mcm - Philadelphia University Faculty Websites

Opportunities and Challenges for
Textile Reinforced Composites
Christopher M. Pastore
Philadelphia University
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
Textile Reinforced Composites
Fiber reinforced composites whose repeating volume element (RVE) is characterized by more than one fiber orientation.
Formed with hierarchical textile processes that manipulate individual fibers or yarn bundles to create an integral structure.
It is possible to join various sub-assemblies together to form even more complex structures.
Hierarchy of Textile Materials
Perceived Benefits
Textiles are considered to have significant cost savings compared to tape lay-up.
Individual layer of fabric is much thicker than tape.
Fewer lay-up steps are necessary to create the final structure.
Formed from dry fiber and infiltrated with resin in a secondary operation.
Handling and storage requirements of the material are reduced compared to prepreg.
A single product is suitable for a variety of matrix materials, reducing inventory and manufacturing costs.
2D and 3D Textiles
Textiles are frequently classified as either 2D or 3D.
Clearly all fabrics are 3D, but 2-D implies that the fabric is fundamentally thin.
That is, the thickness of the fabric is formed by only 2 or 3 yarns in the thickness direction.
A 3-D fabric can have substantial thickness, limited only by the machine, not some fundamental physical phenomenon.
Types of Textiles
Direct-formed fabrics are those made directly from fibers.
Woven , knitted , and braided fabrics are made from manipulation of yarns.
These four classes represent the vast majority of fabrics used in composite materials.
woven fabrics are formed by inter-lacing yarns,
knitted by inter-looping yarns,
braided by inter-twining yarns, and
direct formed fabrics by inter-locking fibers.
Direct Formed Fabrics
Created directly from fibers without a yarn processing step involved.
No interlacing, intertwining, or interlooping of fibers within the structure.
These fabrics are called nonwovens in much of the literature, despite the obvious inadequacy of this term.
Direct Formed Fabrics
Generally there are 2 steps
First a web is constructed of fibers. This sets the distribution of inplane fiber orientation.
Next the web is densified. This typically involves through thickness entanglement or bonding.
Web formation
Opening process: mechanically separates the fibers.
Deposit fiber mass onto a belt, creating a continuous roll of lowdensity material
width of roughly 1-meter and a thickness 10-20 cm called a picker lap .
The fibers have a virtually uniform, random orientation in the plane, with substantial out of plane orientation.
To thin the picker lap, it may be passed through a card.
Individual fibers are mostly oriented in the direction of material flow through the machine.
This orientation allows the fibers to pack closer than previously resulting in a thickness reduction, increased density, and a preferred distribution of fiber orientations in the machine direction.
The resulting material is called a carded web.
Densification of web
The carded web may be used as input to the needle punch, or it may be cross-lapped first.
The cross-lapper places carded web transverse to the machine direction allowing the preferred fiber orientation to be in the cross direction.
Needle punch creates mechanical interlocking through barbed needles
Bonding can be done to chemically adhere the fibers
Adhesive application
Thermal bonding (sacrificial low melt fibers are pre-included in the web)
XYZ Orthogonal Nonwoven
Knitted Fabrics
There are two basic types of knitting - weft knitting and warp knitting.
They are distinguished by the direction in which the loops are formed.
Weft knitting, the most common type of knitting in the apparel industry, forms loops when yarns are moving in the weft direction, or perpendicular to the direction of fabric formation.
Warp knitting differs from weft knitting in that multiple yarns are interlooped simultaneously. A set of yarns are supplied from a creel or warp beam and interlooped in the cross (course) direction.
Jersey Knits
The simplest weft knit structure is the jersey.
Inherently bulky due to curvature of the yarn.
The “natural” thickness of a jersey knit fabric is roughly three times the thickness of the yarns, resulting in maximum yarn packing factors of 20-25%, and thus V f around 15%.
High extensibility (up to 100% strain to failure) which allows complex shape formation capabilities.
Rib Knits
In a rib knit structure it is possible to incorporate large yarns in the weft to create a weft inserted rib knit.
In such a way a “unidirectional” preform can be constructed. However it is difficult to achieve fiber volume fractions greater than 30% in these structures due to the inherent bulkiness of the fabric.
Conformable Rib Knit
Warp Knits
In the WIWK, the load bearing yarns are locked into the structure through the knitting process
Braiding
Biaxial braided fabrics may incorporate a longitudinal yarn creating a triaxial braid.
The braided fabric is characterized mainly by the braid angle, q
, (10 ° - 80°).
Braids are tubular and frequently compared with filament winding. They have been shown to be cost competitive.
The braided fabric is flexible before formation, and thus the fabric can conform to various shapes. The braided fabric may be formed around a mandrel, and rather complex shapes can be formed.
Braiding
Braids are formed by a circular “maypole” pattern of yarn carrier motions
Types of 2D Braids
3D Braiding Machine
Woven Fabrics
Generally characterized by two sets of perpendicular yarns systems
One set is raised and lowered to make “sheds” (these are warp yarns)
The other set is passed through these sheds, perpendicular to the warp yarns (these are fill , or pick or weft yarns)
Elements of a loom
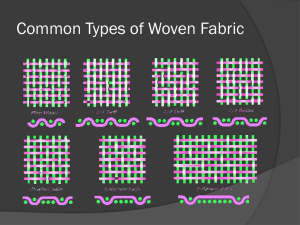
Woven Fabrics
The structure of the woven fabric is the pattern of interlacing between the warp and weft yarns
Yarns can “float”, or not interlace for some distance within a woven fabric
Basic weave structures
Crimp in Weaves
The crimp is defined as one less than the ratio of the yarn's actual length to the length of fabric it traverses.
Crimp levels influence fiber volume fraction, thickness of fabric, and mechanical performance of fabric.
High crimp leads to
Reduced tensile and compressive properties
Increased shear modulus in the dry fabric and the resulting composite
Fewer regions for localized delamination between individual yarns.
Applications of Weaves
Weaves can be formed into composites with fiber volume fractions as high as 65%.
High harness count satins – 8 and 12 –serve the role previously held by 0/90 tape lay-ups.
There is a significant cost benefit to using the fabrics in that much fewer layers need be applied because the woven fabric is usually many times thicker than the tape (depending on the yarns used in the fabric).
Layer-to-layer
XYZ
3D Weaves
Through thickness
Doubly Stiffened Woven Panel
Variations in Weave Design
If large yarns are used in the warp direction and small yarns are infrequently spaced in the weft direction, the resulting fabric resembles a unidirectional material.
Weaves can be formed with gradients in a single or double axis by changing yarn size across the width or length
Complex shapes can be achieved through “floating” and cutting yarns to reduce total number of yarns in some section of the part
Gradations through yarn size
Shape through floats
Issues with shaping woven fabrics
Tailoring the cross-section of a woven fabric will generally result in
a change in weave angle,
a change in the distribution of longitudinal, weaver, and fill, and
a change in fiber volume fraction in consequence to the change in thickness.
Some fiber volume fraction effects can be controlled by tooling. The tailoring occurs in a discrete manner, using individual yarns, whereas most tooling will be approximately continuous.
Example of single taper weave
Consider a tapered panel where gradation in thickness is achieved by changing yarn size/count across the width
Design of tapered woven panel
Pick count is constant, warps and wefts per dent are modified to taper
Z yarn path changes to accommodate the weave.
Number
14
13
12
11
10
9
18
17
16
15
6
5
4
3
2
1
8
7
Pick Columns per inch
Warp per dent
Picks per column
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31
Dent
Variation in Fiber Volume Fraction
60%
This variation in yarn packing results in variations in V f for the resulting composite.
Fiber
Volume
Fraction
58%
56%
54%
52%
50%
48%
46%
44%
42%
40%
0.000
Calculated
Target
0.500
1.000
1.500
Distance from Thin Edge (in)
2.000
2.500
Variation in weave angle
The weave angle will also change throughout
55 ° the width of the part due
50 ° to varying warp yarn count and part thickness.
45 °
Weave
Angle
40 °
35 °
30 °
25 °
0.0
Calculated
Target
0.5
1.0
1.5
Distance from Thin Edge (in)
2.0
2.5
Yarn Distributions
The distribution of warp, weft, and Z yarn will also vary throughout the part.
60%
55%
50%
45%
Yarn
Distribution
40%
35%
30%
25%
20%
15%
0.0
% Z
% Warp
% Fill
0.5
1.0
1.5
Distance from Thin Edge (in)
2.0
2.5
Variations in Modulus
All mechanical properties will vary throughout the part
10
Tensile
Modulus
(Msi)
8
6
14
12
4
2
0
0.0
E11 E22
0.5
1.0
1.5
Distance from Thin Edge (in)
2.0
E33
2.5