From Fibers to Fabric:
advertisement

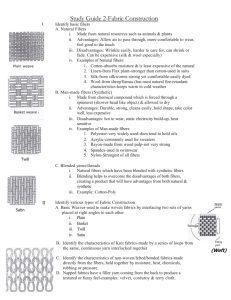
From Fibers to Fabric: Step by step process of the fiber to the yarn to the fabric. Types of Fibers Natural Fibers • Sources: –Animals –Plants Protein Fibers Cellulose Fibers Manufactured or Synthetic Fibers •Chemical or Protein Name Spandex •Generic Name •Trade Name Lycra® Types • Acetate • Acrylic • Nylon • Polyester •Rayon •Spandex •Triacetate Yarns •Fibers overlapped and twisted together Types • Spun • Monofilament • Multifilament Twist • amount varies and increases strength • very low twist - just barely holds together • low twist - fluffy - weak • average twist for short fibers • high twist hard and compact Texture • given to manufactured fibers • adds bulk, stretch, less static Types of Texture Fabric Construction • woven of knit yarns • fibers matted together and glued Woven Fabrics Plain Weave Satin Weave Twill Weave Basket Weave Pile Weave Knits • Stretches • Returns to Original Shape • Wrinkle Resistant Warp Knits • vertical rows of loops - tricot jersey - lace - raschel knit Weft Knit • loops made as yarn added in crosswise direction – double knit – jersey – rib knit – pile knit jersey – velour – purl knit Non Woven • no grain • no stretch or give • requires special sewing techniques Non Wovens Fabric Finishes • changes fiber properties to create a better product Permanent Finish • heat set • improves fabric resistance to wrinkling • stains difficult to remove • no need to iron Shrinkage Resistant • reduce shrinkage Soil Release • aids in removing dirt, oil, and grease Flame Retardant • resists burning Dyeing • changes color of finished product • can be done at fiber, yarn, and fabric stage • printing is done at fabric stage only Care Labels • Law Required - Fiber Content - Care Instructions - Country of Origin Care Requirement • washing method • drying method • bleach type • iron temperature