Magnification and Size
advertisement

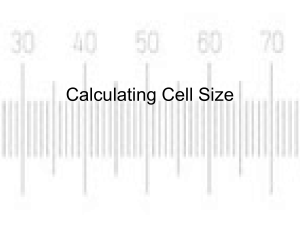
Magnification and Size Measuring biological specimens using millimetres as units SBI3U Body Tube Ocular lens (Eyepiece) Nosepiece Objectives Arm Stage Stage Clips Diaphragm Light Coarse Adjustment Fine Adjustment Base Always carry a microscope with one hand holding the arm and one hand under the What’s my power? To calculate the power of magnification, multiply the power of the ocular lens by the power of the objective. What are the powers of magnification for each of the objectives we have on our microscopes? Field of View (FOV) Field of View – the view you actually see when you look through a microscope Low Field of View (Low FOV) Low FOV = measured with a ruler on the microscope • Count the spaces you see • Count the halves as well • Here we see 5.5 spaces • So Low FOV = 5.5 mm Medium & High Field of View (FOV) Medium FOV = low FOV High FOV = low FOV X _MagnificationLOW MagnificationMEDIUM X _MagnificationLOW MagnificationHIGH REMEMBER…we only use a ruler for LOW FOV Let’s Practice If the low FOV = 2mm, low magnification is 4x, medium magnification is 10x and high magnification is 40x, calculate the high FOV. Let’s Practice If the low FOV = 2mm, low magnification is 4x, medium magnification is 10x and high magnification is 40x, calculate the high FOV. High FOV = 2mm x _____4x___ 40x = 2 mm x 0.1 = 0.2 mm or 200µm Let’s Practice If the low FOV = 2mm, low magnification is 4x, medium magnification is 10x and high magnification is 40x, calculate the high FOV. High FOV = 2mm x _____4x___ 40x = 2 mm x 0.1 = 0.2 mm or 200µm Specimen Size You can estimate specimen size using the field of view. For example, if your field of view is 200 µm, and the specimen takes up about a quarter of the space, you can estimate it to be about 50 µm. Drawing Magnification/Scale • When you are asked to draw what you see under the microscope, your drawings will be much larger than your specimen. You need to indicate approximately how much larger than life your drawings are. Magnification = drawing size Actual size or M= D A Drawing Magnification/Scale • e.g. a student, observing an amoeba under a magnification of 400X, calculates that it is about 50m long. If she then draws the amoeba 8 cm long, what is the magnification and scale of her drawing? Magnification = drawing size = 80000 µm Actual size 50 µm = 1600 X, and the scale is 1cm = 6.25 µm. To accurately measure the size of cellular structures we need a suitable scale: Ideally, we need a scale we can see directly alongside the cells we are observing: Start by putting a ruler under the microscope: Appearance of ruler at medium magnification Appearance of tissue at medium magnification Estimating cell size at medium magnification 12 1 mm 1mm / 12 cells = 0.083 mm 5 1mm / 5cells= 0.2 mm 1 mm Other units Diameter of field of view/mm No. of cells lengthways No. of cells widthways Mean length (mm) Mean width (mm) 1.00 5 12 0.2 0.083 1mm = 1000µm Mean length of cells = 0.2 x 1000 = 200µm Mean width of cells = 0.083 x 1000 = 83µm Calculating actual size: Calculating magnification & actual size: Calculating actual size: Calculating magnification: Calculating magnification & actual size: Calculating actual size: Drawing Magnification/Scale e.g. a student, observing an amoeba under a magnification of 400X, calculates that it is about 50m long. If she then draws the amoeba 8 cm long, what is the magnification and scale of her drawing? Magnification = drawing size = 80000 µm Actual size 50 µm = 1600 X, and the scale is 1cm = 6.25 µm.