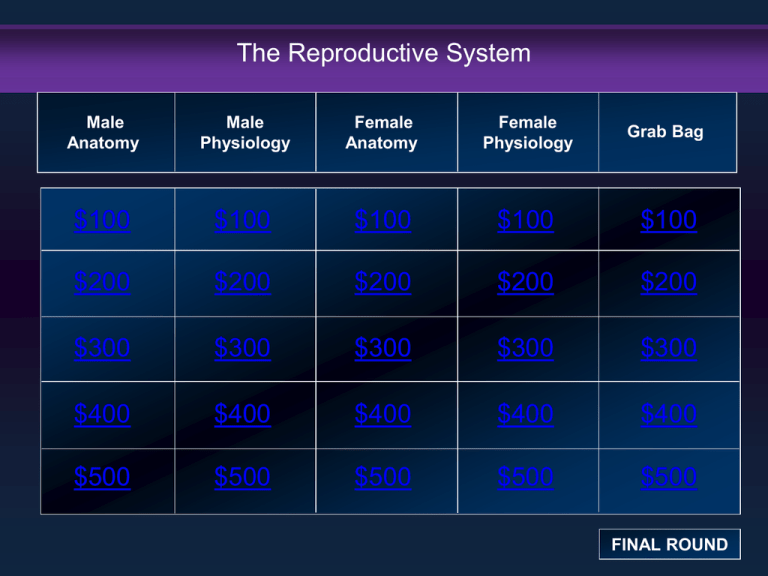
The Reproductive System
Male
Anatomy
Male
Physiology
Female
Anatomy
Female
Physiology
Grab Bag
$100
$100
$100
$100
$100
$200
$200
$200
$200
$200
$300
$300
$300
$300
$300
$400
$400
$400
$400
$400
$500
$500
$500
$500
$500
FINAL ROUND
Male Anatomy:
$100 Question
Sperm cells develop in this region of the
testis:
a. efferent ductules
b. interstitial cells (Leydig cells)
c. rete testis
d. seminiferous tubules
e. tunica albuginea
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Male Anatomy:
$100 Answer
Sperm cells develop in this region of the
testis:
a. efferent ductules
b. interstitial cells (Leydig cells)
c. rete testis
d. seminiferous tubules
e. tunica albuginea
BACK TO GAME
Male Anatomy:
$200 Question
All of the following are part of the
spermatic cord EXCEPT this:
a. testicular artery
b. lymphatic vessels
c. ductus (vas) deferens
d. ejaculatory duct
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Male Anatomy:
$200 Answer
All of the following are part of the
spermatic cord EXCEPT this:
a. testicular artery
b. lymphatic vessels
c. ductus (vas) deferens
d. ejaculatory duct
BACK TO GAME
Male Anatomy:
$300 Question
From the ejaculatory duct, sperm cells
travel directly into this:
a. seminal vesicle
b. prostatic urethra
c. spongy (penile) urethra
d. membranous urethra
e. ductus (vas) deferens
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Male Anatomy:
$300 Answer
From the ejaculatory duct, sperm cells
travel directly into this:
a. seminal vesicle
b. prostatic urethra
c. spongy (penile) urethra
d. membranous urethra
e. ductus (vas) deferens
BACK TO GAME
Male Anatomy:
$400 Question
These erectile columns form the dorsal
surface and sides of the penis:
a. corpus spongiosum
b. corpora cavernosa
c. crus of the penis
d. glans penis
e. root of the penis
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Male Anatomy:
$400 Answer
These erectile columns form the dorsal
surface and sides of the penis:
a. corpus spongiosum
b. corpora cavernosa
c. crus of the penis
d. glans penis
e. root of the penis
BACK TO GAME
Male Anatomy:
$500 Question
Given these cells:
1. primary spermatocytes
2. secondary spermatocytes
3. spermatids
4. spermatogonia
5. sperm cells
Arrange the cells in the order in which they
are produced during spermatogenesis.
a. 1,2,3,4,5
c. 3,1,2,4,5
ANSWER
b. 2,1,3,5,4
d. 4,1,2,3,5
BACK TO GAME
Male Anatomy:
$500 Answer
Given these cells:
1. primary spermatocytes
2. secondary spermatocytes
3. spermatids
4. spermatogonia
5. sperm cells
Arrange the cells in the order in which they
are produced during spermatogenesis.
a. 1,2,3,4,5
c. 3,1,2,4,5
b. 2,1,3,5,4
d. 4,1,2,3,5
BACK TO GAME
Male Physiology:
$100 Question
This is a function of FSH in the male:
a. inhibit progesterone
b. initiate testosterone production
c. increase protein synthesis
d. initiate spermatogenesis
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Male Physiology:
$100 Answer
This is a function of FSH in the male:
a. inhibit progesterone
b. initiate testosterone production
c. increase protein synthesis
d. initiate spermatogenesis
BACK TO GAME
Male Physiology:
$200 Question
The interstitial cells (cells of Leydig) of the
testes produce this:
a. seminal fluid
b. stereocilia
c. sperm cells
d. testosterone
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Male Physiology:
$200 Answer
The interstitial cells (cells of Leydig) of the
testes produce this:
a. seminal fluid
b. stereocilia
c. sperm cells
d. testosterone
BACK TO GAME
Male Physiology:
$300 Question
Testosterone has all of these effects on
males except:
a. hair growth stimulation
b. increased protein synthesis
c. increased metabolic rate
d. growth of corpus luteum
e. deepening of voice
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Male Physiology:
$300 Answer
Testosterone has all of these effects on
males except:
a. hair growth stimulation
b. increased protein synthesis
c. increased metabolic rate
d. growth of corpus luteum
e. deepening of voice
BACK TO GAME
Male Physiology:
$400 Question
This occurs in the male before puberty:
a. FSH levels are higher than after
puberty
b. LH levels are higher than after
puberty
c. GnRH release is inhibited by
testosterone
d. all of the above
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Male Physiology:
$400 Answer
This occurs in the male before puberty:
a. FSH levels are higher than after
puberty
b. LH levels are higher than after
puberty
c. GnRH release is inhibited by
testosterone
d. all of the above
BACK TO GAME
Male Physiology:
$500 Question
This is consistent with erection of the penis:
a. parasympathetic stimulation
b. dilation of arterioles
c. engorgement of sinusoids with blood
d. occlusion of veins
e. all of the above
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Male Physiology:
$500 Answer
This is consistent with erection of the penis:
a. parasympathetic stimulation
b. dilation of arterioles
c. engorgement of sinusoids with blood
d. occlusion of veins
e. all of the above
BACK TO GAME
Female Anatomy:
$100 Question
This ligament associated with the ovaries
helps to connect them with the posterior
body wall:
a. ovarian
b. suspensory
c. round
d. broad
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Female Anatomy:
$100 Answer
This ligament associated with the ovaries
helps to connect them with the posterior
body wall:
a. ovarian
b. suspensory
c. round
d. broad
BACK TO GAME
Female Anatomy:
$200 Question
This tubular portion of the uterus extends
downward into the upper part of the
vagina:
a. fornix
b. cervix
c. fundus
d. isthmus
e. rugae
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Female Anatomy:
$200 Answer
This tubular portion of the uterus extends
downward into the upper part of the
vagina:
a. fornix
b. cervix
c. fundus
d. isthmus
e. rugae
BACK TO GAME
Female Anatomy:
$300 Question
This female structure is the homolog of the
male penis:
a. vagina
b. clitoris
c. vestibule
d. labia majora
e. hymen
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Female Anatomy:
$300 Answer
This female structure is the homolog of the
male penis:
a. vagina
b. clitoris
c. vestibule
d. labia majora
e. hymen
BACK TO GAME
Female Anatomy:
$400 Question
This clear glycoprotein layer is between
the oocyte and the granulosa cells of an
ovarian follicle:
a. theca interna
b. theca externa
c. antrum
d. zona pellucida
e. corona radiata
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Female Anatomy:
$400 Answer
This clear glycoprotein layer is between
the oocyte and the granulosa cells of an
ovarian follicle:
a. theca interna
b. theca externa
c. antrum
d. zona pellucida
e. corona radiata
BACK TO GAME
Female Anatomy:
$500 Question
This statement best describes the
formation of a polar body during the
process of oogenesis:
a. is formed before fertilization
b. is formed after fertilization
c. normally receives most of the
cytoplasm of the cell
d. both a and b
e. all of these
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Female Anatomy:
$500 Answer
This statement best describes the
formation of a polar body during the
process of oogenesis:
a. is formed before fertilization
b. is formed after fertilization
c. normally receives most of the
cytoplasm of the cell
d. both a and b
e. all of these
BACK TO GAME
Female Physiology:
$100 Question
This layer is shed during menses:
a. myometrium
b. perimetrium
c. basal layer of endometrium
(stratum basalis)
d. functional layer of endometrium
(stratum functionalis)
e. both c and d
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Female Physiology:
$100 Answer
This layer is shed during menses:
a. myometrium
b. perimetrium
c. basal layer of endometrium
(stratum basalis)
d. functional layer of endometrium
(stratum functionalis)
e. both c and d
BACK TO GAME
Female Physiology:
$200 Question
Of a 28-day menstrual cycle (ovarian
cycle), ovulation occurs on about this day:
a. 1
b. 7
c. 14
d. 20
e. none of these
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Female Physiology:
$200 Answer
Of a 28-day menstrual cycle (ovarian
cycle), ovulation occurs on about this day:
a. 1
b. 7
c. 14
d. 20
e. none of these
BACK TO GAME
Female Physiology:
$300 Question
In the ovarian cycle, progesterone levels
would be at its highest levels during this
time:
a. during the menstrual phase
b. just prior to ovulation
c. just after ovulation
d. late in the postovulatory phase
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Female Physiology:
$300 Answer
In the ovarian cycle, progesterone levels
would be at its highest levels during this
time:
a. during the menstrual phase
b. just prior to ovulation
c. just after ovulation
d. late in the postovulatory phase
BACK TO GAME
Female Physiology:
$400 Question
This statement best describes the fate of the
corpus luteum if fertilization does not occur:
a. is expelled into the pelvic cavity
b. begins to secrete low levels of FSH
c. degenerates into the corpus albicans
d. continues to secrete progesterone
until the next ovulation
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Female Physiology:
$400 Answer
This statement best describes the fate of the
corpus luteum if fertilization does not occur:
a. is expelled into the pelvic cavity
b. begins to secrete low levels of FSH
c. degenerates into the corpus albicans
d. continues to secrete progesterone
until the next ovulation
BACK TO GAME
Female Physiology:
$500 Question
During the secretory phase of the
menstrual cycle, you normally expect this:
a. maximum levels of progesterone
b. a follicle present in the ovary that is
ready to undergo ovulation
c. that the endometrium reaches its
greatest degree of development
d. both a and b
e. both a and c
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Female Physiology:
$500 Answer
During the secretory phase of the
menstrual cycle, you normally expect this:
a. maximum levels of progesterone
b. a follicle present in the ovary that is
ready to undergo ovulation
c. that the endometrium reaches its
greatest degree of development
d. both a and b
e. both a and c
BACK TO GAME
Grab Bag:
$100 Question
The process of the crossing-over of genes
occurs during this:
a. meiosis I
b. meiosis II
c. spermiogenesis
c. telophase
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Grab Bag:
$100 Answer
The process of the crossing-over of genes
occurs during this:
a. meiosis I
b. meiosis II
c. spermiogenesis
c. telophase
BACK TO GAME
Grab Bag:
$200 Question
A Pap smear is used to detect the
presence of abnormal cells here:
a. urethra
b. ovary
c. cervix
d. vagina
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Grab Bag:
$200 Answer
A Pap smear is used to detect the
presence of abnormal cells here:
a. urethra
b. ovary
c. cervix
d. vagina
BACK TO GAME
Grab Bag:
$300 Question
Following ovulation, a human egg cell can
survive approximately this long:
a. 1 hour
b. 12 hours
c. 24 hours
d. 72 hours
e. 1 week
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Grab Bag:
$300 Answer
Following ovulation, a human egg cell can
survive approximately this long:
a. 1 hour
b. 12 hours
c. 24 hours
d. 72 hours
e. 1 week
BACK TO GAME
Grab Bag:
$400 Question
The hormone oxytocin aids the birth
process by stimulating this:
a. fetal muscular movements
b. uterine wall contractions
c. an increase in progesterone
secretion
d. an increase in estrogen secretion
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Grab Bag:
$400 Answer
The hormone oxytocin aids the birth
process by stimulating this:
a. fetal muscular movements
b. uterine wall contractions
c. an increase in progesterone
secretion
d. an increase in estrogen secretion
BACK TO GAME
Grab Bag:
$500 Question
This gland secretes a thick mucus like
substance that contains fructose to nourish
sperm cells, fibrinogen to cause semen to
clot and prostaglandins that cause uterine
contractions:
a. prostate
b. epididymis
c. bulbourethral gland (Cowper’s)
d. seminal vesicle
e. testis
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
Grab Bag:
$500 Answer
This gland secretes a thick mucus like
substance that contains fructose to nourish
sperm cells, fibrinogen to cause semen to
clot and prostaglandins that cause uterine
contractions:
a. prostate
b. epididymis
c. bulbourethral gland (Cowper’s)
d. seminal vesicle
e. testis
BACK TO GAME
FINAL ROUND Question
This statement best describes why a woman
who is taking birth-control pills that consist of
only progesterone experiences the hot flash
symptoms of menopause:
a. inhibits GnRH in the hypothalamus
b. lack of LH prevents ovulation
c. lack of FSH prevents development
of the follicles
d. inadequate estrogen production
e. all of these
ANSWER
BACK TO GAME
FINAL ROUND Answer
This statement best describes why a
woman who is taking birth-control pills that
consist of only progesterone experiences
the hot flash symptoms of menopause:
a. inhibits GnRH in the hypothalamus
b. lack of LH prevents ovulation
c. lack of FSH prevents development
of the follicles
d. inadequate estrogen production
e. all of these
BACK TO GAME