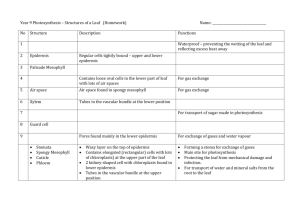
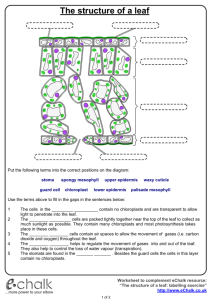
Epidermis
advertisement

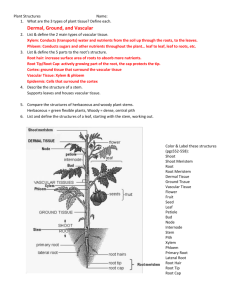
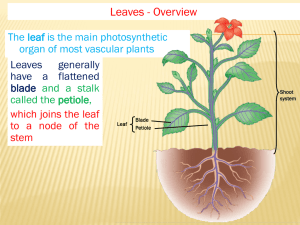
Leaf Anatomy Cross Section of a Leaf Leaf Tissues A leaf is considered a plant organ and typically consists of the following tissues: An epidermis that covers the upper and lower surfaces An interior parenchyma called the mesophyll An arrangement of veins (the vascular tissue). Epidermis The epidermis is the outer one- or multi-layered group of cells covering the leaf. The epidermis has several functions: - protection against water loss (a vaxy cuticle) - regulation of gas and water vapor exchange (stomata) - secretion of metabolic compounds - absorption of water (in some species) . A multi-layered epidermis Mesophyll means "middle of the leaf", i.e. the tissues of a leaf that are located in between the layers of epidermis and carry on photosynthesis. The mesophyll of the leaf consists of parenchyma tissue. Since the mesophyll cells contain chloroplasts the tissue is also referred to as chlorenchyma . Chlorenchyma cell Functions of the Mesophyll In most dicot leaves the mesophyll is differentiated into palisade parenchyma (A) and spongy parenchyma (B). The palisade cells are responsible for photosynthesis because they contain chloroplasts. The spongy mesophyll, together with the intercellular air spaces, allow for the interchange of gases Vascular Tissue Vascular tissue is a complex tissue. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients. Vascular tissue is organized into discrete strands called vascular bundles. Cross Section of Papyrus Leaf e epidermis bb bulliform cells(they cause the leaf to roll up in response to low water availability ) skl sclerenchyma cs vascular bundle Clivia leaf cross section silná kutikula, ztlustlá epidermis The epidermis has a thick cuticle. European Yew (Taxus baccata) Cross Section of a Needle X – xylem f - phloem skl – sclerenchyma e – epidermis ku – cuticle ka – cambium pp – palisade parenchyma hp – spongy parenchyma Rubber fig (Ficus elastica) Cross Section of a Leaf pp - palisade parenchyma e - epidermis cs - vascular bundle hp - spongy parenchyma ku - cuticle st - stoma Resources Internet: http://www.ueb.cas.cz/laboratory_of_pollen_biology/pdf_subo r/anatomie_list.pdf http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/List#Anatomick.C3.A1_stavba_lis tu http://botany.upol.cz/atlasy/anatomie/anatomieCR28.pdf commons.wikimedia.org http://www.uri.edu/cels/bio/plant_anatomy/ www.sci.muni.cz/~anatomy/leaves/html/papyrus_1.htm Thanks for your attention Lenka Rydvalova