leaf
advertisement
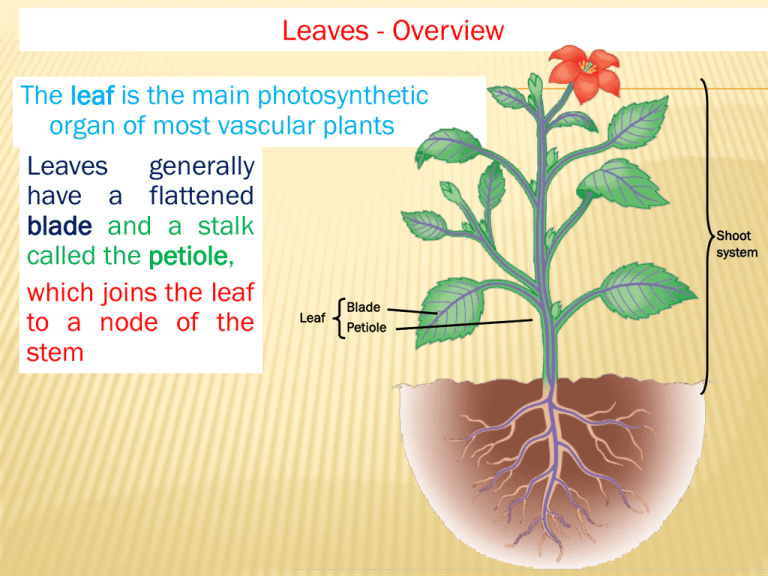
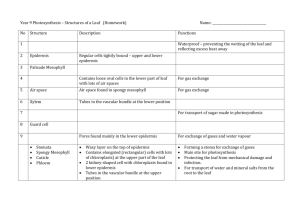
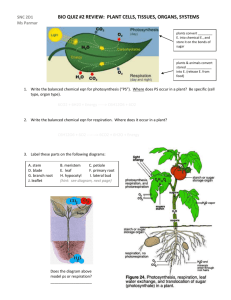
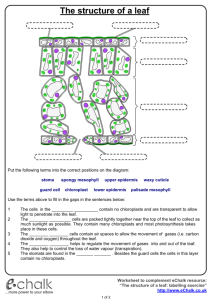
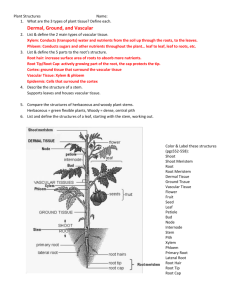
Leaves - Overview The leaf is the main photosynthetic organ of most vascular plants Leaves generally have a flattened blade and a stalk called the petiole, which joins the leaf Blade Leaf to a node of the Petiole stem Shoot system Leaves - Comparisons Monocots and Dicots differ in the arrangement of veins, the vascular tissue of leaves Most Dicots have branch-like veins and palmate leaf shape Monocots have parallel leaf veins and longer, slender blades LEAF PARTS 1. Stoma (stomata) – small pores that act as a doorway for gases involved in photosynthesis (found mainly on the underside of leaves). 2. Guard Cells – Cells that regulate the opening of the stomata. 3. Lower and upper epidermis – outer layer of a plant that serves for protection, like skin. LEAF PARTS CONTINUED… 4. Palisade layer – layer where majority of chloroplasts are found (site of photosynthesis). 5. Spongy layer – cells surrounded by air spaces; allow water, CO2 and O2 to diffuse during photosynthesis. 6. Waxy layer/cuticle – protects leaf from water loss and from feeding insects. Leaves – Structure and Development • Most dicots have 2 types of mesophyll – Palisade mesophyll high photosynthesis – Spongy mesophyll air spaces for gas & water exchange • Monocot leaves have 1 type of mesophyll CROSS SECTION OF A LEAF Leaves – Structure and Development • Leaves are several layers thick – each with different cell types Epidermis Leaves • Leaf epidermis contains stomata - allow CO2 exchange • Stomata flanked by two guard cells, control open vs. closed • The ground tissue in a leaf, called mesophyll, fills the middle Guard cells Key to labels Vascular Cuticle Sclerenchyma fibers 50 µm Dermal Ground Stomatal pore Epidermal cell Stoma (b) Surface view of a spiderwort (Tradescantia) leaf (LM) Upper epidermis Palisade mesophyll 100 µm Spongy mesophyll Bundlesheath cell Lower epidermis Cuticle Xylem Vein Phloem (a) Cutaway drawing of leaf tissues Guard cells Vein Air spaces (c) Cross section of a lilac (Syringa)) leaf (LM) Guard cells VASCULAR TISSUE Xylem – cells that carry water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves. Phloem – cells that carry food (sugar) that is made in the leaves to all parts of the plant. Use: Collectively the vascular tissue, xylem and phloem create a vein or vascular bundle to transport material in plants. STOMA OPEN VS. CLOSED Open – with light and when guard cells are filled with water. Closed – without light and when guard cells are lacking water (dehydrated). Why is it important to have stomata open? Closed vs. Open Question time????????