactants. 4. Define activation energy. Calculating energy change • If the temperature change of a known mass of water in the calorimeter is measured then the E value for the water is given by q = mass x c x T where M= mass of the substance T = final temp - initial temp C= Specific heat capacity (for water is 4.18 J/goC) Answers In an experiment 1.500 g of Mg was burnt to heat up 125 g of water, the Initial temperature for water is 25.0oC, the final temperature is 72.3oC. Calculate the heat released by the magnesium 72.3 – 25.0 = 47.3oC 125mL = 125g E = 4.18 x 125 x 47.3 = 24714.25J Or 25 kJ Answers 1. Would the reaction release or take in heat if the energy in the products is less than the energy in the reactants. Release energy 1. Would the reaction release or take in heat if the energy in the products is more than the energy in the reactants. Take in energy 1. Define activation energy. The energy required to start a reaction. Learning Objective: Explain the significance of Avagadro’s number (N). The Mole and Stoichiometry A mole is defined as the number of atoms present in exactly 12.00 g of the 12C isotope. The number of atoms present in such a sample is 6.02 X 1023 and is called Avogadro’s number (N). The mole then is the measure of the amount of a substance. The mole has the symbol n and units of mol. Learning Objective: Define the term molar mass (M) Molar Mass The molar mass is simply the mass of one mole of an element or compound, it’s unit is g mol-1and it has the same numerical value as the relative molecular or atomic mass. The molar mass, mass and moles are related by the following equation. m n M Work out the molar mass of the following. a) CaSO4 b) Zn(NO3)2 c) Fe3(PO4)2 Work out M of the following. a) CaSO4 136 g mol-1 b) Zn(NO3)2 127 g mol-1 c) Fe3(PO4)2 358 g mol-1 Learning Objective: Use n = m/M equation to inter-convert between moles, mass and molar mass. Molar Mass, mass and the mole Molar mass, the mole and mass are related to each other by the formula. mass (g) moles (mol) m n M molar mass (g mol-1) Example How many moles of water (H2O) are there in 36 g of water? From the periodic table we can work out the molar mass of water. M(H2O) = 18 g mol-1. Therefore n(H2O) = 36 g/18 g mol-1 = 2 mol Learning Objective: Use n = m/M equation to inter-convert between moles, mass and molar mass. If we rearrange the formula we can work out the mass if we know the moles of a substance. mnxM Example What is the mass of 5 mol of water? From the periodic table we can work out the molar mass of water. M(H2O) = 18 g mol-1. Therefore m(H2O) = 5 mol x 18 g mol-1 = 90 g Enthalpy is measured in J per mole The energy calculated must be divided by the amount of reactant. E.g. - 2 moles of fuel gave out 1000KJ of energy, how much energy did 1 mole of fuel give out? - 5 moles of sugar gave out 500KJ of energy, how much energy did 1 mole of sugar give out? -1 Exercise 1: You have burnt 10g of sugar ( C6H12O6 ) to heat up 20mLs of water by 50 degrees. How much energy did 1 mole of sugar give out? (enthalpy change of burning sugar). The specific heat capacity for water is 4.18 J/gC. 1. Work out the total amount of energy that’s absorbed by the water. 2. Work out the number of moles in 10g of sugar. 3. Work out how much energy did one mole of sugar give out. Exercise 1: You have burnt 10g of sugar ( C6H12O6 ) to heat up 20mLs of water by 50 degrees. How much energy did 1 mole of sugar give out? (enthalpy change of burning sugar). The specific heat capacity for water is 4.18 J/gC. 1. Work out the total amount of energy that’s absorbed by the water. 20x4.18x50=4180J 2. Work out the number of moles in 10g of sugar. 10/180=0.05mol 3. Work out how much energy did one mole of sugar give out. 4180 / 0.05mol = 83600 J/mol Exercise 1: Calculate the value of rH in kJ mol -1 for the dissolving of solid NaOH in water, if it is found that when 10 g of NaOH is dissolved in 250 mL water the temperature of the water increases from 25.0 oC to 29.8 oC. First T 29.8 - 25.0 = 4.8 Then energy change 4.8 x 4.18 x 250 = 5016 Now work out amount of NaOH 10g ÷ 40g/mol = 0.25 mol Enthalpy change 5016 ÷ .25 = 20064 Jmol-1 = 20.1kJmol-1 Exothermic so -20.1kJmol