Thermal Energy - Physical Science
advertisement

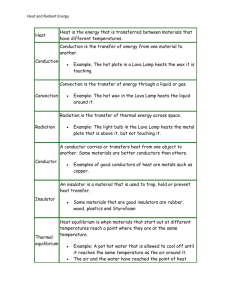
Heat, Temperature, and Review Thermal Energy • Total potential and kinetic energy associated with the random motion and arrangement of the particles of a material! –Not concerned with the kinetic energy of the object itself!! Heat • Thermal Energy that is absorbed, given up, or transferred from one substance to another. – It is thermal energy on the move!! Temperature • Measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter!! Relationship between Heat and Temperature: Which beaker is hotter? Which beaker gives off more heat? 80 oC 80 oC Which could melt more ice? Temperature is the same, amount of heat is different!! Which has a higher temperature? 10 oC 30 oC A B 50 oC 80 oC C D Which gives off more heat? 10 oC A 10 oC B 10 oC C 10 oC D Heat Flow • Heat always flows from a substance with a high temperature to a substance with a low temperature even if lower temperature substance has more thermal energy!! Which direction will heat flow? A. A to B B. B to A C. Neither D. Both A to B and B to A In which choice will heat flow fastest from Y to X? A B C D In which choice will heat flow fastest from X to Y? A B C D Specific Heat • Heat required to change the temperature of a substance. • Different substances have different specific heats. – They conduct heat at different rates!! – Consider Sand and Water!!! – Think about the beach! – Land breezes and Sea breezes!! Specific Heats of some common substances: Substance Specific Heat (J/g oC) Water Iron Lead Silver Copper Aluminum Alcohol Mercury Platinum Ammonia Zinc 4.18 .450 .13 .245 .390 .900 2.43 .14 .13 4.71 .39 The higher the specific heat, the more heat required to change temperature!! Things with high specific heats take a long time to heat up and a long time to cool down!! Things with a low specific heat, get Hot fast, but also cool fast!! Heat required to change the temperature can be determined by: Where: Q = heat energy in Joules(J) m = mass in grams(g) CP = Specific Heat Capacity(in J/g*oC) DT = Temperature in oCelsius(oC) Ex. How much heat is required to change the temperature of a 250 g sample of water from 15 oC to 60 oC? Given: m = 250 g o DT = 45 C Cp = 4.18 Q = ??? Q = 250 g(4.18)(45 oC) Q = 47,025 J Ex. How much heat is required to change the temperature of a 495 g sample of copper from 60 oC to 240 oC? Given: m = 495 g o DT = 180 C Cp = .390 Q = ??? Q = 495 g(.390)(180 oC) Q = 34,749 J Ex. How much heat must be removed from a 210 g iron bar to reduce its temperature from 150 oC to 25 oC? A. B. C. D. 16,536.5 J 11,812.5 J 9,450.5 J 5,480.5 J Given: m = 210 g DT = 125 oC Cp = .450 Q = ??? Q = 210 g(.450)(125 oC) Q = 11,812.5 J How does heat move between substances: • How many different ways are there to cook a hotdog? 3 • Name them: 3 Ways to Cook a Hotdog!!! Convection Conduction Radiation 3 Ways to Transfer Heat 1. Conduction---direct contact 2. Convection—transfer of heat in liquids and gases!! 3. Radiation—transfer through empty space!! Conduction Convection Radiation • Transferring Heat Energy Wst. • Heat Equation Wst.