notes on Intro to Force - Link 308
advertisement

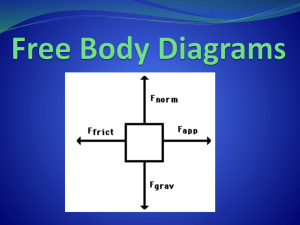
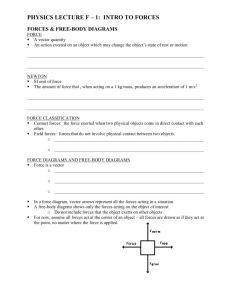
Forces Examples – A force causing an object to start moving – A force causing an object to stop moving – A force causing an object to change direction Force: The cause of an acceleration, or the change in an object’s velocity. Newton (N): The amount of force that, when acting on a 1kg mass, produces an acceleration of 1m/s2 1 N = 1kg x 1m/s2 Two Types of Forces Contact Forces: Physical contact between two objects, results in the change in velocity (that is – acceleration) – Example: pull on a spring, the string will move – Pull on a wagon, the wagon will move – Catching a football, the ball will stop – Kick a soccer ball, the ball will move – Your turn – let’s come up with 2 more examples. How do you know that these are forces? Field Forces: Force that can exist between objects, even in the absence of physical contact between the objects. – Example: gravity magnets static electricity Force Diagrams The effect of a force depends on its magnitude and direction (sound familiar?) Forces are vector quantities Force Diagrams: a diagram of the objects involved in a situation and the forces exerted on the objects. – Arrows represent forces – Attached to the object on which the force is acting Force diagram vs. Free body diagram Force diagram shows the forces exerted by the car on other objects (b) Free Body Diagram: only shows the car and the forces acting on it Free Body Diagrams Free Body Diagram (FBD): shows forces affecting the motion of a single object. – A free body diagram of the car will show all the forces acting on the car as if the forces are acting on the center of the car. -- To draw the free-body diagram, you must first isolate and identify all the forces acting on the car. How to draw a free body diagram. Force exerted on the car by the tow truck Road exerts upward force on the car 5800 N 775 N 14,700 N The interaction between the road and the car’s tires, the road also exerts a backward force of friction on the car Give it a try! Draw a free-body diagram (FBD) of a football being kicked. Assume only forces acting on it are gravity and the force of the kicker. Draw a diagram of a crash-test dummy in a car at the moment of collision. Assume that the forces acting on the car are 19600 N downward, 17800 N forward, 2500 N backward. The forces on the dummy are 585 N downward, 175 N backward, and 585 N upward. Now make 2 FBD – one for car, one for dummy Resolving Derek leaves his physics book on top of a drafting table that is inclined at a 35 degree angle. The free body diagram to the right shows the forces acting on the book. Find the net external force acting on the book, and determine whether the book will remain at rest in this position. F table on book = 18 N F friction = 11 N F gravity on book = 22 N Select a coordinate plane to work with. Try to get the most forces in the x & y plane, then resolve the ones left on an angle. + & - direction is important y x 18 N 11 N 22 N Find the x and y components of all vectors y F table on book (normal): x F gravity on book : X=0N X=? Y = 18 N F friction: Y=? θ θ=? X = -11 N Y=0N Θ =35o y Find the net external force in both the x & y directions x 18 N 11 N 18 N 22 N 13 N X Y ΣFx = Fg,x + Ffriction ΣFy = Fg,y + Fnormal ΣFx = 13N+ -11N ΣFy = -18N + 18N ΣFx = 2 N ΣFy = 0 N The net external force is 2 N Evaluate your answer The book experiences an acceleration in the downhill direction and it will slide off the table Give it a try - Give it a try p. 133 #1-4